출처 - https://www.inflearn.com/course/%EC%8A%A4%ED%94%84%EB%A7%81-mvc-1/dashboard
요청 매핑
단순 url을 매핑하는 방법 뿐만 아니라 여러 요소를 매핑하는 방법도 가지고 있다.
1. RequestMapping
가장 기본적인 방법
@RestController
@Slf4j
public class MappingController{
/**
* 기본 요청
* 둘다 허용 /hello-basic, /hello-basic/
* HTTP 메서드 모두 허용 GET, HEAD, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE
*/
@RequestMapping("/hello-basic")
public String helloBasic() {
log.info("helloBasic");
return "ok";
}
}@RestController?
-
@Controller는 반환 값이 String이면 View이름으로 인식이 된다.ViewResolver가 호출이 되어 뷰를 찾고 뷰가 랜더링 된다.
-
@RestController는 반환 값으로 뷰를 찾는 것이 아니라, HTTP 메시지 바디에 바로 입력한다. 따라서 실행결과로 ok메세지를 받을 수 있다.@ResponseBody와 관련이 있는데, 뒤에서 설명.
@RequestMapping("/hello-basic")
- RequestMapping의 url은 배열로 다중 설정이 가능하다.@RequestMapping({"/hello-basic","/hello-go"})
- "/hello-basic"과 "/hello-basic/"은 다른 url이지만, 스프링은 다음 url요청들을 같은 요청으로 mapping한다.
HTTP 메서드
- @RequsetMapping에 method 속성으로 HTTP 메서드를 지정하지 않으면 HTTP메서드와 무관하게 호출된다.
2. RequestMapping에 method추가
/**
* method 특정 HTTP 메서드 요청만 허용
* GET, HEAD, POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/mapping-get-v1", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String mappingGetV1() {
log.info("mappingGetV1");
return "ok";
}Postman을 사용해서 Test.
만약 POST 요청을 하면 스프링 MVC는 HTTP 상태코드 405(Not Allowed)를 반환한다.
더 간단히 하면?
3. GetMapping, PostMapping
/**
* 편리한 축약 애노테이션 (코드보기)
* @GetMapping
* @PostMapping
* @PutMapping
* @DeleteMapping
* @PatchMapping
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/mapping-get-v2")
public String mappingGetV2() {
log.info("mapping-get-v2");
return "ok";
}HTTP 메서드를 축약한 애노테이션을 사용하는 것이 더 직관적이다.
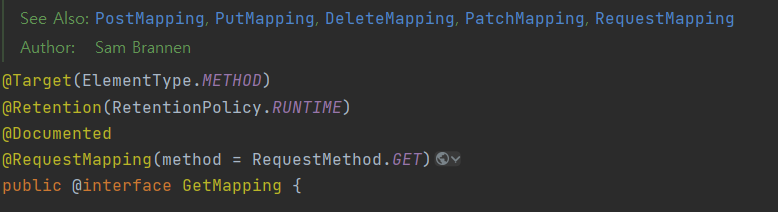
GetMapping 애노테이션 안에 @RequestMapping(method= RequestMethod.GET)이 있음을 볼 수 있다.
자주 사용하는 방식
4. PathVariable사용 - GetMapping("/mapping/{userId}")
url자체에 값이 들어가 있는 것.
/** * PathVariable 사용
* 변수명이 같으면 생략 가능
* @PathVariable("userId") String userId -> @PathVariable userId
*/
@GetMapping("/mapping/{userId}")
public String mappingPath(@PathVariable("userId") String data) {
log.info("mappingPath userId={}", data);
return "ok";
}"/mapping/userA"라고 url을 적으면 userId = "userA"로 나온다.
최근 HTTP API는 다음과 같이 리소스 경로에 식별자를 넣는 스타일을 선호한다.
- url경로를 템플릿화 할 수 있다.
@PathVariable 의 이름과 파라미터 이름이 같으면 생략할 수 있다. - 만약 변수명이 userId로 동일하다면 methodName(@PathVariable String userId)로 축약 가능
5. PathVariable - 다중 mapping
**
* PathVariable 사용 다중
*/
@GetMapping("/mapping/users/{userId}/orders/{orderId}")
public String mappingPath(@PathVariable String userId, @PathVariable Long
orderId) {
log.info("mappingPath userId={}, orderId={}", userId, orderId);
return "ok";
}url - mapping/users/userA/orders/100로 요청을 하면,
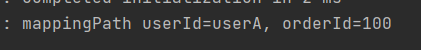
userA와 주문번호 100번이 출력이 됨을 볼 수 있다.
6. 쿼리 파라미터를 조건에 매핑할 수 있다.
(잘 사용하지는 않음)
/**
* 파라미터로 추가 매핑
* params="mode",
* params="!mode"
* params="mode=debug"
* params="mode!=debug" (! = )
* params = {"mode=debug","data=good"}
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/mapping-param", params = "mode=debug")
public String mappingParam() {
log.info("mappingParam");
return "ok";
}mappingParam/mode=debug
특정 파라미터 정보(여기에서는 mode=debug)가 있어야 mapping이 가능하다.
/**
* 특정 헤더로 추가 매핑
* headers="mode",
* headers="!mode"
* headers="mode=debug"
* headers="mode!=debug" (! = )
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/mapping-header", headers = "mode=debug")
public String mappingHeader() {
log.info("mappingHeader");
return "ok";
}header 파라미터를 통해 헤더 조건을 걸 수도 있다.
이 때는 Postman으로 테스트 해야 한다.
미디어 타입 조건 매핑
참고 - http://blog.naver.com/PostView.nhn?blogId=writer0713&logNo=221422059349&parentCategoryNo=&categoryNo=83&viewDate=&isShowPopularPosts=false&from=postView
@PostMapping(value = "/mapping-consume", consumes = "application/json")
public String mappingConsumes() {
log.info("mappingConsumes");
return "ok";Content-Type 헤더 기반 추가 매핑
*content-type: client가 보내는 content의 타입
ContentType에 따라 처리 방법을 다르게 할 수 있다.
/**
* Accept 헤더 기반 Media Type
* produces = "text/html"
* produces = "!text/html"
* produces = "text/*"
* produces = "*\/*"
*/
@PostMapping(value = "/mapping-produce", produces = "text/html")
public String mappingProduces() {
log.info("mappingProduces");
return "ok";
}생산 가능한 미디어 타입의 목록을 지정해서 주요 매핑을 제한할 수 있다. Accept 요청 헤더가 이러한 값 중 하나와 일치할 때만 요청이 매칭될 것이다.
produces: Accept header가 produces에 명시한 MediaType과 같을 때에 해당 type으로 reponse를 한다.
accept: client가 backend 서버에게 어떤 형식(MediaType)으로 달라고 하는 요청의 방식
요청매핑 - API 예시
회원 관리를 HTTP API로 만든다 생각하고 매핑을 어떻게 하는지 알아보자.
회원 관리 API
기능 GET url 회원 목록 조회 GET "/users" 회원 등록 POST "/users" 회원 조회 GET "/users/{userId}" 회원 수정 PATCH "/users/{userId}" 회원 삭제 DELETE "/users/{userId}" GET PATCH DELETE는 url은 같지만 method를 통해 다른 역할을 수행한다.
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/mapping/users")
public class MappingClassController {
/**
* GET /mapping/users
*/
@GetMapping
public String users() {
return "get users";
}
/**
* POST /mapping/users
*/
@PostMapping
public String addUser() {
return "post user";
}
/**
* GET /mapping/users/{userId}
*/
@GetMapping("/{userId}")
public String findUser(@PathVariable String userId) {
return "get userId=" + userId;
}
/**
* PATCH /mapping/users/{userId}
*/
@PatchMapping("/{userId}")
public String updateUser(@PathVariable String userId) { return "update userId=" + userId;
}
/**
* DELETE /mapping/users/{userId}
*/
@DeleteMapping("/{userId}")
public String deleteUser(@PathVariable String userId) {
return "delete userId=" + userId;
}
}회원 관리 API의 url에 공통 부분이 존재- "/mapping/users"
=> 클래스 레벨에 @RequestMapping("/mapping/users")를 사용한다.
=> method 레벨의 @RequestMapping 애노테이션에 공통 url을 없애준다.
HTTP 요청
1. HTTP 요청- 기본, 헤더 조회
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class RequestHeaderController {
@RequestMapping("/headers")
public String headers(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response,
HttpMethod httpMethod,
Locale locale,
@RequestHeader MultiValueMap<String, String>
headerMap,
@RequestHeader("host") String host,
@CookieValue(value = "myCookie", required = false)
String cookie
) {
log.info("request={}", request);
log.info("response={}", response);
log.info("httpMethod={}", httpMethod);
log.info("locale={}", locale);
log.info("headerMap={}", headerMap);
log.info("header host={}", host);
log.info("myCookie={}", cookie);
return "ok";
}
}- HttpServletRequest
- HttpServletResponse (서블릿 편 참조)
- HttpMethod: HTTP 메서드를 조회한다.
- Locale: Locale정보를 조회한다.
가장 우선순위가 높은 locale이 선택된다. (locale 선택 방법 - localeResolver 검색) - @RequestHeader MultiValueMap (String,String) headerMap: 모든 HTTP 헤더를 MultiValueMap형식으로 조회한다.
- @RequestHeader("host") String host: 특정 HTTP 헤더를 조회한다.
- 속성: required=True/False(필수 값 여부), defaultValue(기본 값)
import org.slf4j.Logger
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());다음 코드를 자동으로 생성해서 로그를 선언해준다. 개발자는 편리하게 log라고 사용하면 된다.
2. HTTP 요청 파라미터 - 쿼리 파라미터, HTML Form
HTTP 요청 데이터 조회 - 개요
서블릿에서 학습했던 HTTP 요청 데이터를 조회하는 방법을 다시 떠올려보자.
클라이언트에서 서버로 요청 데이터를 전달할 때는 주로 다음 3가지 방법을 사용한다.
- GET: 쿼리 파라미터
- /url?username=hello&age=20
- 메시지 바디 없이, url의 쿼리 파라미터에 데이터를 포함해서 전달
- 예) 검색, 필터, 페이징 등에서 많이 사용하는 방식
- POST: HTML Form
- content-type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
- 메시지 바디에 쿼리 파리미터 형식으로 전달 username=hello&age=20
- 예) 회원 가입, 상품 주문, HTML Form 사용
- HTTP message body에 데이터를 직접 담아서 요청
- HTTP API에서 주로 사용, JSON,XML,TEXT
- 데이터 형식은 주로 JSON 사용
- POST,PUT,PATCH
여기서 1번과 2번은 결과적으로 형식이 같기 때문에 구분없이 조회할 수 있다.
이것을 간단히 요청 파라미터(request parameter) 조회라 한다.
스프링으로 요청 파라미터를 조회하는 방법을 단계적으로 알아보자.
@Slf4j
@Controller
public class RequestParamController {
/**
* 반환 타입이 없으면서 이렇게 응답에 값을 직접 집어넣으면, view 조회X
*/
@RequestMapping("/request-param-v1")
public void requestParamV1(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse
response) throws IOException {
String username = request.getParameter("username");
int age = Integer.parseInt(request.getParameter("age"));
log.info("username={}, age={}", username, age);
response.getWriter().write("ok");
}
}request.getParameter()
여기서는 단순히 HttpServletRequest가 제공하는 바식으로 요청 파라미터를 조회했다.
hello-form.html 생성
리소스는 /resources/static 아래에 두면 스프링 부트가 자동으로 인식한다.
static 디렉토리 밑에 basic 디렉토리를 생성하여 hello-form.html을 생성한다.
username,age를 작성하는 기본적인 폼
3. HTTP 요청 파라미터 - @RequestParam
RequestParamController Class에 이어서 작성
/**
* @RequestParam 사용
* - 파라미터 이름으로 바인딩
* @ResponseBody 추가
* - View 조회를 무시하고, HTTP message body에 직접 해당 내용 입력
*/
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/request-param-v2")
public String requestParamV2(
@RequestParam("username") String memberName,
@RequestParam("age) int memberAge){
log.info("username={}, age={}",memberName,age);
return "ok";- @RequestParam: 파라미터 이름으로 바인딩
- @ResponseBody: View 조회를 무시하고, Http message body에 직접 해당 내용 입력
(ViewResolver를 호출하지 않음)
@RequestParam의 name(value)속성이 파라미터 이름으로 사용
version1의 request.getParameter("username");
/**
* @RequestParam 사용
* HTTP 파라미터 이름이 변수 이름과 같으면 @RequestParam(name="xx") 생략 가능
*/
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/request-param-v3")
public String requestParamV3(
@RequestParam String username,
@RequestParam int age) {
log.info("username={}, age={}", username, age);
return "ok";
}HTTP 파라미터 이름이 변수 이름과 같으면 @RequestParam(name="xx")생략이 가능하다.
//권장하지 않음
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/request-param-v4")
public String requestParamV4(String username, int age) {
log.info("username={}, age={}", username, age);
return "ok";
}String, int, Integer등의 단순 타입이면 애노테이션도 생략이 가능하다.
