
0. 문제:
n개의 꼭짓점이 0에서 n - 1까지 라벨링된 무방향 가중 그래프가 있습니다.
정수 n과 배열 edges가 주어지는데, 여기서 edges[i] = [ui, vi, wi]는 꼭짓점 ui와 vi사이에 wi의 가중치를 가진 간선이 있음을 나타냅니다.
그래프에서 산책은 꼭짓점과 간선의 연속입니다. 산책은 꼭짓점으로 시작하고 끝납니다. 각 간선은 그 앞에 오는 꼭짓점과 그 뒤에 오는 꼭짓점을 연결합니다. 산책은 같은 간선이나 꼭짓점을 두 번 이상 방문할 수 있다는 점에 유의하는 것이 중요합니다.
노드 u에서 시작하여 노드 v에서 끝나는 산책 비용은 산책 중에 횡단한 간선의 가중치의 비트 단위 AND로 정의됩니다. 즉, 산책 중에 발생하는 간선 가중치의 순서가 w0, w1, w2, ..., wk인 경우 비용은 w0 & w1 & w2 & ... & wk로 계산되며, 여기서 &는 비트 단위 AND 연산자를 나타냅니다.
또한 query[i] = [si, ti]인 2D 배열 query도 제공됩니다. 각 쿼리에 대해 꼭짓점 si에서 시작하여 꼭짓점 ti에서 끝나는 산책의 최소 비용을 찾아야 합니다. 이러한 산책이 존재하지 않는다면 답은 -1입니다.
배열 answer를 리턴합니다. 여기서 answer[i]는 쿼리 i에 대한 산책의 최소 비용을 나타냅니다.
예제 1:
- 입력:
n = 5,edges = [[0,1,7],[1,3,7],[1,2,1]],query = [[0,3],[3,4]] - 출력:
[1,-1] - 설명:
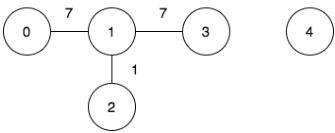
첫번째 쿼리에 대해 비용 1을 달성하기 위해 다음과 같은 순서로 간선을 산책:0->1 (가중치 7),1->2 (가중치 1),2->1(가중치 1),1->3(가중치 7)
두번째 쿼리는 노드3과 노드4가 연결되어 있지 않기 때문에, 산책이 불가능해-1리턴
예제 2:
- 입력:
n = 3,edges = [[0,2,7],[0,1,15],[1,2,6],[1,2,1]],query = [[1,2]] - 출력:
[0] - 설명:
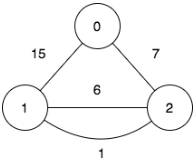
첫번째 쿼리에 대한 비용 0을 달성하기 위해 다음과 같은 순서로 간선을 산책:1->2 (가중치 1),2->1 (가중치 6),1->2 (가중치 1)
제한사항:
2 <= n <= 105
0 <= edges.length <= 105
edges[i].length == 3
0 <= ui, vi <= n - 1
ui != vi
0 <= wi <= 105
1 <= query.length <= 105
query[i].length == 2
0 <= si, ti <= n - 1
si != ti
1. 풀이:
못 해먹겠네... 🥕🥕🥕
핵심:
- 꼭짓점과 간선의 중복 방문이 가능하다.
AND연산은1 -> 1혹은1 -> 0연산은 가능하지만,0 -> 1연산은 불가능. 다시 말해, 특정 숫자를AND연산하면 절대 커질 수 없다. 결과적으로 산책 비용은 항상 가중치의 최소값 이하이다.- 간선을 지나면 지날수록 산책의 비용이 감소하게 된다.
w AND w = w이므로, 같은 간선을 여러번 방문하는 것은 비용 감소에 영향을 미치지 못한다.
접근법: Disjoint-Set (Union-Find) - 권장
직관:
뭐가 보여야 직관이지...
-
쿼리가 -1을 리턴하게 만드는 경우:
두 노드 사이에 간선이 존재하지 않는 경우. 이 경우, 두 노드는 서로 다른 연결 구성요소에 속해 있다고 말한다.연결 구성요소에 속한 노드는 모든 노드 쌍이 연결되어 있음.
-
두 노드가 연결된 구성요소에 속한 경우:
최소 비용을 달성하기 위해서는 가능한 구성요소의 모든 간선을 방문해야 함. -
Disjoint-Set(Union Find) 데이터 구조를 사용.
Find(x) 연산: x가 속한 집합의 대표값(루트 노트 값) 리턴
Union(x ,y) 연산: x가 속한 집합과 y가 속한 집합을 합침. -
노드를 연결 구성요소로 그룹화한 후 각 구성요소의 총 비용을 모든 간선 가중치의 비트 단위 AND로 계산. 결국 동일한 구성요소에 있는 두 노드 사이의 최소 산책 비용은 구성요소의 총 비용과 동일.
알고리즘 설명:
minimumCost(n, edges, queries)
-
사이즈가
n인 배열parent,depth,componentCost를 초기화:parent: 모두 -1로 초기화. 각 노드가 서로 연결되어 있지 않음을 의미.depth: 모두 0으로 초기화.componentCost: 모두 0b1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111로 초기화. 32비트가 모두 1인AND연산에 중립적인 값.
-
연결 구성요소 생성:
edges의 요소를 서로union연산 -
각 구성요소의 비용을 계산:
각 구성요소의 루트 노드를 찾아(find연산),AND연산 결과를 비용에 반영 -
각 쿼리의 결과를 담기 위한 배열
answer를 초기화:
각 쿼리에 대해서start와end의 루트 노드가 같은 판단한 후, 그 결과를 삽입. -
answer리턴
find(node)
-
만약
parent[node] == -1이라면,node는 그 그룹의 루트.node를 리턴 -
아니라면,
find(parent[node])를 리턴하고 그 결과를parent[node]에 저장.
union(node1, node2)
- 각 구성요소의 루트를 탐색.
- 두 노드가 이미 같은 구성요소라면 리턴
depth[root1] < depth[root2]라면, 두 루트를 서로 교환해서root1이 더 깊은 깊이를 가지도록 함.parent[root2] = root1로 설정해서 두 그룹을 병합.- 만약 두 그룹이 같은 깊이라면, 병합된 그룹은 깊이를 1 상승 시킴.
구현:
class Solution {
int[] parent;
int[] depth;
public int[] minimumCost(int n, int[][] edges, int[][] queries) {
// Initialize the parent array with -1 as initially each node belongs to its own component
parent = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
parent[i] = -1;
depth = new int[n];
// All values are initially set to the number with only 1s in its binary representation
int[] componentCost = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
componentCost[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
// Construct the connected components of the graph
for (int[] edge : edges) {
union(edge[0], edge[1]);
}
// Calculate the cost of each component by performing bitwise AND of all edge weights in it
for (int[] edge : edges) {
int root = find(edge[0]);
componentCost[root] &= edge[2];
}
int[] answer = new int[queries.length];
for (int i = 0; i < queries.length; i++) {
int start = queries[i][0];
int end = queries[i][1];
// If the two nodes are in different connected components, return -1
if (find(start) != find(end)) {
answer[i] = -1;
} else {
// Find the root of the edge's component
int root = find(start);
// Return the precomputed cost of the component
answer[i] = componentCost[root];
}
}
return answer;
}
// Find function to return the root (representative) of a node's component
private int find(int node) {
// If the node is its own parent, it is the root of the component
if (parent[node] == -1)
return node;
// Otherwise, recursively find the root and apply path compression
return parent[node] = find(parent[node]);
}
// Union function to merge the components of two nodes
private void union(int node1, int node2) {
int root1 = find(node1);
int root2 = find(node2);
// If the two nodes are already in the same component, do nothing
if (root1 == root2)
return;
// Union by depth: ensure the root of the deeper tree becomes the parent
if (depth[root1] < depth[root2]) {
int temp = root1;
root1 = root2;
root2 = temp;
}
// Merge the two components by making root1 the parent of root2
parent[root2] = root1;
// If both components had the same depth, increase the depth of the new root
if (depth[root1] == depth[root2]) {
depth[root1]++;
}
}
}
