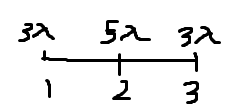출력형식
f'{값:04d}': 정수를 4자리 차지하게 넣는데, 빈자리 있을경우 0을 채운다
f'{값: 4d}': 정수를 4자리 차지하게 넣는데, 빈자리 있을경우 공백(' ')을 채운다
f'{값:,d}': 정수를 1000 단위로 콤마 찍는다
f'{값:.4f}': float을 소숫점 5자리에서 반올림해 4자리까지 채운다
print(f'{123:05d}')
print(f'{123:5d}')
print(f'{12345:,d}')
print(f'{123:.4f}')
00123
123
12,345
123.0000
print('{:05d}'.format(123))
print('{:5d}'.format(123))
print('{:,d}'.format(12345))
print('{:.4f}'.format(123))
00123
123
12,345
123.0000
answer = 540
print('{:02d}:{:02d}'.format(answer // 60, answer % 60))
09:00
문자열
# 영어 대소문자 변환
s = 'AAAAAbbbbb'
print(s.swapcase())
n = 12345
print(list(str(n)))
print(list(map(int, str(n))))
print()
s = "3people unFollowed me"
print(s.split())
print(s.split(' '))
print()
print(' '.join(s))
print(''.join(s))
print()
print(sorted(s)) #숫자 - 대문자 - 소문자 순서
print()
n = '1 2 3 4 -1 -5'
print(n.split())
print(list(map(int, n.split())))
['1', '2', '3', '4', '5']
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
['3people', 'unFollowed', 'me']
['3people', '', '', '', 'unFollowed', 'me']
3 p e o p l e u n F o l l o w e d m e
3people unFollowed me
[' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', ' ', '3', 'F', 'd', 'e', 'e', 'e', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'l', 'm', 'n', 'o', 'o', 'o', 'p', 'p', 'u', 'w']
['1', '2', '3', '4', '-1', '-5']
[1, 2, 3, 4, -1, -5]
s = "{{2},{2,1},{2,1,3},{2,1,3,4}}"
s = s.replace('{','').replace('}','').split(',')
print(s)
s = [int(i) for i in s]
print(s)
s1 = "{{2},{2,1},{2,1,3},{2,1,3,4}}"
s1 = list(map(int, s1.replace('{','').replace('}','').split(',')))
print(s1)
['2', '2', '1', '2', '1', '3', '2', '1', '3', '4']
[2, 2, 1, 2, 1, 3, 2, 1, 3, 4]
[2, 2, 1, 2, 1, 3, 2, 1, 3, 4]
# 문자열 끊어서 출력하기
s = 'hanD-Shake'
a = [s[i:i+2].lower() for i in range(len(s)-1) if s[i:i+2].isalpha()]
print(a)
['ha', 'an', 'nd', 'sh', 'ha', 'ak', 'ke']
# 접두어 비교
phone_book = ["12","123","1235","567","88"]
phone_book.sort()
for i in range(len(phone_book)-1):
if phone_book[i] == phone_book[i+1][:len(phone_book[i])]:
print('True')
print('False')
True
True
False
기본
# 문자열이 '숫자'로만 이루어져있는지 확인
s = '1234'
s.isdigit()
True
# IF - ELIF - ELSE 구문
a = 3
b = 3
winner = 'A' if a > b else 'B' if a < b else 'SAME'
print(winner)
SAME
# boolean type - int형
print(int(True))
print(int(False))
1
0
# 올림, 내림, 소수점 버림, 반올림
import math
print(math.ceil(12.34))
print(math.floor(12.34))
print(math.trunc(12.34))
print(round(123.4567, 3))
13
12
12
123.457
# 문자열 한 줄로 출력하는 방법
s = [str(i) for i in range(10)]
print('result', ' = ', ' + '.join(s), sep='')
result = 0 + 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 + 8 + 9
# deque 회전
from collections import deque
q = deque([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
q.rotate(1) # 1 -> 2
print(q)
q.rotate(-2) # 1 -> -1
print(q)
deque([7, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
deque([2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 1])
q1 = deque([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
q2 = deque([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
a = deque([8, 9, 10])
q1.extendleft(a)
q2.extend(a)
print(q1)
print(q2)
deque([10, 9, 8, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
deque([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10])
# and : 무조건 T만 T
# or : T가 존재하면 T
# xor : 같으면 F 다르면 T
# or and xor
# x y
# T T T T F
# T F T F T
# F T T F T
# F F F F F
a = 0
print(a ^ 1)
print(a ^ 0)
b = 1
print(b ^ 1)
print(b ^ 0)
x = [True, True, True]
y = [True, True, False]
z = [False, False, False]
# all - and 조건 : 모두 True라면 True
print(all(x))
print(all(y))
print(all(z))
print()
# any - or 조건 : 하나라도 True라면 True
print(any(x))
print(any(y))
print(any(z))
1
0
0
1
True
False
False
True
True
False
# 아스키코드
for i in range(65,91):
print(chr(i),end=' ')
print('\n')
for i in range(97,122):
print(chr(i), end=' ')
print('\n')
print(ord('A'), ord('a'))
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y
65 97
# set정의
a = ['fr', 'ra', 'an', 'nc', 'ce']
b = ['fr', 're', 'en', 'nc', 'ch']
a = set(a)
b = set(b)
# 합집합
s1 = a | b
s11 = a.union(b)
print(s1)
# 교집합
s2 = a & b
s22 = a.intersection(b)
print(s2)
# 차집합
s3 = a - b
s33 = a.difference(b)
print(s3)
# 대칭차집합 = 합집합 - 교집합
s4 = a ^ b
print(s4)
# 추가
aa = set(['a','b','c'])
aa.update(['mo', 'de']) # 여러개
print(aa)
aa.add('z') # 하나
print(aa)
#삭제
aa.remove('c')
print(aa)
# 포함되는지 여부
x = {'a', 'b', 'c'}
y = {'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'}
print(x.issubset(y))
print(y.issubset(x))
{'en', 'fr', 'ce', 'ra', 'ch', 'nc', 're', 'an'}
{'fr', 'nc'}
{'an', 'ce', 'ra'}
{'ch', 'ce', 'en', 'ra', 'an', 're'}
{'de', 'a', 'c', 'mo', 'b'}
{'de', 'a', 'c', 'mo', 'z', 'b'}
{'de', 'a', 'mo', 'z', 'b'}
True
False
# 개수 세기
from collections import Counter
res = ['AB', 'AC', 'AF', 'AG', 'BC', 'BF', 'BG', 'CF', 'CG', 'FG', 'AC', 'CD', 'CE', 'DE', 'AC', 'AD', 'AE', 'CD', 'CE',
'DE', 'BC', 'BF', 'BG', 'CF', 'CG', 'FG', 'AC', 'AD', 'AE', 'AH', 'CD', 'CE', 'CH', 'DE', 'DH', 'EH']
info1 = Counter(res)
print(info1, '\n')
info = Counter(res).most_common()
print(info, '\n')
info2 = sorted(Counter(res).most_common(), key = lambda x : (-x[1], x[0]))
print(info2)
Counter({'AC': 4, 'CD': 3, 'CE': 3, 'DE': 3, 'BC': 2, 'BF': 2, 'BG': 2, 'CF': 2, 'CG': 2, 'FG': 2, 'AD': 2, 'AE': 2, 'AB': 1, 'AF': 1, 'AG': 1, 'AH': 1, 'CH': 1, 'DH': 1, 'EH': 1})
[('AC', 4), ('CD', 3), ('CE', 3), ('DE', 3), ('BC', 2), ('BF', 2), ('BG', 2), ('CF', 2), ('CG', 2), ('FG', 2), ('AD', 2), ('AE', 2), ('AB', 1), ('AF', 1), ('AG', 1), ('AH', 1), ('CH', 1), ('DH', 1), ('EH', 1)]
[('AC', 4), ('CD', 3), ('CE', 3), ('DE', 3), ('AD', 2), ('AE', 2), ('BC', 2), ('BF', 2), ('BG', 2), ('CF', 2), ('CG', 2), ('FG', 2), ('AB', 1), ('AF', 1), ('AG', 1), ('AH', 1), ('CH', 1), ('DH', 1), ('EH', 1)]
진법 변환
# 이진변환 + 자리수 맞추기
zero_count = 15
n = 1234
print(bin(n))
print(bin(n)[2:])
print(bin(n)[2:].zfill(zero_count))
0b10011010010
10011010010
000010011010010
# 삼진법
n = 45
answer = ''
while n:
n,mod = divmod(n,3)
print(n, mod)
answer += str(mod)
res = answer[::-1]
print(res)
print(int(res, 3)) # 문자열인 경우만 가능
15 0
5 0
1 2
0 1
1200
45
# 2~16진법 구현하기 -> 0~특정값 까지 n진법 변환 후 문자열 연결
####################################### HARD #########################################
def change(n,k):
s = '0123456789ABCDEF'
n,mod = divmod(n,k)
if n == 0:
return s[mod]
else:
return change(n,k) + s[mod]
res = ''
for i in range(5):
res += change(i,2)
print(res)
print(res)
0
01
0110
011011
011011100
011011100
table = {seq: voc for voc, seq in enumerate('ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789+/')}
print(table)
# 6자리 이진법 변환
sen = 'TGlmZSBpdHNlbGYgaXMgYSBxdW90YXRpb24u'
res = ''.join([bin(table[s])[2:].zfill(6) for s in sen])
print(res)
# 8자리씩 끊어서 십진수 변환
text = ''.join([chr(int(res[i : i+8], 2)) for i in range(0, len(res), 8)])
print(text)
{'A': 0, 'B': 1, 'C': 2, 'D': 3, 'E': 4, 'F': 5, 'G': 6, 'H': 7, 'I': 8, 'J': 9, 'K': 10, 'L': 11, 'M': 12, 'N': 13, 'O': 14, 'P': 15, 'Q': 16, 'R': 17, 'S': 18, 'T': 19, 'U': 20, 'V': 21, 'W': 22, 'X': 23, 'Y': 24, 'Z': 25, 'a': 26, 'b': 27, 'c': 28, 'd': 29, 'e': 30, 'f': 31, 'g': 32, 'h': 33, 'i': 34, 'j': 35, 'k': 36, 'l': 37, 'm': 38, 'n': 39, 'o': 40, 'p': 41, 'q': 42, 'r': 43, 's': 44, 't': 45, 'u': 46, 'v': 47, 'w': 48, 'x': 49, 'y': 50, 'z': 51, '0': 52, '1': 53, '2': 54, '3': 55, '4': 56, '5': 57, '6': 58, '7': 59, '8': 60, '9': 61, '+': 62, '/': 63}
010011000110100101100110011001010010000001101001011101000111001101100101011011000110011000100000011010010111001100100000011000010010000001110001011101010110111101110100011000010111010001101001011011110110111000101110
Life itself is a quotation.
정렬
# 정렬
strings = ["sun", "bed", "car"]
n = 1
strings = sorted(strings, key = lambda x : (x[n], x)) # 1번째 인덱스, 사전순 정렬
print(strings)
# dict 정렬
dict = {4: 2, 2: 3, 3: 4, 1: 1}
sorted_dict = sorted(dict.items(), key = lambda x : -x[1]) # value 기준 내림차순 정렬
print(sorted_dict)
['car', 'bed', 'sun']
[(3, 4), (2, 3), (4, 2), (1, 1)]
# 정규표현식 정렬
import re
files = ["img12.png", "img10.png", "img02.png", "img1.png", "IMG01.GIF", "img2.JPG"]
hnt = [re.split(r'([0-9]+)', s) for s in files]
print(hnt)
sorted_hnt = sorted(hnt, key = lambda x : (x[0].lower(), int(x[1])))
print(sorted_hnt)
answer = [''.join(i) for i in sorted_hnt]
print(answer)
[['img', '12', '.png'], ['img', '10', '.png'], ['img', '02', '.png'], ['img', '1', '.png'], ['IMG', '01', '.GIF'], ['img', '2', '.JPG']]
[['img', '1', '.png'], ['IMG', '01', '.GIF'], ['img', '02', '.png'], ['img', '2', '.JPG'], ['img', '10', '.png'], ['img', '12', '.png']]
['img1.png', 'IMG01.GIF', 'img02.png', 'img2.JPG', 'img10.png', 'img12.png']
배열 회전
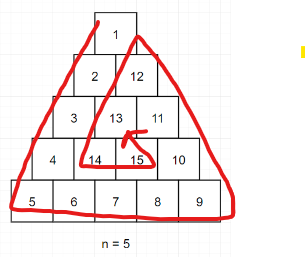
n = 5
arr = [[0] * i for i in range(1, n+1)]
dir = {0 : [1, 0], 1 : [0, 1], 2 : [-1, -1]}
x, y = 0, 0
i = 1
j = 0
answer = []
while i <= (n * (n+1)) // 2:
if 0 <= x < len(arr) and 0 <= y < len(arr[x]) and arr[x][y] == 0:
arr[x][y] = i
i += 1
else:
x -= dir[j][0]
y -= dir[j][1]
j = (j + 1) % 3
x += dir[j][0]
y += dir[j][1]
print(arr)
for i in arr:
for j in i:
answer.append(j)
print(answer)
[[1], [2, 12], [3, 13, 11], [4, 14, 15, 10], [5, 6, 7, 8, 9]]
[1, 2, 12, 3, 13, 11, 4, 14, 15, 10, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
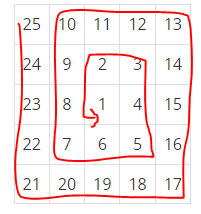
n = 5
t = n * n
r = 0
arr = [[0] * n for _ in range(n)]
dir = {0 : [1,0] ,1 : [0,1] ,2 : [-1,0] ,3 : [0,-1]} # 아래 오른 위 왼
x, y = 0, 0
while True:
if t == 0:
break
if 0 <= x < n and 0 <= y < n and arr[x][y] == 0:
arr[x][y] = t
t -= 1
else:
x-=dir[r][0]
y-=dir[r][1]
r = (r + 1) % 4
x+=dir[r][0]
y+=dir[r][1]
for i in arr:
print(*i)
25 10 11 12 13
24 9 2 3 14
23 8 1 4 15
22 7 6 5 16
21 20 19 18 17
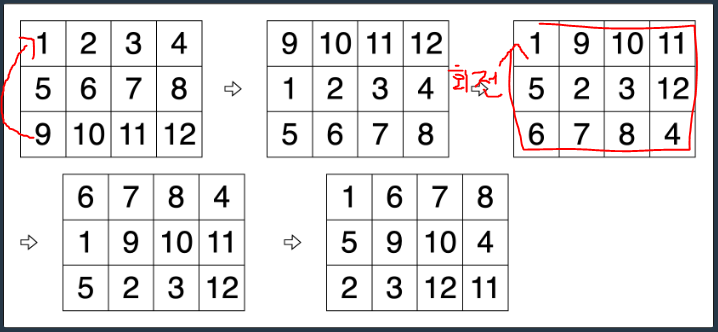
# 행렬 회전 1
rc = [[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8], [9, 10, 11, 12]]
operations = ["ShiftRow", "Rotate", "ShiftRow", "Rotate"]
# result = [[1, 6, 7 ,8], [5, 9, 10, 4], [2, 3, 12, 11]]
from collections import deque
r = len(rc)
c = len(rc[0])
col1 = deque(rc[i][0] for i in range(r))
col2 = deque(rc[i][-1] for i in range(r))
rows = deque(deque(rc[i][j] for j in range(1, c-1)) for i in range(r))
print(col1, col2, rows)
idx = 0
for op in operations:
if op == 'ShiftRow':
col1.rotate(1)
col2.rotate(1)
rows.rotate(1)
else:
rows[0].appendleft(col1.popleft())
col2.appendleft(rows[0].pop())
rows[-1].append(col2.pop())
col1.append(rows[-1].popleft())
for left, mid, right in zip(col1, rows, col2):
print([left] + list(mid) + [right])
deque([1, 5, 9]) deque([4, 8, 12]) deque([deque([2, 3]), deque([6, 7]), deque([10, 11])])
[1, 6, 7, 8]
[5, 9, 10, 4]
[2, 3, 12, 11]
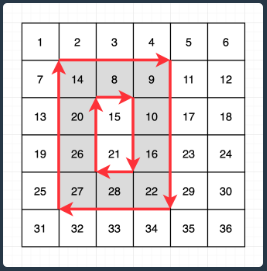
# 행렬 회전 2
from collections import deque
rows, columns = 3,3
queries = [[1,1,2,2],[1,2,2,3],[2,1,3,2],[2,2,3,3]]
# result = [1, 1, 5, 3]
graph = [[i + (columns * j) for i in range(1, columns+1)] for j in range(rows)]
answer = []
for x1,y1,x2,y2 in queries:
x1,y1,x2,y2 = x1-1, y1-1, x2-1, y2-1
col1 = deque([graph[i][y1] for i in range(x1, x2+1)])
col2 = deque([graph[i][y2] for i in range(x1, x2+1)])
rows = [deque([graph[i][j] for j in range(y1+1, y2)]) for i in range(x1, x2+1)]
rows[0].appendleft(col1.popleft())
col2.appendleft(rows[0].pop())
rows[-1].append(col2.pop())
col1.append(rows[-1].popleft())
a, b = 1e9, 1e9
if col1:
x = min(col1)
if col2:
y = min(col2)
if rows[0]:
a = min(rows[0])
if rows[-1]:
b = min(rows[-1])
answer.append(min(x, y, a, b))
tmp = []
for left, mid, right in zip(col1, rows, col2):
tmp.append([left] + list(mid) + [right])
# 그래프 갱신
for i in range(x1, x2+1):
for j in range(y1, y2+1):
graph[i][j] = tmp[i-x1][j-y1]
print(answer)
[1, 1, 5, 3]
아이디어
n, a, b = 16, 8, 9
cnt = 0
while a != b:
cnt += 1
a = a - a // 2
b = b - b // 2
print(cnt)
4
# 길이가 다른 리스트 세로로 출력하기
ans = ''
arr = [['A', 'A'], ['a', 'f', 'z', 'z'], ['0', '9', '1'], ['a', '8', 'E', 'W', 'g', '6'], ['P', '5', 'h', '3', 'k']]
a, b = len(arr), max([len(i) for i in arr])
print(a, b)
for i in range(b):
for j in range(a):
if i < len(arr[j]):
ans += arr[j][i]
print(ans)
5 6
Aa0aPAf985z1EhzW3gk6
# 다각형(6)에서 가장 긴 변 양 옆의 변 차 찾기
# 변의 저장 순서는 순차적으로 되어 있는 경우
result = [50, 160, 30, 60, 20, 100]
x,y = 160,50 # 최대 길이 변
xi,yi = 1,0 # 저장된 변에서 최대길이 변의 인덱스
rx = abs(result[(xi - 1) % 6] - result[(xi + 1) % 6])
ry = abs(result[(yi - 1) % 6] - result[(yi + 1) % 6])
print(rx, ry)
20 60
rc = 0
for i in range(len(arr)):
i -= rc
if 조건만족 X:
arr.remove(arr[i])
rc += 1
-> arr.remove를 통해 첫번째 값 삭제
-> arr[0]값 만을 사용하게 됨
-> i가 증가함에 따라 rc도 증가 i - rc = 0
# 새로운 단어사전 생성
msg = 'KAKAO'
dict = [chr(65+i) for i in range(26)]
print(dict)
i = 0
voc = ''
result = []
while i < len(msg): # i = 1 일때가 두번 실행됨 !!!
voc += msg[i]
if voc in dict:
i+=1
else:
dict.append(voc)
print(voc, voc[:-1], dict.index(voc[:-1]))
result.append(dict.index(voc[:-1]) + 1)
voc = ''
result.append(dict.index(voc) + 1)
print(dict)
print(result)
['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'I', 'J', 'K', 'L', 'M', 'N', 'O', 'P', 'Q', 'R', 'S', 'T', 'U', 'V', 'W', 'X', 'Y', 'Z']
KA K 10
AK A 0
KAO KA 26
['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'I', 'J', 'K', 'L', 'M', 'N', 'O', 'P', 'Q', 'R', 'S', 'T', 'U', 'V', 'W', 'X', 'Y', 'Z', 'KA', 'AK', 'KAO']
[11, 1, 27, 15]
# 팰린드롬 만들기
# AAABB
arr = [('A', 3), ('B', 2)]
odd = 0
mid = ''
for alp, cnt in arr:
if cnt % 2 == 1:
odd += 1
mid += alp
if odd > 1:
print("NO")
else:
ans = ''
for alp, cnt in arr:
ans += alp * (cnt // 2)
print(ans + mid + ans[::-1])
ABABA
# P기준 양옆에 k만큼 움직여서 H가 있는지 없는지 찾아내기
n, k = 20 ,2
arr = 'HHHHHPPPPPHPHPHPHHHP'
v = [False] * n
cnt = 0
for i in range(n):
if arr[i] == 'P':
for j in range(max(0, i - k), min(n, i + k + 1)):
if not v[j] and arr[j] == 'H':
v[j] = True
cnt += 1
break
print(cnt)
7
# 전체 누적 인구의 절반이상이 될때 우체국을 세우면 그 (거리 * 인구)가 최소가 된다
n = 3
arr = [[1, 3], [2, 5], [3, 3]]
p = 11 # 3 + 5 + 3
arr.sort(key = lambda x : x[0])
cnt = 0
for i in range(n):
cnt += arr[i][1]
if cnt >= p / 2:
print(arr[i][0])
break
2
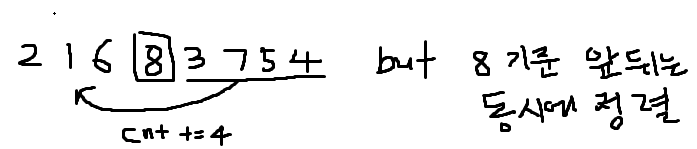
# 동시에 정렬 되기 때문에
# 최대값 8을 만난 이후 그 이전 값이 7이라면 정렬 필요 x (원래 7 - 8 순서)
# 그게 아니라면 8 기준 뒤에값이 정렬되면서 동시에 앞에 값도 동시에 정렬되기 때문에 cnt를 늘려주면서 7값의 위치를 찾아나가야 함
# -> 7이 맨앞으로 가게 된다면 그 다음에 8 앞의 6이 맨 앞으로 가야하기 때문에 동시 정렬이 수행됨 하지만 8 앞에 이미 7이 있다면 그 다음수 6 확인해 나감
n = 8
arr = [2, 1, 6, 8, 3, 7, 5, 4]
MAX = max(arr)
cnt = 0
for i in range(n-1, -1, -1):
if MAX == arr[i]:
MAX -= 1
else:
cnt += 1
print(cnt)
7
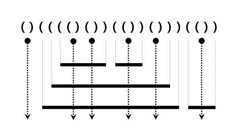
#1 레이저가 쏘는 부분 -> '(' 개수는 즉 막대기가 존재하는 부분 -> += len(stk)
#2 레이저가 쏘지 않지만 () 가 완성되는 부분 -> 막대가 끝나는 부분 -> += 1
s = '()(((()())(())()))(())'
stk = []
cnt = 0
for i in range(len(s)):
if s[i] == '(':
stk.append('(')
elif s[i] == ')':
if s[i-1] == '(':
stk.pop()
cnt += len(stk)
else:
stk.pop()
cnt += 1
print(cnt)
17
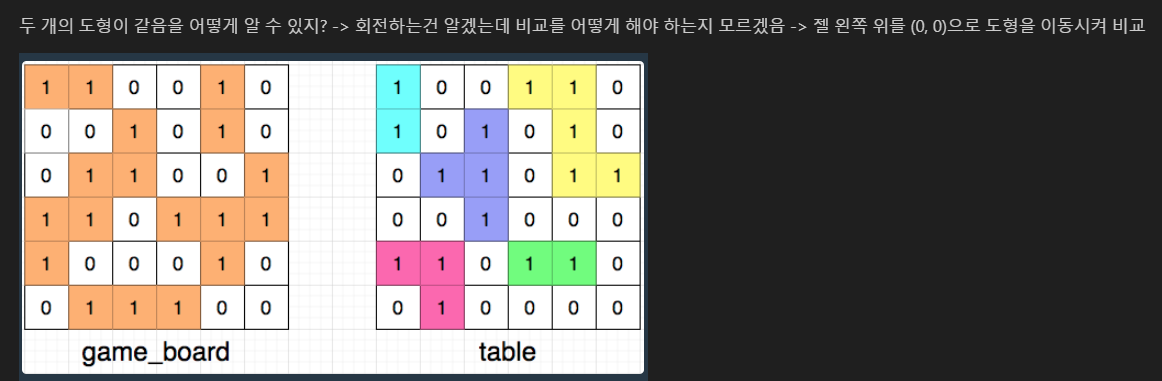
# 배열 회전
def rotate(graph):
return [list(i)[::-1] for i in zip(*graph)]
def dfs(graph, x, y):
b.append([x, y])
graph[x][y] = 1
for dx, dy in [(-1, 0), (1, 0), (0, -1), (0, 1)]:
nx, ny = x + dx, y + dy
if 0 <= nx < len(graph) and 0 <= ny < len(graph) and graph[nx][ny] == 0:
dfs(graph, nx, ny)
return min(b)
from collections import deque
def solution(game_board, table):
global b
answer = 0
n = len(table)
gb = []
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
if game_board[i][j] == 0:
b = []
x1, y1 = dfs(game_board, i, j)
b = [[b[i][0] - x1, b[i][1] - y1] for i in range(len(b))]
gb.append(b)
gb = [sorted(i) for i in gb]
for _ in range(4):
v = [[False] * n for _ in range(n)]
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
if table[i][j] == 1 and not v[i][j]:
v[i][j] = True
t = [[i, j]]
q = deque()
q.append((i, j))
while q:
x, y = q.popleft()
for dx, dy in [(-1, 0), (1, 0), (0, -1), (0, 1)]:
nx, ny = x + dx, y + dy
if 0 <= nx < n and 0 <= ny < n and table[nx][ny] == 1 and not v[nx][ny]:
v[nx][ny] = True
t.append([nx, ny])
q.append((nx, ny))
x2, y2 = min(t)
tmp = [[t[i][0] - x2, t[i][1] - y2] for i in range(len(t))]
tmp = sorted(tmp)
if tmp in gb:
answer += len(tmp)
gb.remove(tmp)
for x, y in t:
table[x][y] = 0
table = rotate(table)
return answer
game_board = [[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]
table = [[1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1],
[1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1]]
solution(game_board, table)
54
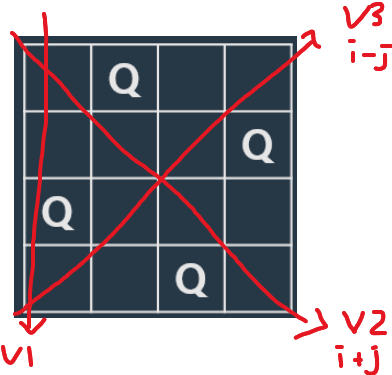
def dfs(x, v1, v2, v3, n):
global answer
if x == n:
answer += 1
return
for y in range(n):
if v1[y] == v2[x + y] == v3[x - y] == 0:
v1[y] = v2[x + y] = v3[x - y] = 1
dfs(x + 1, v1, v2, v3, n)
v1[y] = v2[x + y] = v3[x - y] = 0
def solution(n):
global answer
answer = 0
arr = [[0] * n for _ in range(n)]
v1 = [0] * n
v2 = [0] * (2 * n)
v3 = [0] * (2 * n)
dfs(0, v1, v2, v3, n)
return answer
n = 4
solution(n)
2
# 후보키
## https://school.programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/42890
from itertools import *
def solution(relation):
r, c = len(relation), len(relation[0])
target = len(relation)
arr = list(zip(*relation))
answer = []
for i in range(1, c + 1):
for j in combinations(range(c), i):
key = set(zip(*[arr[idx] for idx in j]))
if len(key) == target:
if all(not set(candidate).issubset(set(j)) for candidate in answer): # 포함하지 않는다면 TRUE
answer.append(j)
return len(answer)
relation = [
["100","ryan","music","2"],
["200","apeach","math","2"],
["300","tube","computer","3"],
["400","con","computer","4"],
["500","muzi","music","3"],
["600","apeach","music","2"]
]
print(solution(relation))
2
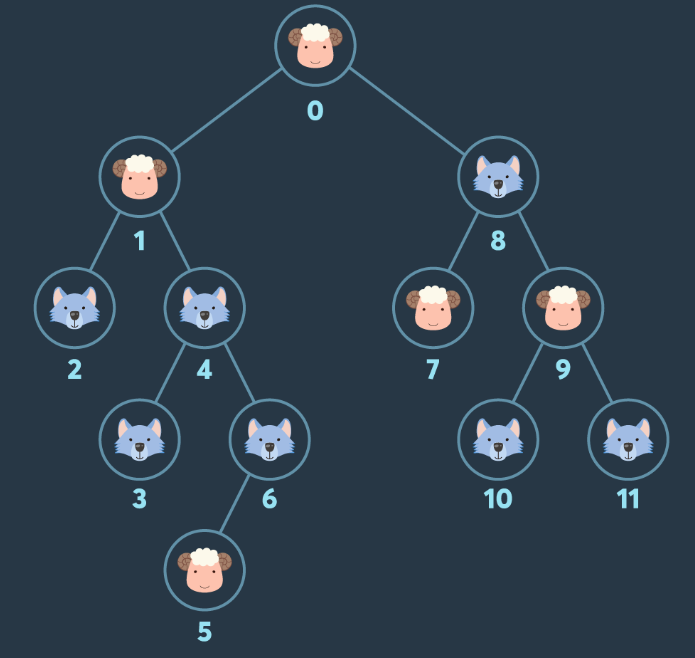
def solution(info, edges):
global answer
answer = 0
def dfs(sheep, wolf):
global answer
if sheep > wolf:
answer = max(answer, sheep)
else:
return
for parent, child in edges:
if v[parent] and not v[child]:
v[child] = True
if not info[child]:
dfs(sheep+1, wolf)
else:
dfs(sheep, wolf+1)
v[child] = False
v = [False] * len(info)
v[0] = True
dfs(1, 0)
return answer
info = [0,0,1,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,1,1]
edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[1,4],[0,8],[8,7],[9,10],[9,11],[4,3],[6,5],[4,6],[8,9]]
solution(info, edges)
5
투 포인터
# 투 포인터
#1 (처음 ~ 끝 - 1) vs (처음 + 1 ~ 끝) -> 처음, 끝 0, 0 놓고 비교 시작
#2 (음수, 음수, 양수, 양수) : 0에 가까운 값 -> (처음 + 끝) < 0 then 처음 +=1 else 끝 -= 1
#3 처음 + 끝 = target -> (처음 + 끝) < target then 처음 += 1 else 끝 -= 1
# 누적합 + 투 포인터
target = 41
arr = [0, 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41]
for i in range(1, len(arr)):
arr[i] += arr[i-1]
print(arr)
s,e = 0, 1
cnt = 0
while e < len(arr):
if arr[e] - arr[s] == target:
cnt += 1
if arr[e] - arr[s] >= target:
s += 1
else:
e += 1
print(cnt)
[0, 2, 5, 10, 17, 28, 41, 58, 77, 100, 129, 160, 197, 238]
3
순열, 조합
# A E I O U 순서대로 생성
from itertools import product
words = []
for i in range(1, 3):
for j in product(['A', 'E', 'I', 'O', 'U'], repeat=i):
words.append(''.join(list(j)))
print(words)
words.sort()
print(words)
['A', 'E', 'I', 'O', 'U', 'AA', 'AE', 'AI', 'AO', 'AU', 'EA', 'EE', 'EI', 'EO', 'EU', 'IA', 'IE', 'II', 'IO', 'IU', 'OA', 'OE', 'OI', 'OO', 'OU', 'UA', 'UE', 'UI', 'UO', 'UU']
['A', 'AA', 'AE', 'AI', 'AO', 'AU', 'E', 'EA', 'EE', 'EI', 'EO', 'EU', 'I', 'IA', 'IE', 'II', 'IO', 'IU', 'O', 'OA', 'OE', 'OI', 'OO', 'OU', 'U', 'UA', 'UE', 'UI', 'UO', 'UU']
from itertools import product
s = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]
for v in product(*s):
print(v)
(1, 4, 7)
(1, 4, 8)
(1, 4, 9)
(1, 5, 7)
(1, 5, 8)
(1, 5, 9)
(1, 6, 7)
(1, 6, 8)
(1, 6, 9)
(2, 4, 7)
(2, 4, 8)
(2, 4, 9)
(2, 5, 7)
(2, 5, 8)
(2, 5, 9)
(2, 6, 7)
(2, 6, 8)
(2, 6, 9)
(3, 4, 7)
(3, 4, 8)
(3, 4, 9)
(3, 5, 7)
(3, 5, 8)
(3, 5, 9)
(3, 6, 7)
(3, 6, 8)
(3, 6, 9)
행렬
arr1 = [1,2]
arr2 = [3,4]
print(list(zip(arr1,arr2)))
print(list(map(sum, zip(arr1,arr2))))
print()
arr3 = [[1,2],[2,3]]
arr4 = [[3,4],[5,6]]
print(list(zip(arr3,arr4)))
print([list(map(sum, i)) for i in zip(arr3,arr4)])
print([list(map(sum, zip(*i))) for i in zip(arr3,arr4)])
[(1, 3), (2, 4)]
[4, 6]
[([1, 2], [3, 4]), ([2, 3], [5, 6])]
[[3, 7], [5, 11]]
[[4, 6], [7, 9]]
relation = [
["100","ryan","music","2"],
["200","apeach","math","2"],
["300","tube","computer","3"],
["400","con","computer","4"],
["500","muzi","music","3"],
["600","apeach","music","2"]
]
arr = list(zip(*relation))
for i in arr:
print(i)
print()
s = (1, 2)
print([arr[idx] for idx in s])
print(set(zip(*[arr[idx] for idx in s])))
('100', '200', '300', '400', '500', '600')
('ryan', 'apeach', 'tube', 'con', 'muzi', 'apeach')
('music', 'math', 'computer', 'computer', 'music', 'music')
('2', '2', '3', '4', '3', '2')
[('ryan', 'apeach', 'tube', 'con', 'muzi', 'apeach'), ('music', 'math', 'computer', 'computer', 'music', 'music')]
{('apeach', 'math'), ('muzi', 'music'), ('apeach', 'music'), ('tube', 'computer'), ('ryan', 'music'), ('con', 'computer')}
# 위치, 순서 찾기
## tank -> 3번의 사이클 3번째 사람
n = 3
w = ["tank", "kick", "know", "wheel", "land", "dream", "mother", "robot", "tank"]
print(len(set(w)))
print(8 % n + 1, 8 // n + 1)
8
3 3
# 행렬 오른쪽 90도 회전
def rotate(piece):
# rpiece = [list(l) for l in zip(*piece[::-1])]
rpiece = [list(l)[::-1] for l in zip(*piece)]
return rpiece
# graph = [[i for i in range(1,4)] for _ in range(3)]
graph = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
print(graph)
print(rotate(graph))
[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]
[[7, 4, 1], [8, 5, 2], [9, 6, 3]]
# 2차원 행렬 누적합
r, c = 2,3
arr = [[1, 2, 4], [8, 16, 32]]
dp = [[0] * (c+1) for _ in range(r+1)]
# 누적합
for i in range(1, r+1):
for j in range(1, c+1):
dp[i][j] = (dp[i][j-1] + dp[i-1][j] - dp[i-1][j-1]) + arr[i-1][j-1]
print(dp)
# 누적합에서 범위지정 값 구하기
i,j,x,y = 1, 3, 2, 3
print(dp[x][y] - dp[x][j-1] - dp[i-1][y] + dp[i-1][j-1])
[[0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 1, 3, 7], [0, 9, 27, 63]]
36
# 행렬 곱셈
arr1 = [[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]] # 3행 2열
arr2 = [[-1, -2, 0], [0, 0, 3]] # 2행 3열
N = len(arr1) # 3
M = len(arr2) # 2
K = len(arr2[0]) # 3
res = [[0 for _ in range(K)] for _ in range(N)] # 3행 3열
print(res)
for n in range(N):
for m in range(M):
for k in range(K):
res[n][k] += (arr1[n][m] * arr2[m][k])
print(res)
[[0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0]]
[[-1, -2, 6], [-3, -6, 12], [-5, -10, 18]]
수학
# 페르마의 소정리
p = 1234567891
# 펙토리얼
def factorial(x):
ans = 1
for i in range(2, x + 1):
ans = (ans * i) % p
return ans
def power(x, y):
if y == 1:
return x
ans = power(x, y // 2) % p
if y % 2 == 0:
return (ans ** 2) % p
else:
return (ans ** 2 * x) % p
factorial(100)
514148002
# 제곱 수 구하기
def solution(x, y):
if y == 1:
return x
nx = solution(x, y//2) * solution(x, y//2)
if y % 2 == 0:
return nx
else:
return nx * x
answer = solution(2,8)
print(answer)
256
# 소수 찾기 / 판별
from math import sqrt
def prime(n):
if n == 0 or n == 1:
return False
for i in range(2, int(sqrt(n))+1):
if not n % i:
return False
return True
def prime_list(n):
# n >= 2
p = [False,False] + [True for _ in range(n-1)]
for i in range(2, int(sqrt(n)) + 1):
if p[i]:
j = 2
while i * j <= n:
p[i*j] = False
j += 1
return p
prime(13)
prime_list(13)
[False,
False,
True,
True,
False,
True,
False,
True,
False,
False,
False,
True,
False,
True]
# 약수
from math import sqrt
answer = set()
n = 1
for i in range(1, int(sqrt(n)) + 1):
if n % i == 0:
answer.add(i)
answer.add(n//i)
print(answer)
{1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12}
# 최대공약수, 최소공배수
n = 2
m = 5
# 최대,최소 구분
a = min(n,m)
b = max(n,m)
# GCD
def gcd(x,y):
while y:
x,y = y,x % y
return x
# LCM
def lcm1(n,m):
for i in range(max(n,m), n*m+1):
if i % n == 0 and i % m == 0:
print(i)
def lcm(x,y):
return (x * y) / gcd(x, y)
gcd(6,18) # 크기 순서 상관 없음
lcm1(6,18)
18
36
54
72
90
108
# 피보나치
def fib(n):
if n == 0:
return 0
else:
f =[0,1]
for i in range(2,n+1):
f.append(f[i-1]+f[i-2])
return f
fib(12)
[0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, 144]
from itertools import combinations
s = ["ABCFG", "AC", "CDE", "ACDE", "BCFG", "ACDEH"]
res = []
for sen in s:
for i in combinations(sen,2):
res.append(''.join(sorted(i))) # AB = BA
print(res, '\n')
['AB', 'AC', 'AF', 'AG', 'BC', 'BF', 'BG', 'CF', 'CG', 'FG', 'AC', 'CD', 'CE', 'DE', 'AC', 'AD', 'AE', 'CD', 'CE', 'DE', 'BC', 'BF', 'BG', 'CF', 'CG', 'FG', 'AC', 'AD', 'AE', 'AH', 'CD', 'CE', 'CH', 'DE', 'DH', 'EH']
# 순열
num = [1,2,3]
m = 3
result = []
def dfs_per(): # 자신 x 중복 o
if len(result) == m:
print(*result)
else:
for i in num:
if i not in result:
result.append(i)
dfs_per()
result.pop()
def dfs_per(): # 자신 o, 중복 o
if len(result) == m:
print(*result)
else:
for i in num:
result.append(i)
dfs_per()
result.pop()
# 조합
def dfs_comb(): # 자신 x 중복 x
if len(result) == m:
print(*result)
else:
for i in num:
if i not in result:
if len(result) == 0 or max(result) < i:
result.append(i)
dfs_comb()
result.pop()
def dfs_comb(): # 자신 o, 중복 x
if len(result) == m:
print(*result)
else:
for i in num:
if len(result) == 0 or max(result) <= i:
result.append(i)
dfs_comb()
result.pop()
from itertools import *
n, k = 5, 3
case = set()
for comb in combinations_with_replacement([i for i in range(1, n - k + 2)], r = k):
if sum(comb) == n:
for perm in permutations(comb, k):
case.add(perm)
print(case)
{(1, 1, 3), (1, 3, 1), (1, 2, 2), (2, 1, 2), (2, 2, 1), (3, 1, 1)}
그래프
# 다익스트라(최소거리) - 1차원
V, E = map(int, input().split())
k = int(input())
graph = [[] for _ in range(V+1)]
for _ in range(E):
u, v, w = map(int, input().split())
graph[u].append((v, w))
def dijkstra(x):
distance = [1e9] * (V+1)
distance[x] = 0
q = []
heapq.heappush(q, (x, distance[x]))
while q:
now, dist = heapq.heappop(q)
if distance[now] < dist: # 결과리스트의 값이 이미 작다면 계산할 필요 x
continue
for next, c in graph[now]:
cost = dist + c
if cost < distance[next]:
distance[next] = cost
heapq.heappush(q, (next, cost))
return distance
answer = dijkstra(k)
# Bellman-Ford - 다익스트라 음수 포함된 경우
n ,m = map(int, input().split())
graph = []
for _ in range(m):
a, b, c = map(int, input().split())
graph.append((a, b, c))
def bellman_ford(x):
distance[x] = 0
for i in range(1,n+1):
for j in range(m):
cur, next, cost = graph[j]
if distance[cur] != 1e9 and distance[cur] + cost < distance[next]:
distance[next] = distance[cur] + cost
if i == n:
return False
return True
distance = [1e9] * (n+1)
negative_cycle = bellman_ford(1)
if not negative_cycle:
print(-1)
else:
for i in distance[2:]:
if i == 1e9:
print(-1)
else:
print(i)
# 플로이드 - 워셜
V, E = map(int, input().split())
graph = [[1e9] * (V+1) for _ in range(V+1)]
for _ in range(E):
a, b, c = map(int, input().split())
graph[a][b] = c
def floyd(graph):
for k in range(1, V+1):
for i in range(1, V+1):
for j in range(1, V+1):
if graph[i][k] + graph[k][j] < graph[i][j]:
graph[i][j] = graph[i][k] + graph[k][j]
floyd(graph)
# Union-find
def find(x):
if x != parents[x]:
parents[x] = find(parents[x])
return parents[x]
def union(x, y):
_x = find(x)
_y = find(y)
if _x != _y:
parents[_y] = _x # x부모노드에 y부모노드 편입
n,m = map(int, input().split())
parents = [0] * (n + 1)
for i in range(1, n + 1):
parents[i] = i
# 최소 신장 트리
# data
# 3 3
# 1 2 1
# 2 3 2
# 1 3 3
#1. Kruskal 알고리즘 -> 큰 루트값을 작게 만들자
# cost로 오름차순 정렬 필수
v,e = map(int, input().split())
root = [i for i in range(v+1)]
answer = 0
graph = [list(map(int, input().split())) for _ in range(e)]
graph.sort(key = lambda x : x[2])
def find(x):
if x != root[x]:
root[x] = find(root[x])
return root[x]
for a, b, c in graph:
ra = find(a)
rb = find(b)
if ra != rb:
if ra > rb:
root[ra] = rb
else:
root[rb] = ra
answer+=c
print(answer)
#2.Prim 알고리즘
import heapq
v,e = map(int, input().split())
# 시작비용 0, 시작정점 랜덤값 가능(v 범위 내에서)
q = [[0, 1]]
visited = [False] * (v+1)
graph = [[] for _ in range(v+1)]
for _ in range(e):
a, b, c = map(int, input().split())
graph[a].append([c, b])
graph[b].append([c, a])
answer = 0
cnt = 0
while q:
# 정점의 개수 만큼 카운트 되면 종료
if cnt == v:
break
cost, now = heapq.heappop(q)
if not visited[now]:
visited[now] = True
answer += cost
cnt+=1
for c, next in graph[now]:
heapq.heappush(q, [c, next])
print(answer)
알고리즘
# LRU 알고리즘
# 새로운 값이 들어가는데 같은 값이 리스트내에 있으면 hit(+1), 없으면 miss(+5)
# 순차적으로 리스트에 넣기 / 캐시크기를 넘어가면 앞에서 pop
cacheSize = 3
cities = ["Jeju", "Pangyo", "Seoul", "NewYork", "LA", "Jeju", "Pangyo", "Seoul", "NewYork", "LA"]
cache = []
time = 0
for city in cities:
city = city.lower()
if cacheSize:
if city in cache: # 이미 존재한다면 -> 어차피 제거할꺼니까 꽉 차든 상관없음
time += 1
cache.remove(city)
else:
time += 5
if len(cache) == cacheSize: # cache안에 없지만 이미 꽉차있는 경우
cache.pop(0)
cache.append(city)
else: # 사이즈에 비해 cities가 작을 때
time = len(cities) * 5
break
print(time)
# Topological Sort(위상 정렬)
from collections import deque
def topology_sort():
global result
q = deque()
for i in range(1,n+1):
if indegree[i] == 0:
q.append(i)
while q:
x = q.popleft()
result.append(x)
for nx in graph[x]:
indegree[nx] -= 1
if indegree[nx] == 0:
q.append(nx)
return
n,m = map(int, input().split())
graph = [[] for _ in range(n+1)]
indegree = [0] * (n+1)
result = []
for _ in range(m):
a,b = map(int, input().split())
graph[a].append(b) # a -> b
indegree[b] += 1 # 진입차수 증가
topology_sort()
print(*result)
플로이드 워셜 - k i j = i,j = i,k + k,j
2차원 행렬 곱 - i j k = i,j += (i,k * k,j)
# 최소 공통 조상
def lca(a, b):
while depth[a] != depth[b]:
if depth[a] > depth[b]:
a = p[a]
else:
b = p[b]
while a != b:
a = p[a]
b = p[b]
return a
depth = [0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 4]
p = {1: 0, 2: 1, 3: 1, 4: 2, 5: 2, 6: 2, 7: 3, 8: 3, 9: 4, 10: 4, 11: 5, 12: 5, 13: 7, 14: 7, 15: 11}
a, b = 6, 11
print(lca(a, b))
스택
# 1924에서 수 두 개(k)를 제거하면 [19, 12, 14, 92, 94, 24] -> 최대값 찾기 stack
# number k return
# "1924" 2 "94"
def solution(number, k):
stack = []
for i in number:
while stack and stack[-1] < i and k > 0:
k-=1
stack.pop()
stack.append(i)
if k > 0:
stack = stack[:-k]
return ''.join(stack)
print(solution('1924',2))
94
# '(' 앞에 첫 숫자 * (숫자개수) + '(' 앞에 숫자개수 - 1
s = '33(562(71(9)))'
stk = []
ans = 0
b = ''
for i in s:
if i == '(':
stk.append((ans - 1, b))
ans = 0
elif i == ')':
x, y = stk.pop()
ans = x + ans * y
else:
ans += 1
b = int(i)
print(ans)
19
# 후위 표기식
# 열기 -> append
# 닫기 -> 열기 나올때까지 pop , 자신 pop
# +, - -> 열기 나올때까지 pop , 자신 append
# *, / -> 자신이 나올때까지 Pop, 자신 append
# 후위 표기식
s = '(9+(5*2+1)+(3*3*7*6*9*1*7+1+8*6+6*1*1*5*2)*4*7+4*3*8*2*6+(7*8*4*5)+3+7+(2+6+5+1+7+6+7*3*(6+2)+6+6)*2+4+2*2+4*9*3)'
ans = ''
stk = []
for i in s:
if i.isdigit():
ans += i
else:
if i == '(':
stk.append(i)
elif i == ')' or i == '+' or i == '-':
while stk and stk[-1] != '(':
ans += stk.pop()
stk.pop() if i == ')' else stk.append(i)
elif i == '*' or i == '/':
while stk and (stk[-1] == '*' or stk[-1] == '/'):
ans += stk.pop()
stk.append(i)
while stk:
ans += stk.pop()
print('후위 표기식 결과 : {}'.format(ans))
tmp = []
for i in ans:
if i.isdigit():
tmp.append(int(i))
elif i == '+':
tmp.append(tmp.pop() + tmp.pop())
else:
tmp.append(tmp.pop() * tmp.pop())
print('연산 결과 : {}'.format(*tmp))
후위 표기식 결과 : 952*1++33*7*6*9*1*7*1+86*+61*1*5*2*+4*7*+43*8*2*6*+78*4*5*+3+7+26+5+1+7+6+73*62+*+6+6+2*+4+22*+49*3*+
연산 결과 : 672676
# 현재 값을 기준으로 stk안의 과거의 값을 연속적으로 계속 비교하는 방법 (오큰수)
n = 4
arr = [3, 5, 2, 7]
ans = [-1] * n
stk = []
for i in range(n):
while stk and arr[i] > arr[stk[-1]]:
ans[stk.pop()] = arr[i]
stk.append(i)
print(ans)
[5, 7, 7, -1]
순회
n = 5
tree=[[0 for _ in range(4)] for _ in range(n+1)]
tree = [[0, 0, 0, 0], [1, '-', 2, 3], [2, '-', 4, 5], [3, 10, 0, 0], [4, 88, 0, 0], [5, 65, 0, 0]]
print(tree)
op = []
[[0, 0, 0, 0], [1, '-', 2, 3], [2, '-', 4, 5], [3, 10, 0, 0], [4, 88, 0, 0], [5, 65, 0, 0]]
# 전위
def preorder(node):
if node:
op.append(tree[node][1])
preorder(tree[node][2])
preorder(tree[node][3])
# 중위
def inorder(node):
if node:
inorder(tree[node][2])
op.append(tree[node][1])
inorder(tree[node][3])
# 후위
def postporder(node):
if node:
postporder(tree[node][2])
postporder(tree[node][3])
op.append(tree[node][1])