
자바스크립트는 왜 그 모양일까?를 읽던 중에 객체의 상속, 프로토타입, 템플릿 리터럴을 보고 이전에 진행했던 토이 프로젝트가 생각났습니다.
브라우저와 Javascript가 발전하는 과정에서 클라이언트 단에서 렌더링을 하고, 서버에서는 렌더링에 필요한 데이터만 제공하는 형태로 기술이 변화했습니다. 게다가 사용자와의 상호작용이 많은 웹 애플리케이션이 많은 요즘, jQuery와 같이 직접 DOM에 접근하여 조작하는 방식은 성능상의 문제를 일으킬 가능성이 높았습니다.
상태(State)를 기준으로 DOM을 렌더링 하는 형태로 발전하였으며, State변화에 따라 DOM의 변화가 결정되었습니다. 그리고 이러한 과정 속에서 Client-Side Rendering 이라는 개념과 상태관리라는 개념이 생기게 되습니다. 현대 웹 어플리케이션은 컴포넌트 단위로 설계되고 개발됩니다. 그리고 컴포넌트마다 컴포넌트를 렌더링할 때 필요한 상태를 관리하게 되었습니다.
저는 컴포넌트 아키텍처에 대한 이해와 State와 DOM의 관계를 더 깊이 이해하고자 Vanilla JS로 구현하기로 마음 먹었습니다.
컴포넌트 만들기
기본적으로 컴포넌트는 state를 가지고 있으며 상태가 변경되면 재렌더링 되는 구조를 가집니다. 이를 function과 prototype으로 구현해보겠습니다.
Component.js
Component 모듈은 현재 진행하는 프로젝트에서 모든 컴포넌트가 상속받는 상위 모듈입니다. 모든 컴포넌트는 공통적으로 가지고 있는 속성과 메서드가 있습니다.
function Component($el, props) {
this.$el = $el;
this.props = props;
this.state = this.initState();
this.render();
this.setEvent();
this.mounted();
}
Component.prototype.initState = function () {
return {};
};
Component.prototype.template = function () {
return "";
};
Component.prototype.render = function () {
this.$el.innerHTML = this.template();
};
Component.prototype.setEvent = function () {};
Component.prototype.mounted = function () {};
Component.prototype.setState = function(newState) {
this.state = { ...this.state, ...newState };
this.render();
};- $el: 컴포넌트 부모 요소 (DOM 객체)
- props: 컴포넌트에 전달되는
properties(Object) - state: 컴포넌트의 상태
- initState(): 컴포넌트의 상태를 초기화하는 메서드
- render(): 렌더링 메서드
- setEvent(): 현재 컴포넌트 요소들에 이벤트를 설정하는 메서드
- mounted(): 컴포넌트 렌더링 이후 실행되는 메서드
- setState(): 컴포넌트의 상태를 변경하는 메서드
공통기능 메서드들은 Component Prototype에 정의되어 있으며, 이를 상속받는 컴포넌트들은 자신만의 메서드를 정의할 수 있게됩니다. render, setEvent, mounted 메서드들은 컴포넌트가 생성될 때 반드시 실행되어야 합니다.
⭐ setEvent함수는 한 번만 실행되어야 하기에 컴포넌트 생성시에만 호출되도록 한다.
컴포넌트 구현하기 / App.js
call()은 이미 할당되어있는 다른 객체의 함수/메소드를 호출하는 해당 객체에 재할당할때 사용됩니다. this는 현재 객체(호출하는 객체)를 참조합니다. 메소드를 한번 작성하면 새 객체를 위한 메소드를 재작성할 필요 없이 call()을 이용해 다른 객체에 상속할 수 있습니다. - MDN
컴포넌트의 생성자 연결에 call을 사용합니다. 호출시 Component의 생성자는 $el 및 props를 매개변수로 정의됩니다. 함수 App은 this 및 $el, props를 전달하는 Component를 호출합니다.
Component.call()가 호출되면 상속받은 프로토타입에서 재정의한 메서드들이 차례대로 호출됩니다.
function App($target, props) {
Component.call(this, $target, props);
}- App.initState() => App.render() => App.setEvent() => App.mount()
import Component from "../core/Component.js";
function App($target, props) {
Component.call(this, $target, props);
}
// 프로토타입 상속
Object.setPrototypeOf(App.prototype, Component.prototype);
// .. 프로토타입 메서드 오버라이딩
App.prototype.initState = function () {
return { // initState };
};
App.prototype.template = function () {
return ""; // template reteral
};
App.prototype.render = function () {
this.$el.innerHTML = this.template();
};
App.prototype.setEvent = function () {
// addEventListener ....
};
App.prototype.mounted = function () {
// 렌더링 이후 수행 할 작업
};메서드 오버라이딩
Component의 프로토타입을 연결(chain)해 메서드에 접근했다면 각 컴포넌트마다 적절한 동작을 수행하도록 재정의 해줘야합니다.
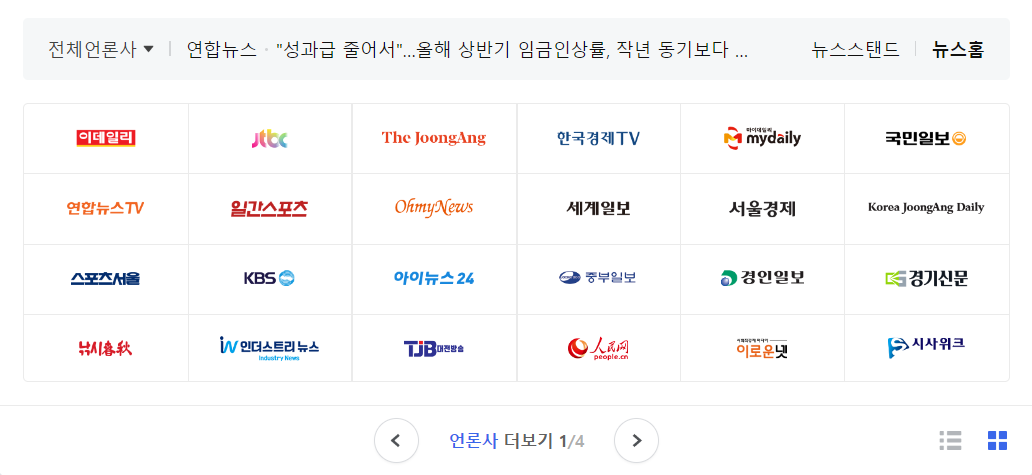
네이버 뉴스스탠드 화면을 클론코딩한다고 가정해보겠습니다. 크게 두 부분의 영역으로 나눠볼 수 있을 것 같습니다.
- AutoRolling : 뉴스의 제목이 자동으로 롤링되는 영역
- Main : 언론사 그리드/리스트 뷰 영역, 페이지 전환 영역, 뷰 형태 전환 영역
상태관리가 필요해보이는 영역은 Main 컴포넌트이므로 간단하게 구현해 보겠습니다.
import Component from "../core/Component.js";
function Main($target, props) {
Component.call(this, $target, props);
}오버라이딩 할 메서드는 initState, template, mounted입니다.
initState
Main.prototype.initState = function () {
return { view: 'grid', page: 1 }; // view 형태와 페이지
};template
Main.prototype.template = function () {
return `
<div class="press-view">
<div class="footer">
`;
};mounted
Main.prototype.mounted = function () {
const $pressView = this.$target.querySelector('press-view');
const $footer = this.$target.querySelector('footer');
new PressView($pressView, props);
new Footer($footer, props);
};전체 Main 컴포넌트 코드를 JS, React와 비교하면 다음과 같습니다.
JavaScript
function Main($target, props) {
Component.call(this, $target, props);
}
Object.setPrototypeOf(App.prototype, Component.prototype);
Main.prototype.initState = function () {
return { view: 'grid', page: 1 };
};
Main.prototype.template = function () {
return `
<div class="press-view">
<div class="footer">
`;
};
Main.prototype.mounted = function () {
const $pressView = this.$target.querySelector('press-view');
const $footer = this.$target.querySelector('footer');
new PressView($pressView, props);
new Footer($footer, props);
};React
function Main(props){
const [view, setView] = useState('grid');
const [page, setPage] = useState(1);
// ... code
return (
<>
<PressView />
<Footer />
</>
)
}index.js / index.html
브라우저에 렌더링되는 HTML 코드는 JS 파일들에서 관리되기 때문에 React와 비슷한 html코드를 작성할 수 있습니다.
<!-- index.html -->
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>News Stand</title>
<!-- css -->
<script type="module" src="./index.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
</html>// index.js
import App from "./src/App.js";
const root = document.querySelector("#root");
new App(root);참고자료
Vanilla Javascript로 웹 컴포넌트 만들기 - 황준일
Function.prototype.call() - MDN
상속과 프로토타입 - MDN
