
Combine Framework FREE course: write you first iOS app - use Subscriptions & Publishers like Subject
Combine: TodoList Using Combine
구현 목표
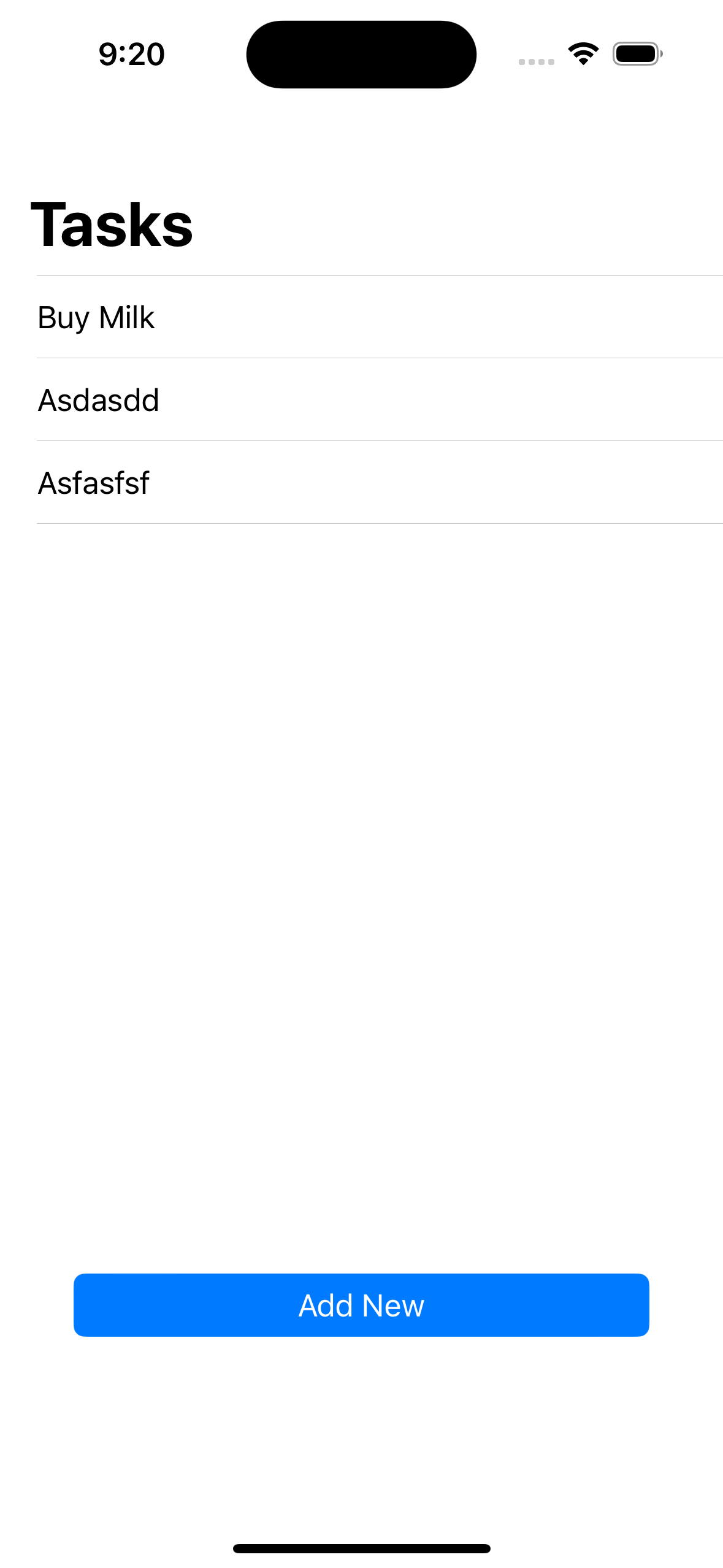
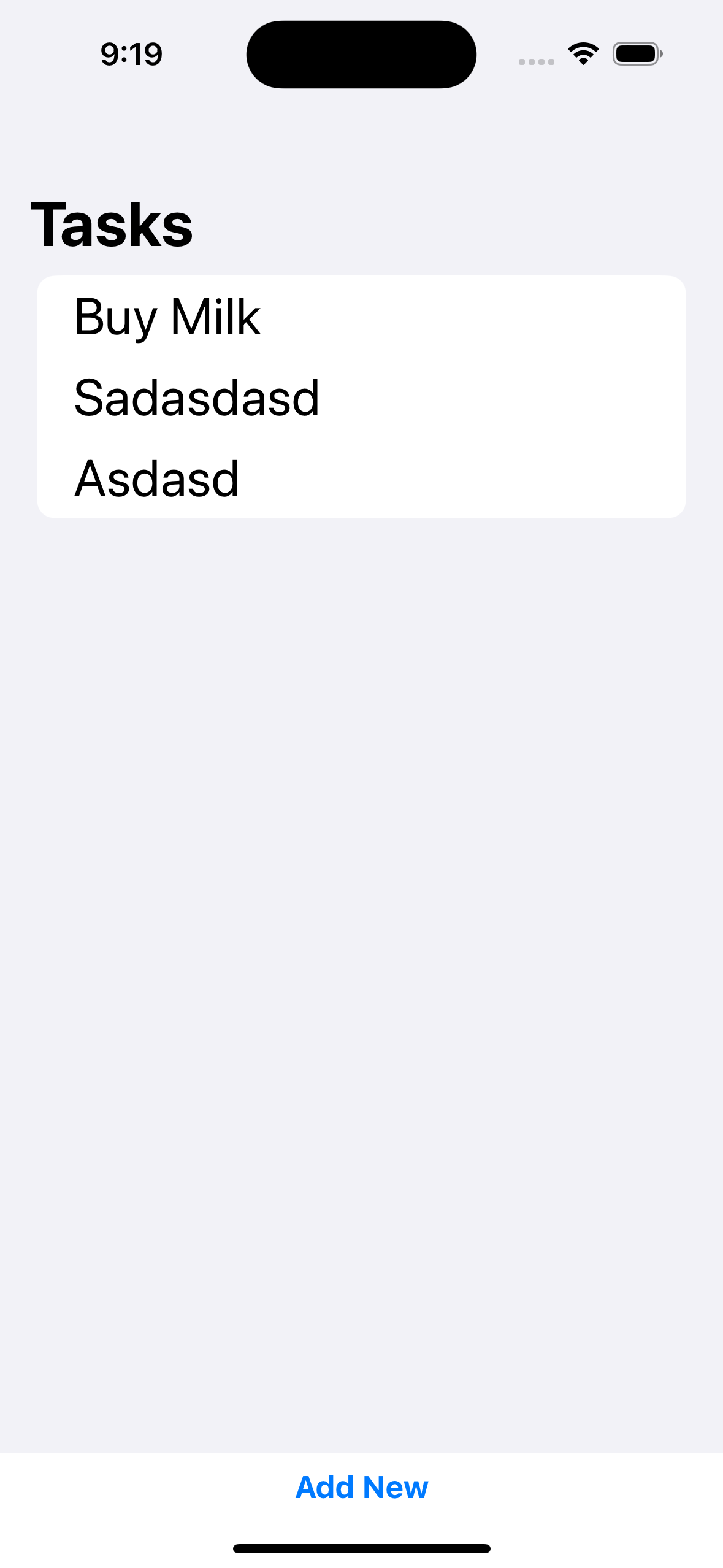
- UIKit과 SwiftUI의 서로 다른
Combine프레임워크 사용법 익히기 ObservableObject내@Published및 일반 뷰 모델 클래스에서의AnyPublished간의 사용 방법 차이
구현 태스크
- UIKit의 테이블뷰, SwiftUI의 리스트를 그리는 데 사용하는 데이터가 동적으로 추가될 때 UI 동적 변경
- 뷰 모델 내 데이터 퍼블리셔 값 변경 이벤트 감지
CurrentValueSubject,@Published등 퍼블리셔 종류에 따른 구독 방법PassthroughSubject를 통해 데이터 동적 추가- 데이터를 그리는 데 사용하는 데이터 퍼블리셔는 읽기 전용으로 데이터 안전성 확보하기
핵심 코드
class TaskListViewModel {
// replace CurrentValueSubject with @Published
let tasks = CurrentValueSubject<[String], Never>(["Buy Milk"])
// @Published var tasks = ["Buy Milk"]
var addNewTask = PassthroughSubject<String, Never>()
private var cancellables = Set<AnyCancellable>()
init() {
// data stream to create new task
addNewTask
.filter {$0.count > 3}
.sink { [weak self] newTask in
guard let self = self else { return }
// self.tasks.append(newTask)
self.tasks.send(self.tasks.value + [newTask])
}
.store(in: &cancellables)
// get initial values at launch like from file system
// save changes to tasks in file system
}
}- 초깃값을 가지고 있는 데이터 퍼블리셔
tasks는 다른 뷰에서 UI를 그리기 위해 구독하고 있음 - 해당 데이터 스트림은 읽기 전용으로, 데이터 추가하기 위한 통로는
addNewTask의send를 통해 이루어짐
@objc private func doneButtonDidTap() {
taskListModel?.addNewTask.send(text)
dismiss(animated: true, completion: nil)
}- 데이터 추가 이벤트
addNewTask의 데이터는sink를 통해 내려와 이후 UI를 그리는 데 사용할tasks의 데이터에 추가됨
private func addSubscription() {
// add data stream that calls tableView.reloadData() when data changes
taskViewModel.tasks
.sink { [weak self] values in
guard let self = self else { return }
print("Received values: \(values)")
self.tableView.reloadData()
}
.store(in: &cancellables)
}- 값 변화가 일어날 때 UI를 다시 그리는 함수를 수동으로 다시 호출해야 하는 현재 상황
소스 코드
import UIKit
import Combine
class TodoListViewController: UIViewController {
private let tableView: UITableView = {
let tableView = UITableView()
tableView.register(UITableViewCell.self, forCellReuseIdentifier: "tableViewCell")
return tableView
}()
private let button: UIButton = {
let button = UIButton()
var config = UIButton.Configuration.filled()
config.background.backgroundColor = .systemBlue
button.configuration = config
button.setTitle("Add New", for: .normal)
button.setTitleColor(.white, for: .normal)
return button
}()
private var taskViewModel = TaskListViewModel()
private var cancellables = Set<AnyCancellable>()
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
setTodoListViewUI()
addSubscription()
}
private func setTodoListViewUI() {
title = "Tasks"
navigationController?.navigationBar.prefersLargeTitles = true
tableView.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
button.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
view.addSubview(tableView)
tableView.leadingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.leadingAnchor).isActive = true
tableView.trailingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.trailingAnchor).isActive = true
tableView.topAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.topAnchor, constant: 100).isActive = true
tableView.bottomAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.bottomAnchor, constant: -200).isActive = true
tableView.dataSource = self
view.addSubview(button)
button.leadingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.leadingAnchor, constant: 40).isActive = true
button.trailingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.trailingAnchor, constant: -40).isActive = true
button.topAnchor.constraint(equalTo: tableView.bottomAnchor, constant: 40).isActive = true
button.addTarget(self, action: #selector(didButtonTap), for: .touchUpInside)
}
private func addSubscription() {
// add data stream that calls tableView.reloadData() when data changes
taskViewModel.tasks
.sink { [weak self] values in
guard let self = self else { return }
print("Received values: \(values)")
self.tableView.reloadData()
}
.store(in: &cancellables)
}
@objc private func didButtonTap() {
let addNewVC = AddNewViewController()
addNewVC.taskListModel = taskViewModel
navigationController?.present(addNewVC, animated: true)
}
}
extension TodoListViewController: UITableViewDataSource {
func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, numberOfRowsInSection section: Int) -> Int {
return taskViewModel.tasks.value.count
}
func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, cellForRowAt indexPath: IndexPath) -> UITableViewCell {
let cell = tableView.dequeueReusableCell(withIdentifier: "tableViewCell", for: indexPath)
cell.textLabel?.text = taskViewModel.tasks.value[indexPath.row]
return cell
}
}- 해당 뷰의 테이블 뷰는 뷰 모델의 데이터 퍼블리셔를 데이터 소스로 사용
- 데이터 변화를 감지, 새롭게 테이블 뷰를 그리기 위해
tasks를 구독할 때sink파트에서tableView.reloadData()를 호출 Combine을 사용하고 있지만 일반적인 UIKit 프레임워크의target-action패턴을 그대로 사용하고 있기 때문에 완전한 반응형 프로그래밍이라고 보기에 부족(RxCocoa에서의 바인딩과 비교)
import UIKit
import Combine
class AddNewViewController: UIViewController {
private let label: UILabel = {
let label = UILabel()
label.text = "Add New Task"
label.textColor = .black
label.font = .preferredFont(forTextStyle: .title1)
return label
}()
private let textField: UITextField = {
let textField = UITextField()
textField.font = .preferredFont(forTextStyle: .headline)
textField.textColor = .black
textField.borderStyle = .roundedRect
return textField
}()
private let cancelButton: UIButton = {
let button = UIButton()
var config = UIButton.Configuration.filled()
config.background.backgroundColor = .clear
button.configuration = config
button.setTitle("Cancel", for: .normal)
button.setTitleColor(.systemRed, for: .normal)
return button
}()
private let doneButton: UIButton = {
let button = UIButton()
var config = UIButton.Configuration.filled()
config.background.backgroundColor = .clear
button.configuration = config
button.setTitle("Done", for: .normal)
button.setTitleColor(.systemBlue, for: .normal)
return button
}()
var taskListModel: TaskListViewModel?
private var text = ""
private var cancellables = Set<AnyCancellable>()
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
setAddNewViewUI()
}
private func setAddNewViewUI() {
view.backgroundColor = .systemBackground
label.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
textField.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
cancelButton.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
doneButton.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
view.addSubview(label)
view.addSubview(textField)
view.addSubview(cancelButton)
view.addSubview(doneButton)
label.centerXAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.centerXAnchor).isActive = true
label.topAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.topAnchor, constant: 200).isActive = true
textField.leadingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.leadingAnchor, constant: 40).isActive = true
textField.trailingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.trailingAnchor, constant: -40).isActive = true
textField.topAnchor.constraint(equalTo: label.bottomAnchor, constant: 50).isActive = true
textField.backgroundColor = UIColor.systemGray6
cancelButton.topAnchor.constraint(equalTo: textField.bottomAnchor, constant: 50).isActive = true
cancelButton.leadingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.leadingAnchor, constant: 100).isActive = true
doneButton.topAnchor.constraint(equalTo: textField.bottomAnchor, constant: 50).isActive = true
doneButton.leadingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: cancelButton.trailingAnchor, constant: 50).isActive = true
textField.addTarget(self, action: #selector(updateText), for: .editingChanged)
cancelButton.addTarget(self, action: #selector(cancelButtonDidTap), for: .touchUpInside)
doneButton.addTarget(self, action: #selector(doneButtonDidTap), for: .touchUpInside)
}
@objc private func doneButtonDidTap() {
taskListModel?.addNewTask.send(text)
dismiss(animated: true, completion: nil)
}
@objc private func cancelButtonDidTap() {
dismiss(animated: true, completion: nil)
}
@objc private func updateText() {
text = textField.text ?? ""
}
}- 모달 뷰로 올라오는 뷰로 이전 뷰에서 사용하는 뷰 모델을
present시에 그대로 입력받음 addNewTask에게 텍스트를 입력하는send가 해당 데이터 추가 이벤트 →tasks는 해당addNewTask의sink에서 값이 변화
import Foundation
import Combine
class TaskListViewModel {
// replace CurrentValueSubject with @Published
let tasks = CurrentValueSubject<[String], Never>(["Buy Milk"])
// @Published var tasks = ["Buy Milk"]
var addNewTask = PassthroughSubject<String, Never>()
private var cancellables = Set<AnyCancellable>()
init() {
// data stream to create new task
addNewTask
.filter {$0.count > 3}
.sink { [weak self] newTask in
guard let self = self else { return }
// self.tasks.append(newTask)
self.tasks.send(self.tasks.value + [newTask])
}
.store(in: &cancellables)
// get initial values at launch like from file system
// save changes to tasks in file system
}
}tasks를 데이터 퍼블리셔로addNewTask를 해당tasks에게 값을 건네주는 연결 통로로 사용하는 뷰 모델@Published를 사용하지 않는 까닭은 UIKit의 데이터 인풋/아웃풋 타이밍에서 한 스텝 느리기 때문
import SwiftUI
struct TodoListView: View {
@StateObject private var viewModel = TaskListViewModel()
@State private var isPresented: Bool = false
var body: some View {
NavigationView {
VStack {
List {
ForEach(viewModel.tasks, id:\.self) { task in
Text(task)
.font(.title)
}
}
Button {
isPresented.toggle()
} label: {
Text("Add New")
.font(.headline)
.fontWeight(.bold)
}
}
.sheet(isPresented: $isPresented, content: {
AddNewTaskView(viewModel: viewModel)
})
.navigationTitle("Tasks")
}
}
}- SwiftUI 프레임워크에서 뷰 모델의 태스크를 표현하기 위한 리스트 뷰
TaskListViewModel을StateObject로 받아 값의 변화를 감지하고 있기 때문에viewModel.tasks를 통해 그려지는 리스트가 데이터 소스의 값 변화가 일어날 때 뷰를 다시 그릴 수 있음
import SwiftUI
struct AddNewTaskView: View {
@Environment(\.dismiss) private var dismiss
var viewModel: TaskListViewModel
@State private var text: String = ""
var body: some View {
VStack(alignment: .center, spacing: 30) {
Text("Add New Task")
.font(.largeTitle)
.foregroundColor(.black)
TextField("", text: $text)
.frame(height: 60)
.background(Color.gray.opacity(0.4).cornerRadius(15))
.padding(.leading, 40)
.padding(.trailing, 40)
HStack(alignment: .center, spacing: 50) {
Button {
dismiss()
} label: {
Text("Cancel")
.font(.headline)
.foregroundColor(.red)
}
Button {
viewModel.addNewTask.send(text)
dismiss()
} label: {
Text("Done")
.font(.headline)
.foregroundColor(.blue)
}
}
}
}
}- UIKit 구현에서와 마찬가지로 건네받은
TaskListViewModel의addNewTask에 값을send하는 이벤트를 통해 리스트가 구독하는tasks의 값을 변화시킴
import Foundation
import Combine
class TaskListViewModel: ObservableObject {
@Published var tasks = ["Buy Milk"]
// let tasks = CurrentValueSubject<[String], Never>(["Buy Milk"])
var addNewTask = PassthroughSubject<String, Never>()
private var cancellables = Set<AnyCancellable>()
init() {
addSubscriber()
}
private func addSubscriber() {
addNewTask
.filter{$0.count > 3}
.sink { [weak self] task in
guard let self = self else { return }
self.tasks.append(task)
// self.tasks.send(self.tasks.value + [task])
}
.store(in: &cancellables)
// tasks
// .sink { [weak self] values in
// guard let self = self else { return }
// print("tasks were update to \(values)")
// self.objectWillChange.send()
// }
// .store(in: &cancellables)
}
}@Published를 사용, 값 변화가 일어날 때 곧바로 이를 관찰하는StateObject를 받고 있는 파트에서 감지 가능
구현 화면


