백준 7562 - 나이트의 이동 (Sliver1, JS, DFSBFS)
1. 문제 해설
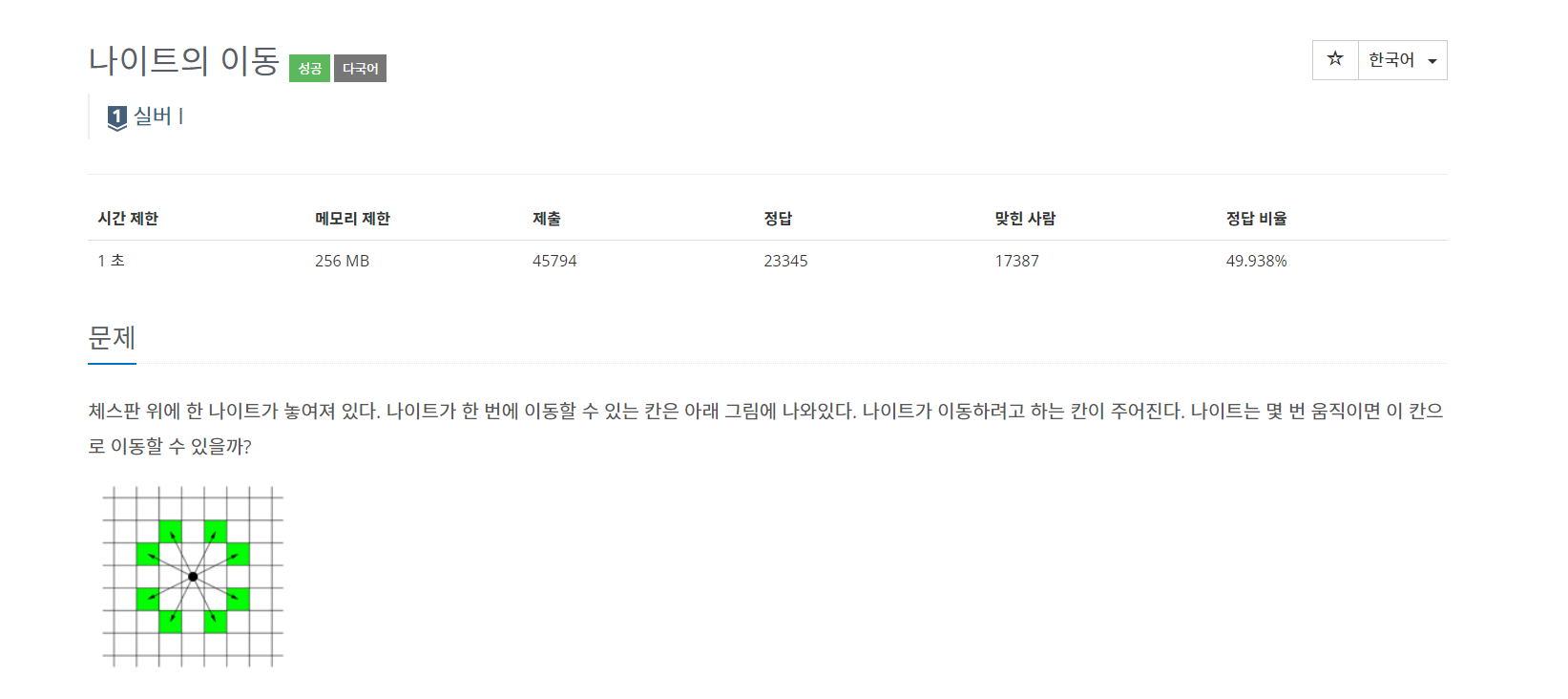
2. 제한사항 & 입출력 예

Solution
크으 오로지 내 힘만으로 도달한 결과~!!
DFSBFS 3일만에 드디어 성공.
const fs = require('fs');
const input = fs.readFileSync('/dev/stdin').toString().trim().split('\n');
const count = parseInt(input[0]);
let width = [];
let start = [];
let end = [];
for (let i = 1; i < input.length; i+=3) {
let [w,s,e] = input.slice(i,i+3);
start = [...start, s.split(' ').map(v=>+v)]
end = [...end, e.split(' ').map(v=>+v)];
width = [...width, parseInt(w)];
}
function initMaps(w) {
let maps = [];
let map = [];
for (let i = 0; i < w; i++){
map = [];
for (let j = 0; j < w; j++){
map.push(0)
}
maps.push(map)
}
return maps;
}
function solution(start, end, width) {
let Case = 0;
while (Case < count) {
const [startX, startY] = start[Case];
const [endX, endY] = end[Case];
const w = width[Case];
let map = initMaps(w);
let queue = [[startX, startY]];
map[startX][startY] = 1;
while (queue.length > 0) {
if (startX === endX && startY === endY) {
console.log(0);
break;
}
const [x,y] = queue.shift();
for (let [nx, ny] of [
[x - 2, y + 1],
[x - 1, y + 2],
[x + 1, y + 2],
[x + 2, y + 1],
[x + 2, y - 1],
[x + 1, y - 2],
[x - 1, y - 2],
[x - 2, y - 1],
]) {
if (nx >= 0 && ny >= 0 && nx < w && ny < w ) {
if (map[nx][ny] === 0) {
map[nx][ny] = map[x][y] + 1;
queue.push([nx, ny]);
if (nx === endX && ny === endY) {
console.log(map[nx][ny] - 1);
queue = [];
break;
}
}
}
}
}
Case++;
}
}
solution(start, end, width);
위 코드를 조금 더 정리한 솔루션
const fs = require('fs');
const input = fs.readFileSync('/dev/stdin ').toString().trim().split('\n');
const count = parseInt(input[0]);
function initData(input) {
let width = [];
let start = [];
let end = [];
for (let i = 1; i < input.length; i+=3) {
let [w,s,e] = input.slice(i,i+3);
start = [...start, s.split(' ').map(v=>+v)]
end = [...end, e.split(' ').map(v=>+v)];
width = [...width, parseInt(w)];
}
return [start,end,width];
}
function initMaps(width) {
let maps = []
for (let i = 0; i < width.length; i++){
maps.push(
Array(width[i])
.fill()
.map(() => Array(width[i]).fill(0)),
);
}
return maps;
}
function solution(start, end, width) {
let Case = 0;
let maps = initMaps(width);
while (Case < count) {
const [startX, startY] = start[Case];
const [endX, endY] = end[Case];
const w = width[Case];
if (startX === endX && startY === endY) {
console.log(0);
Case++;
continue;
}
let map = maps[Case];
let queue = [[startX, startY]];
map[startX][startY] = 1;
while (queue.length > 0) {
const [x,y] = queue.shift();
for (let [nx, ny] of [
[x - 2, y + 1],
[x - 1, y + 2],
[x + 1, y + 2],
[x + 2, y + 1],
[x + 2, y - 1],
[x + 1, y - 2],
[x - 1, y - 2],
[x - 2, y - 1],
]) {
if (nx >= 0 && ny >= 0 && nx < w && ny < w ) {
if (map[nx][ny] === 0) {
map[nx][ny] = map[x][y] + 1;
queue.push([nx, ny]);
if (nx === endX && ny === endY) {
console.log(map[nx][ny] - 1);
queue = [];
break;
}
}
}
}
}
Case++;
}
}
solution(...initData(input));
4. 공부한것
2차원 배열 만들기
let arr = new Array(3).fill([]);fill 메서드가 얕은 복사로 값을 채우기 때문에 빈 배열이 들어가게 되면 같은 주소값을 가르키게 된다.
// 아래 것을 써야 다른 배열 주소값을 가르킨다.
let arr = Array.from({ length: 3 }, () => []);
// fill(0) 메소드를 쓰는 이유는
// 빈 배열의 경우 map 함수가 제대로 실행되지 않기 때문이다. 실제로 초기화 되지는 않는다.
const arr = new Array(5).fill(0).map(() => new Array(4));생성과 동시에 초기화 하고 싶다면
// 4 X 5 의 모든 원소가 1 로 초기화 됨
const arr = new Array(5).fill(0).map(() => new Array(4).fill(1));