모듈 예제를 풀어보자!
모듈은__name__과__main__총 2개의 창을 만들어 작업해야 한다.
모듈 예제(1)
📌return
- 파이썬 기초 함수의 핵심 return! return은 output 입니다.
def sum(x, y)
return x + y
result = sum(2, 3)
print(result)- 제일 먼저 sum 안에서 print(x + y)였던 것이 return x + y로 바뀌었고 파이썬 함수는 x + y를 돌려주는 것이 된 것.
- 그렇다면 그 돌아오는 값을 받는 변수는 result가 됨.
- 즉 호출할때 result = sum(2, 3)으로 return 값을 result에 저장하라고 명령한 것!
- 그 이후 print(result) 를 하게 되면 5가 나옴!
Q. 모듈을 이용한 프로그래밍
- 과목별 점수를 입력하면 합격 여부를 출력하는 모듈 제작
- 평균 60점 이상 합격, 과락 40점
- s1 (40) s2(45) s3(85) s4(75) s5(90)
- 40점 미만은 FINAL FAIL
📝문제 풀이
[passOrFail.py]
def exampleResult(s1, s2, s3, s4, s5):
passAvgScore = 60
limitScore = 40
def getTotal():
totalScore = s1 + s2 + s3 + s4 + s5
print(f'총점 : {totalScore}')
return totalScore
def getAverage():
avg = getTotal() / 5
print(f'평균 : {getAverage}')
return getAverage
def printPassOrFail():
print(f'{s1}: Pass') if s1 >= limitScore else print(f'{s1}: Fail')
print(f'{s2}: Pass') if s2 >= limitScore else print(f'{s2}: Fail')
print(f'{s3}: Pass') if s3 >= limitScore else print(f'{s3}: Fail')
print(f'{s4}: Pass') if s4 >= limitScore else print(f'{s4}: Fail')
print(f'{s5}: Pass') if s5 >= limitScore else print(f'{s5}: Fail')
def printFinalPassOrFail():
if getAverage() >= passAvgScore:
if s1 >= limitScore and s2 >= limitScore and s3 >= limitScore and s4 >= limitScore and s5 >= limitScore:
print('FINAL PASS')
else:
print('FINAL FAIL')
else:
print('Final Fail')
getAverage()
printPassOrFail()
printFinalPassOrFail()[ex.py]
import passOrFail as pf
if __name__ == '__main__':
sub1 = int(input('과목1 점수 입력: '))
sub2 = int(input('과목2 점수 입력: '))
sub3 = int(input('과목3 점수 입력: '))
sub4 = int(input('과목4 점수 입력: '))
sub5 = int(input('과목5 점수 입력: '))
pf.exampleResult(sub1, sub2, sub3, sub4, sub5)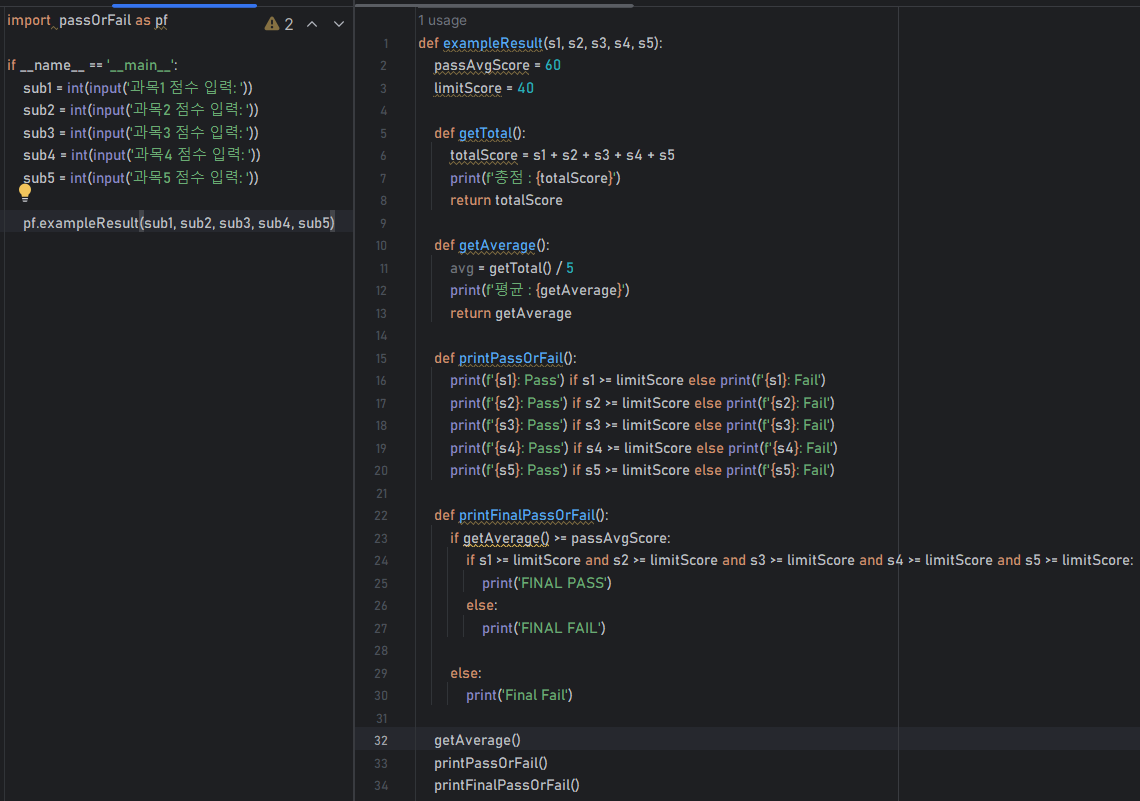
모듈 예제(2)
📌flag 변수
flag=True
- 대표적인 불변수로 사용한다. ex) 더하기 변수를 'sum'으로 하는 것과 같은 이치
- 조건식은 참(True) 과 거짓(False)으로 판별되는데 이를 저장하는 변수를 불(bool)변수라고 한다.
- 불 변수로 플래그 변수를 사용한다.
📌append()
리스트이름.append(데이터 이름)
- 리스트 맨뒤에 값 추가 : 리스트.append(값)
- 리스트 맨뒤에 여러개 추가 : 리스트.extend(리스트)
Q. 모듈을 이용한 프로그래밍
- 상품 구매 개수에 따라 할인율이 결정되는 모듈 제작
- 다음과 같이 계산 결과가 출력되는 프로그램 제작
- 1개(5%) 2개(10%) 3개(15%) 4개(20%) 5개 이상(25%)
📝문제 풀이
[discount.py]
#gs : 상품들
def calculatorTotalPrice(gs):
if len(gs) <= 0:
print('구매 상품이 없습니다.')
return
rate = 25
totalPrice = 0
rates = {1:5, 2:10, 3:15, 4:20}
if len(gs) in rates:
rate = rates[len(gs)]
for g in gs:
totalPrice += g + (1 - rate * 0.01)
return [rate, int(totalPrice)] # 정수로 캐스팅
# , 원 단위 포맷
def formatedNumber(n):
return format(n, ',')[ex.py]
import discount as dc
if __name__ == '__mail__':
flag = True
gs = []
while flag:
selectNumber = int(input('상품을 구매하시겠어요? 1. 구매 2. 구매 종료'))
if selectNumber == 1:
goods_price = int(input('상품 가격 입력'))
gs.append(goods_price)
elif selectNumber == 2:
result = dc.calculatorTotalPrice(gs)
flag = False
print(f'할인율: {result[0]}')
print(f'합계: {dc.formatedNumber[1]}')모듈 예제(3)
📌range()
range(start, stop, step)
- start : 시퀀스 시작 값
- stop : 시퀀스 끝 값
- step : 시퀀스 간격
- range(5) : 0 ~ 4
- range(2, 8) : 2 ~ 7
- range(1, 10, 2) : 1 ~ 9 중 간격이 2인 숫자로 이뤄짐- range() 반복문
for i in range(5):
print(i)
--> 0,1,2,3,4- range() 리스트 생성
myList = list(range(1, 6)):
print(myList)
--> [1,2,3,4,5]- range() 숫자합
total = 0
for i in range(1, 11):
total += 1
print(total)
--> 1~10 까지의 합계- range() 구구단
for i in range(2, 10):
for j in range(1, 10):
print(f"{i} * {j} = {i*j}")
print()
-->
2 ~ 9단까지의 구구단을 출력
외부 반복문 : 2 ~ 9 숫자 생성
내부 반복문 : 1 ~ 9 까지 숫자 생성, 출력📌전역변수 global 선언
📍지역변수
- 함수 밖에서 a = 1로 선언한 뒤, 메소드 내에서 a = 100으로 선언해보았지만, scope를 벗어난 순간 기존 값인 1로 a가 초기화된 점을 확인
- 이 경우에는 함수 내 a는 지역변수였던 것
a = 1 def a_is_100(): a = 100 print(a) a_is_100() # 100 print(a) # 1
반면, 함수 내에서 선언했던 변수를 메소드 실행 뒤에도 유지하고 싶다면,
global 키워드를 통하여 해당 변수를 전역변수로 사용하겠다고 선언해주면 됨
📍전역변수
- global a로 함수 내에서 변수를 선언
- 함수의 scope를 벗어난 경우에도 a = 100으로 값이 유지된 점을 확인
a = 1 def a_is_100(): global a # 전역 변수 선언 a = 100 print(a) a_is_100() # 100 print(a) # 100
Q. 로또 모듈
로또모듈을 다음과 같이 로또 결과가 출력될 수 있도록 프로그램을 만들자.
📝문제 풀이
[lotto.py]
import random
# 난수를 발생하는 번호가 있어야 함
# 사용자가 입력하는 번호도 있어야 함
#사용자 숫자와 기계 발생 숫자가 몇개가 일치하는지, 일치 자료 구조도 만들어야 함
#보너스 숫자도 만들기
userNums = []; randNums = []; collNums = []
randBonuNum = 0
#함수를 만들자.
#사용자가 입력한 번호를 매개 변수로 주면 userNums에 대입될 수 있도록 함
def setUserNums(ns):
global userNums
userNums = ns
#사용자 입력을 뺴오는 userNums를 만듬
def getUserNums():
return userNums # 반환
#기계가 발생하는 숫자 만들기, 1~45 까지, 겹치지 않게 6개 숫자
def setRandNums():
global randNums
randNums = random.sample(range(1, 46), 6)
#기계가 발생하는 숫자 만들기
def getRandNums():
return randNums # 랜덤 모듈에서 뺴오기
#보너스 숫자도 필요함. 1개 필요하니까 Num 단수!
def setBonuNum():
global randBonuNum
#보너스 숫자는 난수와 겹치면 안되니까, 겹치지 않을떄 까지 반복하는 while문 생성.
while True:
randBonuNum = random.randint(1, 45) # 정수 중 하나 뽑아라
if randBonuNum not in randNums: #randNums에 있으면 안됨. 그래서 없으면
break # 빠져나와라. 만약에 있으면 계쏙 돌려라. 그뜻의 반복문
def getBonuNum():
return randBonuNum
#로또 결과 반환 함수
#사용자 입력, 기계 생성번호, 일치 구조
def lottoResult():
global userNums
global randNums
global collNums
#과거의 데이터가 있으면 안되니까, [초기화]를 for문을 이용해서 해줌
collNums = []
for un in userNums: # 숫잘를 하나 꺼내옴
if un in randNums: #반복문, randNums에 있으면
collNums.append(un) #collNums에 넣어주기.
if len(collNums) == 6: # 만약에 맞는 갯수가 6개면
print(f'1등 담첨!!') # 1등 당첨
print(f'번호: {collNums}')
# 그렇지 않은 경우
# 5개 + 보너스가 맞음
elif (len(collNums) == 5) and (randBonuNum in userNums):
print(f'2등 담첨!!')
print(f'번호: {collNums}, 보너스 번호: {randBonuNum}')
# 5개 맞은 경우
elif len(collNums) == 5:
print(f'3등 담첨!!')
print(f'번호: {collNums}')
#4개 맞은 경우
elif len(collNums) == 4:
print(f'4등 담첨!!')
print(f'번호: {collNums}')
# 3개맞은 경우
if len(collNums) == 3:
print(f'5등 담첨!!')
print(f'번호: {collNums}')
# 2개 이하는 아닌걸로.
else:
print('아쉽습니다. 다음 기회에~')
print(f'기계 번호: {randNums}')
print(f'보너스 번호: {randBonuNum}')
print(f'선택 번호: {userNums}')
print(f'일치 번호: {collNums}')
#기계에서 처리하는 함수는 다 만듬!
# 사용자에게 번호 입력을 요청하는 문
def startLotto():
n1 = int(input('번호(1~45) 입력: '))
n2 = int(input('번호(1~45) 입력: '))
n3 = int(input('번호(1~45) 입력: '))
n4 = int(input('번호(1~45) 입력: '))
n5 = int(input('번호(1~45) 입력: '))
n6 = int(input('번호(1~45) 입력: '))
selectNums = [n1, n2, n3, n4, n5, n6] # 선택한 번호를 자료구조에 담는다.
# 위에 만든걸 세팅하는 과정
setUserNums(selectNums) #setUserNums에 selectNums숫자를 넣는다.
setRandNums() #기계가 뽑은 6개의 숫자를 넣기
setBonuNum() # 보너스 숫자 넣기
lottoResult() # 결과를 확인하기 위한 실행 문구[ex.py]
import lotto as lt
lt.startLotto()
모듈 예제(4)
Q.순열 계산 모듈 만들고 다음 순열 계산 결과를 출력
- 모듈로 만들어 놓고, m/r만 넣어서 값을 출력하는 모듈 제작
📝문제 풀이
[permutation.py]
def getPermutaionCnt(n, r, logPrint = True):
result = 1
for n in range(n, (n-r), -1):
if logPrint: print('n : {}'.format(n))
result = result * n
return result[ex.py]
import permutation as pt
numN = int(input('numN 입력: '))
numR = int(input('numR 입력: '))
print(f'{numN}P{numR}: {pt.getPermutaionCnt(numN, numR, logPrint=False)}')모듈 예제(5)
Q. 조합 계산 모듈 제작
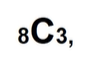
📝문제 풀이
[combination.py]
def getCombinationCnt(n, r):
resultP = 1 # 순열P
resultR = 1 #r 팩토리얼 값 #0으로 하지 않은 이유는 곱셈에서 문제가 생기기 때문
resultC = 1 # 콤비네이션 값
for n in range(n, (n - r), -1): #순열은 n ~ n-r 까지
resultP = resultP * n
for n in range(r, 0, -1): #r의 팩토리얼 구하는 문
resultR = resultR * n
resultC = int(resultP / resultR) # 순열 / r팩토리얼
return resultC[ex.py]
import combination as ct
numN = int(input('numN 입력: ')) # 사용자 입력을 받아야 함
numR = int(input('numR 입력: '))
print(f'{numN}C{numR}: {ct.getCombinationCnt(numN, numR)}')모듈 예제(6)
📌게터 & 세터
게터 & 세터
프라이빗 변수의 값을 추출하거나 변경할 목적으로 간접적으로 속성에 접근하도록 하는 함수
- 게터 : 자기가 가지고 있는, 외부에 노출하지 않은 속성을 return하는 방법
def getWidth(self):
return self.__width- 세터 : 외부에서 접근할 수 없는 속성의 값을 지정하는 역할
def set_width(self, width):
self._width = width참고. https://blog.naver.com/takudaddy/221992615858
Q.
📝문제 풀이
[utilityBill.py]
income = 0
waterPrice = 0; electricPrice = 0; gasPrice = 0
#세터 : 설정하는 함수
def setIncome(ic): # income의 값을 세팅해주는 값
global income # income : 전역변수
income = ic # 전역변수를 ic로 세팅
#게터 : 데이터를 가져오는 함수
def getIncome(): # 외부에서 수입의 값을 가져오겠다
return income
def setWaterPrice(wp):
global waterPrice
waterPrice = wp
def setElectricPrice(ep):
global electricPrice
electricPrice = ep
def setGasPrice(gp):
global gasPrice
gasPrice = gp
def getUtilityBill(): #공과금액 총액
result = waterPrice + electricPrice + gasPrice
return result
def getUtilityBillRate(): #전체 수입에서 공과금이 차지하는 비율
result = getUtilityBill() / getIncome() * 100
return round(result, 2)
def formatedNumber(n):
return format(n, ',')[ex.py]
import utilityBill as ub
inputIncome = int(input('수입 입력: '))
ub.setIncome(inputIncome)
inputWaterPrice = int(input('수도요금 입력: '))
ub.setWaterPrice(inputWaterPrice)
inputElectricPrice = int(input('전기요금 입력: '))
ub.setElectricPrice(inputElectricPrice)
inputGasPrice = int(input('가스요금 입력: '))
ub.setGasPrice(inputGasPrice)
print(f'공과금: {ub.formatedNumber(ub.getUtilityBill())}원')
print(f'수입 대비 공과금 비율: {ub.getUtilityBillRate()}%')모듈 예제(7)
📌round()
숫자를 반올림하여 소수점 이하 **자리로 표시
#소수점 2번째 자리까지
number = 3.14159265359
rounded = round(number, 2)
print(rounded)
--> 3.14Q. 다음과 같이 패키지모듈을 만들고 연산 결과 출력
▶rithmetic
▶basic_operator.py -> 덧셈, 뺼셈, 곱셈, 나눗셈
▶developer_operator.py -> 나머지, 몫, 거듭제곱
▶shape
▶circle_area.py -> 원의 넓이
▶triangle_square_area.py -> 삼각형, 사각형의 넓이📝문제 풀이
[▶rithmetic
▶basic_operator.py -> 덧셈, 뺼셈, 곱셈, 나눗셈]
def add(n1, n2):
return round(n1 + n2, 2)
def sub(n1, n2):
return round(n1 - n2, 2)
def mul(n1, n2):
return round(n1 * n2, 2)
def div(n1, n2):
return round(n1 / n2, 2)[▶rithmetic
▶developer_operator.py -> 나머지, 몫, 거듭제곱]
def mod(n1, n2):
return round(n1 % n2, 2)
def flo(n1, n2):
return round(n1 // n2, 2)
def exp(n1, n2):
return round(n1 ** n2, 2)▶shape
▶circle_area.py -> 원의 넓이
def calCircleArea(r):
return round(r ** 2 * 3.14, 2)▶shape
▶triangle_square_area.py -> 삼각형, 사각형의 넓이
def calTriangleArea(w, h):
return round(w * h / 2, 2)
def calSquareArea(w, h):
return round(w * h, 2)[ex.py]
from arithmetic import basic_operator as bo
from arithmetic import developer_oerator as do
from shape import triangle_square_area as tsa
from shape import circle_area as ca
inputNumber1 = float(input('숫자1 입력: '))
inputNumber2 = float(input('숫자2 입력: '))
print(f'{inputNumber1} + {inputNumber2} = {bo.add(inputNumber1, inputNumber2)}')
print(f'{inputNumber1} - {inputNumber2} = {bo.sub(inputNumber1, inputNumber2)}')
print(f'{inputNumber1} * {inputNumber2} = {bo.mul(inputNumber1, inputNumber2)}')
print(f'{inputNumber1} / {inputNumber2} = {bo.div(inputNumber1, inputNumber2)}')
print(f'{inputNumber1} % {inputNumber2} = {do.mod(inputNumber1, inputNumber2)}')
print(f'{inputNumber1} // {inputNumber2} = {do.flo(inputNumber1, inputNumber2)}')
print(f'{inputNumber1} ** {inputNumber2} = {do.exp(inputNumber1, inputNumber2)}')
inputWidth = float(input('가로 길이 입력: '))
inputHeight = float(input('세로 길이 입력: '))
print(f'삼각형 넓이: {tsa.calTriangleArea(inputWidth, inputHeight)}')
print(f'사각형 넓이: {tsa.calSquareArea(inputWidth, inputHeight)}')
inputRadius = float(input('반지름 입력: '))
print(f'사각형 넓이: {ca.calCircleArea(inputRadius)}')