튜플(Tuple)은 한번 아이템을 설정하면 변경, 수정, 삭제가 불가능 하다..!
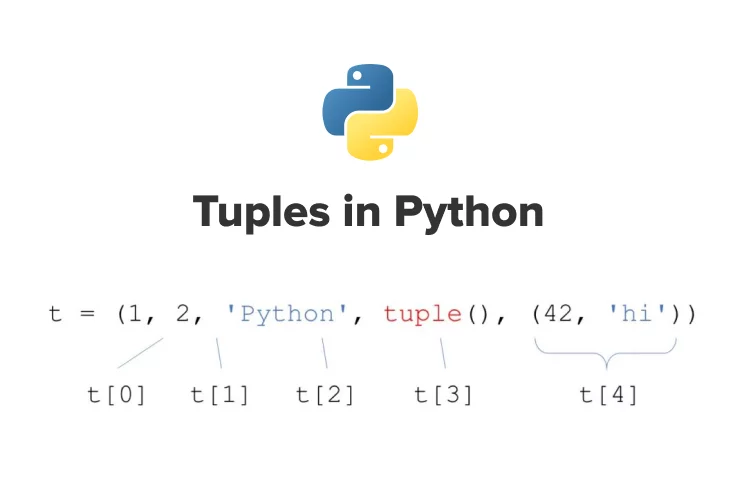
1. 튜플 선언
()를 이용해 선언하고 데이터 구분은 , 를 이용 한다
myFamilyNames = ('아빠', '엄마','나','동생')
print(myFamilyNames)2. item 조회
numbers = (1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9)
print('numbers[4]: {}'.format(numbers[4]))▼
numbers[4]: 5- 🏷️실습
students = ('A','B','C','D')
print('---인덱스 짝수---')
print('students[0] : {}'.format(students[0]))
print('students[2] : {}'.format(students[2]))
print('---인덱스 홀수---')
print('students[1] : {}'.format(students[1]))
print('students[3] : {}'.format(students[3]))
for i in range(len(students)):
= 🏷️for i in range(4) " 4명이라서 4회 반복, len()과 동일한 결과로 출력됨
if i % 2 == 0:
print('인덱스 짝수 : students[{}] : {}'.format(i, students[i]))
else:
print('인덱스 홀수 : students[{}] : {}'.format(i, students[i]))▼
인덱스 짝수 : students[0] : A
인덱스 홀수 : students[1] : B
인덱스 짝수 : students[2] : C
인덱스 홀수 : students[3] : D3. in, not in 키워드
- in : 있으면 True / 없으면 False
- not in : 있으면 False / 없으면 True
studentsTuple = ('A','B','C','D','E')
searchName = input('이름 입력 : ')
if searchName in studentsTuple:
print('{}은 우리반이 맞아요'.format(searchName))
else:
print('{}은 우리반이 아니에요'.format(searchName))▼
이름 입력 : H
H은 우리반이 아니에요- 🏷️실습1
Q> 컴퓨터가 1부터 10까지 5개의 난수를 생성한 후 사용자가 입력한 숫자가 있는지 없는지 출력하는 프로그램 제작
- (range(1,11),5) : 1~10까지 5개 출력
import random
randomNumbers = random.sample(range(1,11),5)
userNumber = int(input('숫자 입력(확률 50%): '))
if userNumber in randomNumbers:
print('빙고')
else:
print('다음!')
print('randomNumbers : {}'.format(randomNumbers))
print('userNumber : {}'.format(userNumber))▼
숫자 입력(확률 50%): 5
빙고
randomNumbers : [8, 7, 2, 9, 5]
userNumber : 5- 🏷️실습2
Q> 문장 속에 비속어사 있는지 알아내는 프로그램
wrongWord = ['쩔었다','짭새','꼽사리','먹튀','지린','쪼개다','뒷담 까다']
sentence = '짭새 등장에 강도들은 모두 쩔었다. 그리고 강도 들은 지린 듯 도망갔다'
for word in wrongWord:
if word in sentence:
print('비속어 : {}'.format(word))▼
비속어 : 쩔었다
비속어 : 짭새
비속어 : 지린4. len()
1) 길이_ len
students = ('A','B','C','D','E')
sLength = len(students)
print('length of students : {}'.format(sLength))▼
length of students : 52) 조회_ for/while
- for() + 이터러블 ⭐간단⭐
for student in students:
print('student : {}'.format(student))▼
student : A
student : B
student : C
student : D
student : E- for()
for i in range(len(students)):
print('i : {}'.format(i))
print('students[{}] : {}'.format(i, students[i]))▼
i : 0
students[0] : A
i : 1
students[1] : B
i : 2
students[2] : C
i : 3
students[3] : D
i : 4
students[4] : E- while()
n = 0
sLength = len(students)
while n < sLength:
print('n : {}',format(n))
print('students[{}] : {}'.format(n, students[n]))
n += 1▼
n : {} 0
students[0] : A
n : {} 1
students[1] : B
n : {} 2
students[2] : C
n : {} 3
students[3] : D
n : {} 4
students[4] : E5. + 연산
list() : extend(), + 연산 이용
tuple() : + 연산을 이용

myFavoriteNumber = (1,3,5,6,7)
friendFavoriteNumber = (2,3,5,8,10)
print('myFavoriteNumber : {}'.format(myFavoriteNumber))
print('friendFavoriteNumber : {}'.format(friendFavoriteNumber))
for n in friendFavoriteNumber:
if n not in myFavoriteNumber:
myFavoriteNumber = myFavoriteNumber + (n, )
# 친구 번호에서 아이템을 추출하겠다
# 그 아이템들이 나의 번호에 없다면
# ★(값, ) 하면 순간 튜플로 바뀜!
# 나의 번호에 추가해라
print('myFavoriteNumber: {}'.format(myFavoriteNumber))▼
myFavoriteNumber: (1, 3, 5, 6, 7, 2, 8, 10)6. slice()

7. list() <-> Tuple()



🏷️실습
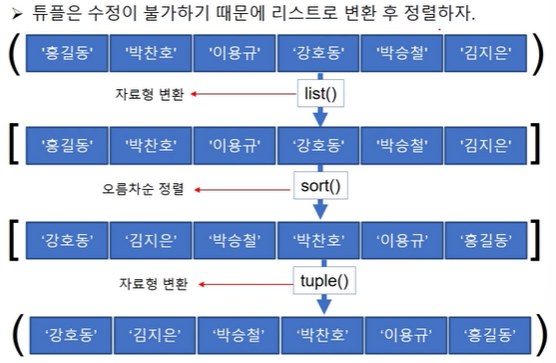
Q> 튜플을 이용한 점수표에서 최저, 최고 점수를 삭제한 후 총점과 평균 출력
playerScore = (9.5,8.9,9.2,9.8,8.8,9.8)
print('playerScore {}'.format(playerScore))
print(type(playerScore))
playerScore = list(playerScore)
print(type(playerScore))
playerScore.sort()
print('playerScore: {}'.format(playerScore))
playerScore.pop(0)
playerScore.pop(len(playerScore)-1)
playerScore = tuple(playerScore)
print('playerScore: {}'.format(playerScore))
print(type(playerScore))
sum =0
ang =0
for s in playerScore:
sum =+ s
avg = sum / len(playerScore)
print('총점 : {}'.format(sum))
print('평균: {}'.format(avg))▼
playerScore (9.5, 8.9, 9.2, 9.8, 8.8, 9.8)
<class 'tuple'>
<class 'list'>
playerScore: [8.8, 8.9, 9.2, 9.5, 9.8, 9.8]
playerScore: (8.9, 9.2, 9.5, 9.8)
<class 'tuple'>
총점 : 9.8
평균: 2.458. sorted()_ 정렬
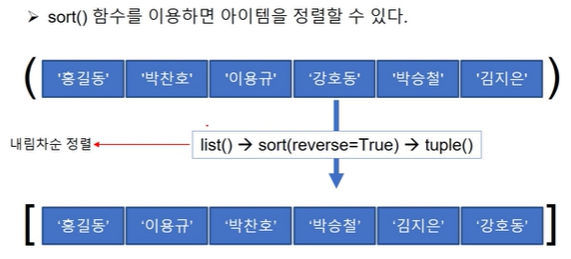
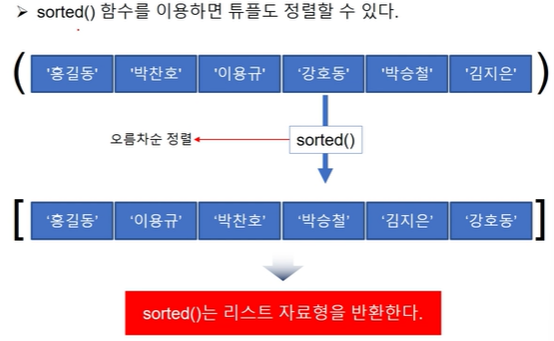
🏷️실습
platScore = (9.5,8.9,9.2,9.8,8.8,9.0)
print('platScore : {}'.format(platScore))
print(type(platScore))
print('-'*50)
platScore = list(platScore)
print(type(platScore))
platScore.sort()
print('platScore: {}'.format(platScore))
print('-'*50)
platScore.pop(0)
platScore.pop(len(platScore)-1)
print('platScore: {}'.format(platScore))
print('-'*50)
platScore = tuple(platScore)
print(type(platScore))
print('platScore: {}'.format(platScore))▼
platScore : (9.5, 8.9, 9.2, 9.8, 8.8, 9.0)
<class 'tuple'>
--------------------------------------------------
<class 'list'>
platScore: [8.8, 8.9, 9.0, 9.2, 9.5, 9.8]
--------------------------------------------------
platScore: [8.9, 9.0, 9.2, 9.5]
--------------------------------------------------
<class 'tuple'>
platScore: (8.9, 9.0, 9.2, 9.5)9. for() 조회 _ 전체 조회
studentCnt = (1,19), (2,20), (3,22), (4,18), (5,21)
for classNo, cnt in studentCnt:
print('{}학급 학생수 : {}'.format(classNo, cnt))▼
1학급 학생수 : 19
2학급 학생수 : 20
3학급 학생수 : 22
4학급 학생수 : 18
5학급 학생수 : 21🏷️실습
studentCnt = (1,18), (2,19), (3,23), (4,21), (5,20), (6,22), (7,17)
sum =0
avg =0
for classNo, s in studentCnt:
print('{}학급 학생수 : {}'.format(classNo, s))
sum += s
print('전체 학생수 : {}'.format(sum))
print('평균 : {}'.format(sum/len(studentCnt)))▼
1학급 학생수 : 18
2학급 학생수 : 19
3학급 학생수 : 23
4학급 학생수 : 21
5학급 학생수 : 20
6학급 학생수 : 22
7학급 학생수 : 17
전체 학생수 : 140
평균 : 20.010. for() if() 조회 _ 각 item을 조회
🏷️실습_1
minScore = 60
korS = int(input('국어 점수 : '))
engS = int(input('영어 점수 : '))
matS = int(input('수학 점수 : '))
sciS = int(input('과학 점수 : '))
scores = (
('국어', korS),
('영어', engS),
('수학', matS),
('과학', sciS)
)
for subject, score in scores:
if score < minScore:
print('{}과목 과락 점수 : {}'.format(subject, score))▼
국어 점수 : 81
영어 점수 : 71
수학 점수 : 61
과학 점수 : 41
과학과목 과락 점수 : 41🏷️실습_2
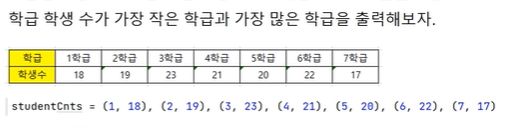
[최저]
-
for classNo, s in studentsCnt:: 학급과 학생수 [전체 아이템]을 조회 -
if minStudent == 0: 처음 들어오는 값을 먼저 대입 -
minStudent > c: 최저 값이 아닌 경우 -
minClass = classNo: 최저 학급으로 바꿔줌, =으로 진행 -
minStudent = s: 최저 학생수를 바꿔 줌, =으로 진행
[최고]
-
if maxStudent < s:: s보다 최대 학생수가 작다 = maxStudent가 최고 값인줄 알았는데 최고가 아니라면 -
maxClass = classNo: 최고 학급을 바꾸고 -
maxStudent = s: 최고 학생수도 바꾼다
studentsCnt = (1,18),(2,19),(3,23), (4,21),(5,20),(6,22),(7,17)
minClass =0
maxClass =0
minStudent =0
maxStudent =0
for classNo, s in studentsCnt:
if minStudent == 0 or minStudent > s:
minClass = classNo
minStudent = s
if maxStudent < s:
maxClass = classNo
maxStudent = s
print('학생수가 가장 작은 학급(학생수) : {}학급({}명)'.<format(minClass, minStudent))
print('학생수가 가장 많은 학급(학생수) : {}학급({}명)'.format(maxClass, maxStudent))▼
학생수가 가장 작은 학급(학생수) : 7학급(17명)
학생수가 가장 많은 학급(학생수) : 3학급(23명)
11. while()

🏷️실습_1
studentCnt = (1,18), (2,19), (3,23), (4,21), (5,20), (6,22), (7,17)
sum =0
avg =0
n =0
while n < len(studentCnt):
classNo = studentCnt[n][0]
cnt = studentCnt[n][1]
print('{}학급 학생수 : {}명'.format(classNo, cnt))
sum += cnt
n += 1
print('전체학생수 : {}명'.format(sum))
print('평균 : {}명'.format(sum/len(studentCnt)))▼
1학급 학생수 : 18명
2학급 학생수 : 19명
3학급 학생수 : 23명
4학급 학생수 : 21명
5학급 학생수 : 20명
6학급 학생수 : 22명
7학급 학생수 : 17명
전체학생수 : 140명
평균 : 20.0명🏷️실습_2
Q> while과 if 문을 이용해 과락과목 출력하기
-1번 방법 : while() if()
minScore = 60
scores = (
('국어', 58),
('영어', 77),
('수학', 89),
('과학', 99),
('국사', 50),
)
n =0
while n < len(scores):
if scores[n][1] < minScore:
print('{}과목 과락 : {}점'.format(scores[n][0], scores[n][1]))
n += 1-2번 방법 : while() if() + continue
minScore = 60
scores = (
('국어', 58),
('영어', 77),
('수학', 89),
('과학', 99),
('국사', 50),
)
n =0
while n <len(scores):
if scores[n][1] >= minScore:
n += 1
continue
print('{}과목 과락 : {}점'.format(scores[n][0], scores[n][1]))
n += 1▼
국어과목 과락 : 58점
국사과목 과락 : 50점🏷️실습_3
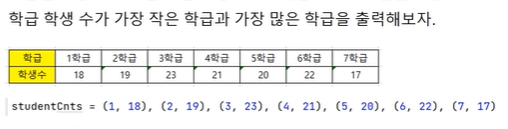
minCnt > studentsCnt[n][1]:: 인덱스 0번째 점수(18점) 보다 클때minClassNo = studentsCnt[n][0]: 최저 학급인 studentsCnt[n][0]로 바꾸고minCnt = studentsCnt[n][1]:최저 학생수인 studentsCnt[n][1]로 바꾼다.
studentsCnt = (1,18),(2,19),(3,23), (4,21),(5,20),(6,22),(7,17)
minClassNo =0
maxClassNo =0
minCnt =0
maxCnt =0
n =0
while n < len(studentsCnt):
if minCnt ==0 or minCnt > studentsCnt[n][1]:
minClassNo = studentsCnt[n][0]
minCnt = studentsCnt[n][1]
if maxCnt < studentsCnt[n][1]:
maxClassNo = studentsCnt[n][0]
maxCnt = studentsCnt[n][1]
n += 1
print('최저 학급{}의 학생수 : {}'.format(minClassNo, minCnt))
print('최고 학급{}의 학생수 : {}'.format(maxClassNo, maxCnt))▼
최저 학급7의 학생수 : 17
최고 학급3의 학생수 : 23