Loops
definition >> 규칙적 반복 코드를 단순화하는 문법. 이를 반복문이라 한다. 이를 통해 코드 압축이 가능하다.
case >> 대표적 반복문으로는 while 문과 for 문이 있다. while 문은 반복 횟수가 상황따라 다른 경우에 사용한다. 이와 반면, for 문은 반복획수가 명확할 때 좋다.
While
structure >> while 문의 구조 및 실행 흐름은 아래와 같다.
// ①➝②를 반복(조건식이 거짓이 될 때까지) while (①조건식) { ②반복 내용 }
exampleint n = 1; while (n <= 10) { System.out.println(n); n++; }
For
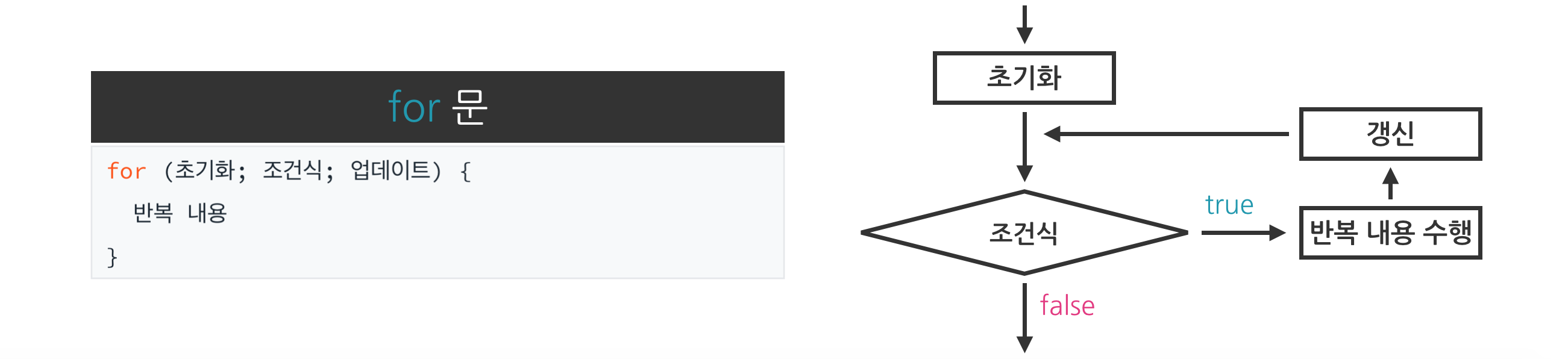
structure >> for 문의 구조 및 실행 흐름은 아래와 같다.
// ⓪초기화 수행 후, // ①➝②➝③ 반복(거짓이 될 때까지) for (⓪초기값; ①조건식; ③갱신) { ②반복 내용 }
example// 구구단 3단 출력 예 for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) { System.out.printf("3 x %d = %d\n", i, 3 * i); }
1) while
how to use >> while 문은 대표적인 반복문으로서, 아래와 같은 구조를 가집니다. 조건식이 참인 경우, 반복 내용을 수행합니다. 거짓이 될 때까지 계속 수행되므로, 무한 루프에 빠지지 않도록 주의해야 합니다.
while (조건식) { // 반복 내용 }reversing >> while 문을 사용해서, 아래와 같은 출력 결과를 만들려면 어떻게 해야할까요?
// 변수 생성 int n = 4; // 반복 수행 while (n > 0) { // n의 값이 0보다 크면 반복! System.out.println(n); n--; // n을 1 감소 }CODE
public class WhileStatement { public static void main(String[] args) { // 입력값 받기 int startNum = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); // 카운트 다운 출력 countDown(startNum); } public static void countDown(int num) { System.out.println("카운트 다운을 시작합니다.."); while (num >= 0) { System.out.printf("%d..\n", num); num--; } System.out.println("발사!!"); } }
2) for
how to use >> for 문은 가장 많이 쓰이는 반복문으로서, 아래와 같은 구조를 가집니다. for 문이 실행되면 초기설정 부분은 단 한 번 수행되며, 조건식이 참인 경우, 반복 내용을 수행합니다. 반복 내용을 다 마치면 매번 갱신영역을 수행한 뒤, 다시 또 조건식을 검사합니다. 이러한 실행 흐름은, 조건식이 거짓이 될 때까지 수행됩니다.
for (초기설정; 조건식; 매회 갱신) { // 반복 내용 }incresing sum of num >> for문을 사용하여 아래와 같은 실행 결과를 만드려면, 어떻게 해야할까요?
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) { System.out.println(i); }CODE
public class ForStatement { public static void main(String[] args) { // 입력값 받기 int n = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); // 메소드를 통한, 결과 출력 printNumbers(n); } // 1부터 N까지, 정수를 출력 public static void printNumbers(int max) { // 출력 시작! System.out.println("출력을 시작합니다.."); for(int i = 1; i <= max; i++) { System.out.printf("%d ",i); } // 끝! System.out.println("\n끝!!"); } }
3) sum of integers
CODE
public class SumNumbers { public static void main(String[] args) { // 입력값 받기 int n = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); // "5" => 5 // 총합 계산 int result = sum(n); // 결과 출력 System.out.printf("정수의 총합(1~%d) => %d", n, result); } public static int sum(int max) { // 변수 생성 int sum = 0; // 반복 계산: 1 + 2 + ... + max for (int i = 1; i <= max; i++) { sum += i; } // 결과 반환 return sum; } }
4) break
while and for >> 우리는 앞서 두 가지 대표적인 반복문 for 문과 while 문에 대해 배웠습니다. 해당 구문들은 조건식이 참이라면, 반복 내용을 처음부터 끝까지 다 수행해야만 했습니다.
// 조건식이 참이면, A -> B -> C를 연속적으로 수행 while (조건식) { action A action B action C } for (int i = 0; 조건식; i++) { action A action B action C }if want break?? >> 만약 A와 B까지만 수행 후, 반복을 탈출하고 싶다면 어떻게 해야 할까요?
break 문을 사용하면 됩니다. break 문은 보통 조건문과 함께 사용되며, 그 예는 아래와 같습니다.if (조건식) { // 조건식이 참이면 break; // 반복문 탈출! }example of break >> 아래는 break 문의 활용 예입니다. for 문은 1부터 10까지 총 10번의 반복을 수행하려 합니다. 그러나 중간의 break 문에 의해, 1부터 3까지의 합만을 출력하게 됩니다.
// 총합을 위한 변수 생성 int sum = 0; // 반복 수행 for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { // 수행 도중, 반복문 탈출! if (i == 4) { break; } // i값을 sum에 더함 sum += i; } // 결과 출력 System.out.println(sum); // 6CODE
public class Break { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1부터 10까지 총합 출력 및 계산 printSum(1, 10); } // start부터 end까지의 총합을 출력 public static void printSum(int start, int end) { // 변수 생성 int sum = 0; // 총합 계산 for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) { System.out.printf("%d", i); sum += i; // end(마지막 숫자)인 경우, if (i == end) { break; } System.out.printf(" + "); } // 결과 출력 System.out.printf("\n=> %d", sum); } }
5) continue
while and for >> 우리는 앞서 두 가지 대표적인 반복문 for 문과 while 문에 대해 배웠습니다.
// 조건식이 참이면, A -> B -> C를 연속적으로 수행 while (조건식) { action A action B action C } for (int i = 0; 조건식; i++) { action A action B action C }Being force to next loop >> 위 코드에서, A만 수행 하고 다음 반복으로 넘어가고 싶은 경우 어떻게 해야 할까요?
continue 문을 사용하면 됩니다. 이는 반복 수행을 멈추고 다음 반복으로 실행 흐름을 강제 이동시킵니다. continue 문은 조건문과 함께 사용되며, 그 예는 아래와 같습니다.if (조건식) { // 조건식이 참이면 continue; // 다음 반복으로 강제 이동! }example >> 아래는 continue 문의 활용 예입니다. for 문은 1부터 7까지 총 7번 반복하며 총합을 구합니다. 이때 짝수는 continue 문으로 인해 제외됩니다. 따라서 1 + 3 + 5 + 7 의 결과인 16이 출력됩니다.
// 총합을 위한 변수 생성 int sum = 0; // 반복 수행: 1부터 7까지 홀수의 총합 for (int i = 1; i <= 7; i++) { // 짝수는 제외! if (i % 2 == 0) { continue; } // i값을 sum에 더함 sum += i; } // 결과 출력 System.out.println(sum); // 16CODE
public class Continue { public static void main(String[] args) { printSum(1, 10); } public static void printSum(int start, int end) { // 변수 생성 int sum = 0; // 반복 수행 for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) { if (i % 3 == 0) { continue; } System.out.printf("%d", i); sum += i; if (i == end) { break; } System.out.printf(" + "); } // 결과 출력 System.out.printf("\n=> %d", sum); } }
6) overlap loops
overlap loop >> 중첩 반복문이란, 반복문 속에 또 다른 반복문이 들어가는 것을 말합니다. 이를 활용하여 7행 4열 구조의 별 표시를 출력해보도록 합시다.
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *System.out.println("* * * * "); System.out.println("* * * * "); System.out.println("* * * * "); System.out.println("* * * * "); System.out.println("* * * * "); System.out.println("* * * * "); System.out.println("* * * * ");using loop code
// 반복 방식 출력(row: 0 ~ 6) for (int row = 0; row < 7; row++) { System.out.println("* * * * "); }loop in loop code >> 다음으로, 위 코드의 한 행(4개의 별)에 대한 내용을 반복문으로 대체합니다.
// 총 7개의 행 출력 for (int row = 0; row < 7; row++) { // 행마다 4개의 별 출력(col: 0 ~ 3) for (int col = 0; col < 4; col++) { System.out.printf("* "); } // 줄 내림으로 행 구분 System.out.println(); }CODE
public class Matrix { public static void main(String[] args) { // 입력값 받기 int r = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); int c = Integer.parseInt(args[1]); // 매트릭스 출력 printMatrix(r, c); } public static void printMatrix(int rowMax, int columnMax) { for (int i = 0; i < rowMax; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < columnMax; j++) { System.out.printf("* "); } System.out.println(); } } }
7) review: 9x9
CODE
public class GuGuDan { public static void main(String[] args) { // 구구단 출력 printGuGuDan(); } public static void printGuGuDan() { for (int i = 2; i <= 9; i ++) { printDan(i); // 2단 출력 } } public static void printDan(int dan) { System.out.printf("%d단\n", dan); // dan x 1, dan x 2, ... , dan x 9 for (int j = 1; j <= 9; j++) { System.out.printf("\t"); // 들여쓰기 System.out.printf("%d x %d = %d\n", dan, j, dan * j); } } }