Column Decorater
@PrimaryGeneratedColumn() // 1, 2, 3, 4 ...
@PrimaryGeneratedColumn('uuid') // string asd21edasd-asd12das-erg34rte-e534wefsdv
@PrimaryColumn() // 자동 증가는 X 하지만 PK@CreateDateColumn() // 데이터가 생성되는 날짜와 시간이 자동으로 찍힘
@UpdateDateColumn() // 데이터가 업데이트 되는 날짜와 시간이 자동으로 찍힘@VersionColumn() // 데이터가 업데이트 될때마다 1씩 증가, 처음 값(Default)은 1, save()함수가 몇번 불렸는지 기억
@Generated() // @PrimaryGeneratedColumn()는 아니지만 자동으로 1씩 증가시키는 것, @Column()같이 사용
@Generated('uuid') // string
@Column()Column property
@Column({
// 데이터베이스에서 인지하는 칼럼 타입 -> 자동으로 유추됨
type: 'text',
// 데이터베이스 칼럼 이름
// 프로퍼티 이름으로 자동 유추됨
name: 'title',
// 값의 길이
// 입력할 수 있는 글자의 길이가 300
length: 300,
// null이 가능한지
nullable: false,
// true 면 처음 지정할때만 값 지정 가능
// 이후에는 값 변경 불가능
update: true,
// find()를 실행할 때 기본으로 값을 불러올지
// 기본값이 true
select: true,
// 기본값
// 아무것도 입력하지 않았을 때 입력되게 되는 값
default: 'default value',
// 칼럼중에서 유일무이한 값이 돼야하는지
unique: false,
})
title: string;Enum column
enum Role {
USER = 'user',
ADMIN = 'admin',
}
.
.
.
@Column({
type: 'enum',
enum: Role,
default: Role.USER,
})
role: Role;Entity Embedding
export class Name { // Entity Embedding는 @Entity를 선언하면 안됨!
@Column()
first: string;
@Column()
last: string;
}
@Entity()
export class StudentModel {
@PrimaryGeneratedColumn()
id: number;
@Column(() => Name)
name: Name; // nameFirst, nameLast
@Column()
class: string;
}
@Entity()
export class TeacherModel {
@PrimaryGeneratedColumn()
id: number;
@Column(() => Name)
name: Name; // nameFirst, nameLast
@Column()
salary: number;
}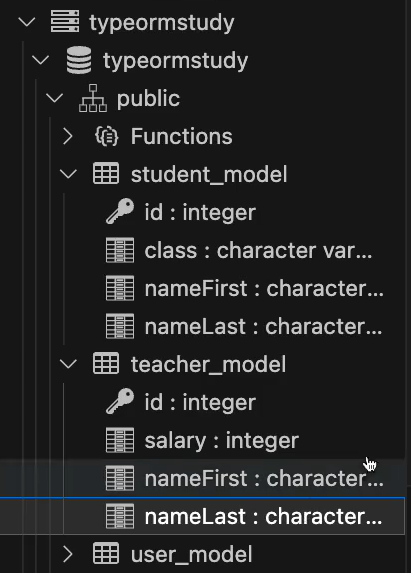
student_model과 teacher_model 생성 및 Column명 순서 Check!
Table inheritance
export class BaseModel { // @Entity등록 X
@PrimaryGeneratedColumn()
id: number;
@CreateDateColumn()
createdAt: Date;
@UpdateDateColumn()
updatedAt: Date;
}
@Entity() //**
export class BookModel extends BaseModel {
@Column()
name: string;
}
@Entity() //**
export class CarModel extends BaseModel {
@Column()
name: string;
}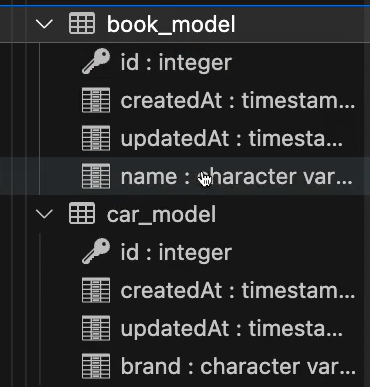
// 싱글 테이블 전략, 잘 사용 X
@Entity()
@TableInheritance({ //**
column: {
name: 'type', // 무엇으로 구분을 할 것인지(컬럼이 추가됨)
type: 'varchar' // tpye은 varchar 형태
}
})
export class SingleBaseModel {
@PrimaryGeneratedColumn()
id: number;
@CreateDateColumn()
createdAt: Date;
@UpdateDateColumn()
updatedAt: Date;
}
@ChildEntity() //**
export class ComputerModel extends SingleBaseModel {
@Column()
brand: string;
}
@ChildEntity() //**
export class AirplaneModel extends SingleBaseModel {
@Column()
country: string;
}
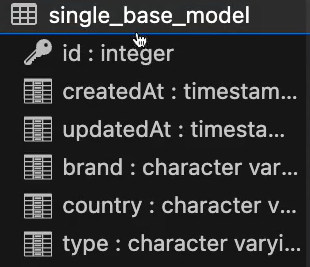
즉, DB에 들어갈 때 Computer인지 Airplane인지 구분을 하기 위해서 type를 넣는 것
OneToOne Relationship
어디다가 FK를 들고 있을거야?!! @JoinColumn()
@Entity()
export class ProfileModel {
@PrimaryGeneratedColumn()
id: number;
@OneToOne(() => UserModel, (user) => user. profile) // 서로가 연동되는 property를 작성
@JoinColumn() // FK는 이쪽에
user: UserModel;
@Column()
profileImg: string;
}
.
.
.
@Entity()
export class UserMode{
@OneToOne(() => ProfileModel, (profile) => profile.user)
profile: ProfileModel;
.
.
.
}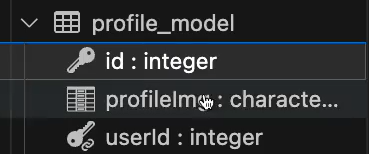
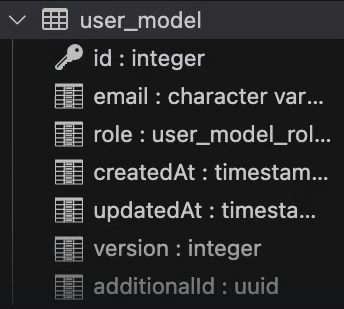
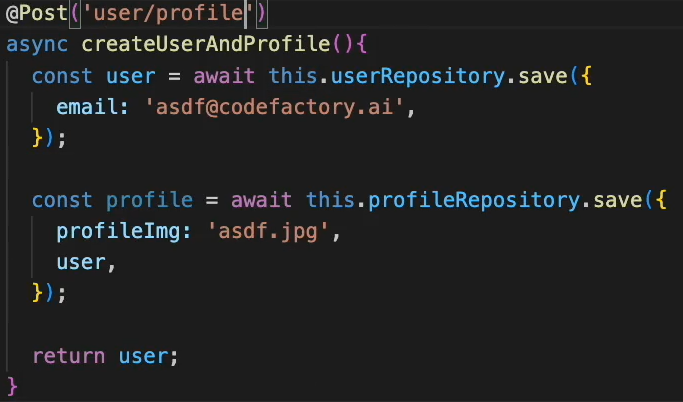
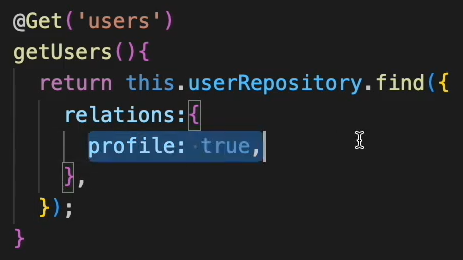
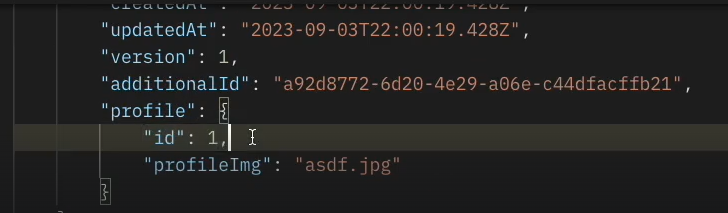
user 조회시 profile도 같이 조회
ManyToOne OneToMany Relationship
@Entity()
export class PostModel {
@PrimaryGeneratedColumn()
id: number;
@ManyToOne(() => UserModel, (user) => user.posts) // 복수 기억, 여기에 FK가 생긴다
author: UserModel;
@Column()
title: string;
}
.
.
.
@Entity()
export class PostModel {
@OneToMany(() => PostModel, (post) => post.author)
posts: PostModel[];
.
.
.
@Post('user/post')
async createUserAndPosts() {
const user = await this.userRepository.save({
email: 'postuser@naver.com',
});
await this.postRepository.save({
author: user,
title: 'post 1',
});
await this.postRepository.save({
author: user,
title: 'post 2',
});
return user;
}
user에 posts들이 연결되어서 나온다
ManyToMany Relationship
@Entity()
export class TagModel {
@PrimaryGeneratedColumn()
id: number;
@ManyToMany(() => PostModel, (post) => post.tags)
// @JoinTable() // tag_model_posts_post_model
posts: PostModel[];
@Column()
name: string;
}
.
.
.
@Entity()
export class PostModel {
@PrimaryGeneratedColumn()
id: number;
@ManyToOne(() => UserModel, (user) => user.posts)
author: UserModel;
@ManyToMany(() => TagModel, (tag) => tag.posts)
@JoinTable() // post_model_tags_tag_model
tags: TagModel[];
@Column()
title: string;
}
@Post('posts/tags')
async createPostsTags() {
const post1 = await this.postRepository.save({
title: 'NestJS lecture',
});
const post2 = await this.postRepository.save({
title: 'Java lecture',
});
const tag1 = await this.tagRepository.save({
name: 'Javascript',
posts: [ //**
post1, post2
]
});
const tag2 = await this.tagRepository.save({
name: 'Typescript',
posts: [ //**
post1
]
});
const post3 = await this.postRepository.save({
title: 'Spring lecture',
tags: [ //**
tag1, tag2
]
});
return true;
}
@Get('posts')
getPosts() {
return this.postRepository.find({
relations: { //**
tags: true,
}
});
}
@Get('tags')
getTags() {
return this.tagRepository.find({
relations: { //**
posts: true,
}
})
}tag의 posts를 볼수 있고 post의 tags를 볼 수 있다
Relation Option
@OneToOne(() => ProfileModel, (profile) => profile.user, {
// find() 실행 할때마다 항상 같이 가져올 relation
eager: false,
// 저장할 때 relation을 한번에 같이 저장 가능, 기본값 false
cascade: true,
// null이 가능한지
nullable: true,
// 관계가 삭제했을 때
// no-action -> 아무것도 안함
// cascade -> 참조하는 Row도 같이 삭제
// set null -> 참조하는 Row에서 참조 id를 null로 변경
// set default -> 기본 세팅으로 설정(테이블의 기본 세팅)
// restrict -> 참조하고 있는 row가 있는 경우 참조당하는 Row 삭제 불가
onDelete: 'SET NULL',
})
@JoinColumn()
profile: ProfileModel;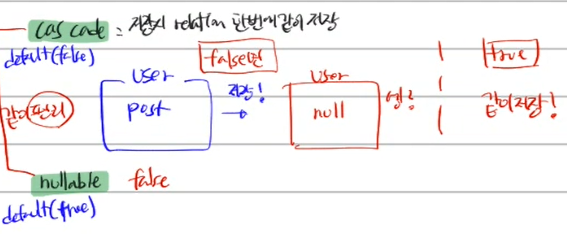
cascade가 같이 묶는다는 의미여서, false이고 user가 post를 생성하고 저장시 user는 저장되지만 post는 null이 된다.
하지만 true면 같이 묶어버리는 것이기 때문에 같이 저장이 된다.
findManyOptions parameter
@Get('users')
getUsers() {
return this.userRepository.find({
// 어떤 프로퍼티를 불러올지
// 기본은 모든 프로퍼티를 가져온다
// 만약에 select를 정의하지 않으면
// select를 정의하면 정의한 프로퍼티만 가져온다
select:{ // 이곳에서 선택
id: true,
createdAt: true,
updatedAt: true,
version: true,
profile: {
id: true
},
},
// 필터링할 조건 (&&)
where: {
{
id: 3 // 같은 Block -> and
},
// 분리 or
{
version: 1
},
},
// 관계를 가져오는 법
relations: {
profile: true
},
// 오름차 내림차
// ASC DESC
order: {
id: 'ASC'
},
// 처음 몇개를 제외하고 가져올지 (0 default)
skip: 0,
// 몇개를 데이터를 가져올지 (0 default) skip과 같이 사용
take: 0TypeORM 유틸리티 탐구
where: {
// 아닌경우 불러오기
id: Not(1),
// 적은 경우 불러오기
id: LessThan(30)
// 적은경우 or 같은경우
id: LessThanOrEqual(30)
// 많은 경우
id: MoreThan(30)
// 많거나 같은 경우
id: LessThanOrEqual(30)
// 같은 경우
id: Equal(30)
// 유사값 -> %% 앞뒤로 어떤 글자가 와도 상관없음, 대분자 구분 X
email: Like('%google*')
// 대문자 소문자 구분 안하는 유사값
email: ILike('%GOOGLE%')
// 사이값
id: Between(10, 15)
// 해당되는 여러개의 값
id: In([1, 3, 5, 7, 99])
// 아이디가 Null인경우
id: IsNull()
}자주사용하는 메소드
@Post('sample')
async sample() {
// 모델에 해당되는 객체 생성 - 저장은 안함
const user1 = this.userRepository.create({
email: 'asdf@gmail.com'
});
// 저장
const user2 = this.userRepository.save({
email: 'asdf@gmail.com'
});
// preload
// 입력된 값을 기반으로 데이터베이스에 있는 데이터를 불러오고
// 추가 입력된 값으로 데이터베이스에서 가져온 값들을 대체함
// 저장하지는 않음
const user3 = this.userRepository.preload({
id: 101,
email: 'haha@gmail.com'
});
// 삭제하기
await this.userRepository.delete(
101,
)
// 값을 증가시킴
await this.userRepository.increment({
id: 1
}, 'count', 2); // 아이디 1이면 2씩 증가시켜라
// 값을 감소시킴
await this.userRepository.decrement({
id: 1
}, 'count', 1);
// 갯수 카운팅하기
const count = await this.userRepository.count({
where: {
email: ILike('%0%'),
}
})
// sum
const sum = await this.userRepository.sum('count', {
email: ILike('%0%')
})
// average
const average = await this.userRepository.average('count', {
id: LessThan(4)
})
// 최소값
const minimum = await this.userRepository.minimum('count', {
id: LessThan(4)
})
// 최대값
const maximum = await this.userRepository.maximum('count', {
id: LessThan(4)
})
await users = await this.userRepository.find();
const userOne = await this.userRepository.findOne({
where: {
id: 3
}
});
const usersAndCount = await this.userRepository.findAndCount({
take:3,
})
return usersAndCount;
}