1. Python Operator 실습
-
Python Operator를 사용해서 Airflow DAG를 만듦.
-
Python Operator 기본 구조.
from airflow.operators.python import PythonOperator load_nps = PythonOperator( dag=dag, # 부모 dag task_id="task_id", # task_id 지정 python_callable=python_func, # 해당 테스크가 실행될 때 실행될 함수 지정. params={ # python_func에 인자를 넘겨 주고 싶을 때 사용. "table":"deleted_nps", "schema":"raw_data" }, ) def python_func(**cxt): table = cxt["params"]["table"] schema = cxt["params"]["schema"] ex_date = cxt["execution_date"] # 함수의 실행 내용 ... -
print_hello와 print_goodbye라는 함수를 Python Operator로 구현해 보기.
from airflow import DAG from airflow.operators.python import PythonOperator from datetime import datetime dag = DAG( dag_id = 'HelloWorld', start_date = datetime(2022,5,5), catchup=False, tags=['example'], schedule = '0 2 * * *') def print_hello(): print("hello!") return "hello!" def print_goodbye(): print("goodbye!") return "goodbye!" print_hello = PythonOperator( task_id = 'print_hello', #python_callable param points to the function you want to run python_callable = print_hello, #dag param points to the DAG that this task is a part of dag = dag) print_goodbye = PythonOperator( task_id = 'print_goodbye', python_callable = print_goodbye, dag = dag) # Assign the order of the tasks in our DAG print_hello >> print_goodbye # print_hello 실행 후 print_goodbye 실행. -
다른 방식인 Airflow Decorators로 구현해 보기.
from airflow import DAG from airflow.decorators import task from datetime import datetime @task def print_hello(): print("hello!") return "hello!" @task def print_goodbye(): print("goodbye!") return "goodbye!" with DAG( dag_id = 'HelloWorld', start_date = datetime(2022,5,5), catchup=False, tags=['example'], schedule = '0 2 * * *' ) as dag: print_hello() >> print_goodbye() # 별도의 지정이 없다면 함수 이름이 테스크 아이디가 됨.
Airflow Decorators를 통해서 구현하면 더욱 더 코드가 직관적이고 간편하다는 장점이 있음.
- 중요한 DAG 파라미터
- max_active_runs : 한 번에 동시에 실행될 수 있는 DAG 인스턴스 수. (보통은 1개지만, backfill이 필요한 경우 추가될 수 있음. upper bound: airflow worker의 CPU 수)
- max_active_tasks : 한 번에 동시에 실행될 수 있는 테스크 수.
- catchup : backfill 실행 여부. (Incremental Update가 필요한 DAG에만 사용됨.)
- 중요한 점은 DAG 파라미터와 Task 파라미터의 차이점을 명확히 구분하고 있어야 한다는 점.
2. CSV 파일 -> Redshift 실습
-
기존의 Colab Python 코드를 Airflow로 포팅하기.
from airflow import DAG from airflow.operators.python import PythonOperator from datetime import datetime import requests import logging import psycopg2 def get_Redshift_connection(): host = "learnde.cduaw970ssvt.ap-northeast-2.redshift.amazonaws.com" user = "" # 본인 ID 사용 password = "" # 본인 Password 사용 port = 5439 dbname = "dev" conn = psycopg2.connect(f"dbname={dbname} user={user} host={host} password={password} port={port}") conn.set_session(autocommit=True) return conn.cursor() def extract(url): logging.info("Extract started") f = requests.get(url) logging.info("Extract done") return (f.text) def transform(text): logging.info("Transform started") lines = text.strip().split("\n")[1:] # 첫 번째 라인을 제외하고 처리 records = [] for l in lines: (name, gender) = l.split(",") # l = "Keeyong,M" -> [ 'keeyong', 'M' ] records.append([name, gender]) logging.info("Transform ended") return records def load(records): logging.info("load started") """ records = [ [ "Keeyong", "M" ], [ "Claire", "F" ], ... ] """ schema = "keeyong" # BEGIN과 END를 사용해서 SQL 결과를 트랜잭션으로 만들어주는 것이 좋음 cur = get_Redshift_connection() try: cur.execute("BEGIN;") cur.execute(f"DELETE FROM {schema}.name_gender;") # DELETE FROM을 먼저 수행 -> FULL REFRESH을 하는 형태 for r in records: name = r[0] gender = r[1] print(name, "-", gender) sql = f"INSERT INTO {schema}.name_gender VALUES ('{name}', '{gender}')" cur.execute(sql) cur.execute("COMMIT;") # cur.execute("END;") except (Exception, psycopg2.DatabaseError) as error: print(error) cur.execute("ROLLBACK;") logging.info("load done") def etl(): link = "https://s3-geospatial.s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/name_gender.csv" data = extract(link) lines = transform(data) load(lines) dag_second_assignment = DAG( dag_id = 'name_gender', catchup = False, start_date = datetime(2023,4,6), # 날짜가 미래인 경우 실행이 안됨 schedule = '0 2 * * *') # 매일 오전 2시에 실행이 됨. task = PythonOperator( task_id = 'perform_etl', python_callable = etl, dag = dag_second_assignment)-
위 코드에서 개선 사항은 다음과 같다.
- host, user, pw, link 등이 하드코딩되어 있으니, 해당 부분을 외부 config로 구성하는 것이 좋다.
- extract, transform, load 등을 task화하는 것이 좋다.
-
-
개선 버전 1.
-
prams를 통한 변수 넘기기.
-
execution_date 읽기.
-
"delete from" vs. "truncate"
- delete from은 WHERE 조건을 통해서 삭제함. 트랜잭션 적용. - truncate는 조건 없이 삭제함. 트랜잭션 적용 X.... def etl(**context): link = context["params"]["url"] # task 자체에 대한 정보 (일부는 DAG의 정보가 되기도 함)를 읽고 싶다면 context['task_instance'] 혹은 context['ti']를 통해 가능 # https://airflow.readthedocs.io/en/latest/_api/airflow/models/taskinstance/index.html#airflow.models.TaskInstance task_instance = context['task_instance'] execution_date = context['execution_date'] logging.info(execution_date) data = extract(link) lines = transform(data) load(lines) dag = DAG( dag_id = 'name_gender_v2', start_date = datetime(2023,4,6), # 날짜가 미래인 경우 실행이 안됨 schedule = '0 2 * * *', # 적당히 조절 catchup = False, max_active_runs = 1, default_args = { 'retries': 1, 'retry_delay': timedelta(minutes=3), } ) task = PythonOperator( task_id = 'perform_etl', python_callable = etl, params = { 'url': "https://s3-geospatial.s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/name_gender.csv" }, dag = dag)
-
-
Connections & Variables in Airflow
- Connections : Redshift와 연동할 때 주요한 정보들을 환경 설정 형태로 코드 밖으로 빼내는 역할.
- Variables : CSV 파일 링크와 같은 정보를 환경 설정 형태로 코드 밖으로 빼내는 역할.
-
개선 버전 2.
-
Variable 적용.
-
Xcom을 사용하여 3개의 태스크로 나누기.
from airflow import DAG from airflow.operators.python import PythonOperator from airflow.models import Variable from datetime import datetime from datetime import timedelta import requests import logging import psycopg2 def get_Redshift_connection(): host = "learnde.cduaw970ssvt.ap-northeast-2.redshift.amazonaws.com" redshift_user = "keeyong" # 본인 ID 사용 redshift_pass = "..." # 본인 Password 사용 port = 5439 dbname = "dev" conn = psycopg2.connect(f"dbname={dbname} user={redshift_user} host={host} password={redshift_pass} port={port}") conn.set_session(autocommit=True) return conn.cursor() def extract(**context): link = context["params"]["url"] task_instance = context['task_instance'] execution_date = context['execution_date'] logging.info(execution_date) f = requests.get(link) return (f.text) def transform(**context): logging.info("Transform started") # task_ids가 extract인 테스크를 읽어서 해당 테스크의 리턴값을 text에 저장. text = context["task_instance"].xcom_pull(key="return_value", task_ids="extract") lines = text.strip().split("\n")[1:] # 첫 번째 라인을 제외하고 처리 records = [] for l in lines: (name, gender) = l.split(",") # l = "Keeyong,M" -> [ 'keeyong', 'M' ] records.append([name, gender]) logging.info("Transform ended") return records def load(**context): logging.info("load started") schema = context["params"]["schema"] table = context["params"]["table"] # transform이라는 테스크의 리턴값을 lines에 저장. lines = context["task_instance"].xcom_pull(key="return_value", task_ids="transform") """ records = [ [ "Keeyong", "M" ], [ "Claire", "F" ], ... ] """ # BEGIN과 END를 사용해서 SQL 결과를 트랜잭션으로 만들어주는 것이 좋음 cur = get_Redshift_connection() try: cur.execute("BEGIN;") cur.execute(f"DELETE FROM {schema}.name_gender;") # DELETE FROM을 먼저 수행 -> FULL REFRESH을 하는 형태 for r in records: name = r[0] gender = r[1] print(name, "-", gender) sql = f"INSERT INTO {schema}.name_gender VALUES ('{name}', '{gender}')" cur.execute(sql) cur.execute("COMMIT;") # cur.execute("END;") except (Exception, psycopg2.DatabaseError) as error: print(error) cur.execute("ROLLBACK;") logging.info("load done") dag = DAG( dag_id = 'name_gender_v3', start_date = datetime(2023,4,6), # 날짜가 미래인 경우 실행이 안됨 schedule = '0 2 * * *', # 적당히 조절 catchup = False, max_active_runs = 1, default_args = { 'retries': 1, 'retry_delay': timedelta(minutes=3), } ) extract = PythonOperator( task_id = 'extract', python_callable = extract, params = { 'url': Variable.get("csv_url") }, dag = dag) transform = PythonOperator( task_id = 'transform', python_callable = transform, params = { }, dag = dag) load = PythonOperator( task_id = 'load', python_callable = load, # params를 통해서 config 정보 전달. params = { 'schema': 'keeyong', 'table': 'name_gender' }, dag = dag) extract >> transform >> load
-
-
Xcom이란?
- 태스크(Operator) 간에 데이터를 주고 받기 위한 방식.
# Xcom이 적용되지 않은 방식. 하나의 태스크로 구성된 e.t.l. # 3개의 태스크 : extract, transform, load는 서로 데이터를 주고 받아야 함. data = extract(link) lines = transform(data) load(lines) - 위 값들은 Airflow 메타 데이터 DB에 저장되기에 큰 데이터를 주고 받는 것은 불가하며, 보통 S3 등에 로드하여 해당 링크를 전달함.
- 태스크(Operator) 간에 데이터를 주고 받기 위한 방식.
-
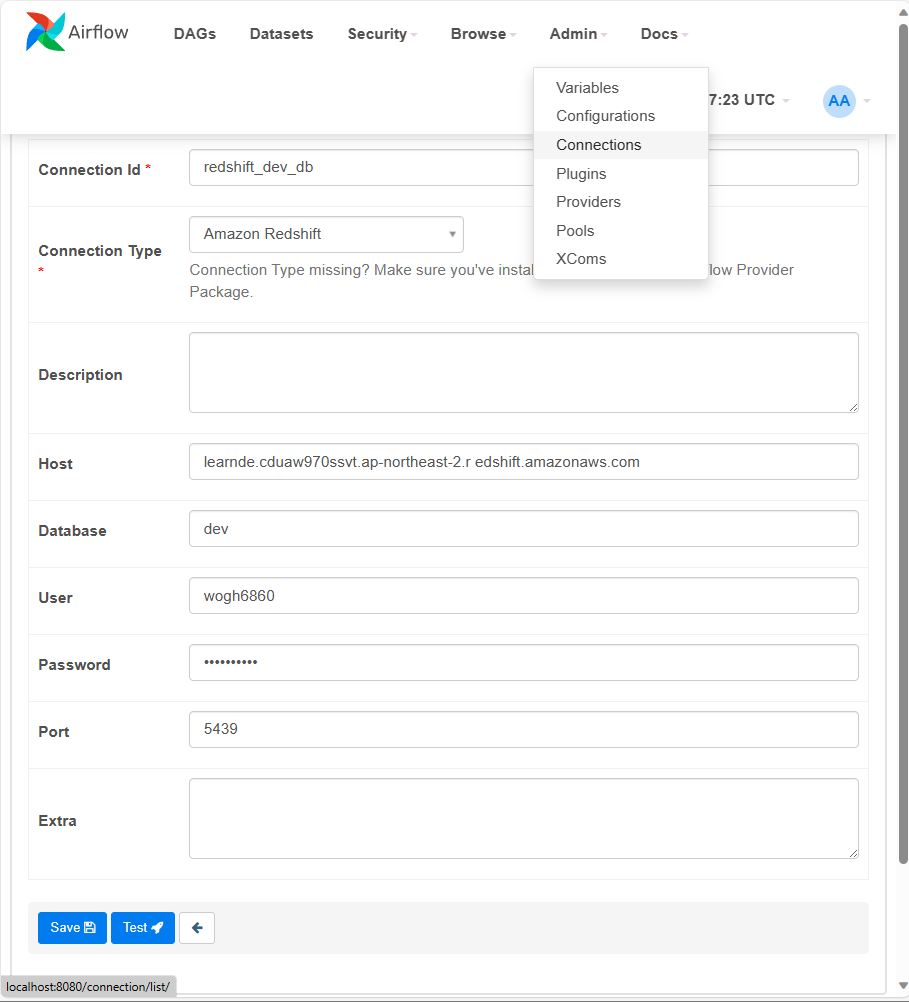
Airflow 웹 UI에서 Redshift Connection 설정.
-
위 사항을 고려하여 코드 수정.
from airflow import DAG from airflow.operators.python import PythonOperator from airflow.models import Variable from airflow.providers.postgres.hooks.postgres import PostgresHook from datetime import datetime from datetime import timedelta # from plugins import slack import requests import logging import psycopg2 def get_Redshift_connection(autocommit=True): # 앞에서 추가한 redshift connection을 통해서 간단하게 config를 설정함. hook = PostgresHook(postgres_conn_id='redshift_dev_db') conn = hook.get_conn() conn.autocommit = autocommit return conn.cursor() def extract(**context): link = context["params"]["url"] task_instance = context['task_instance'] execution_date = context['execution_date'] logging.info(execution_date) f = requests.get(link) return (f.text) def transform(**context): logging.info("Transform started") text = context["task_instance"].xcom_pull(key="return_value", task_ids="extract") lines = text.strip().split("\n")[1:] # 첫 번째 라인을 제외하고 처리 records = [] for l in lines: (name, gender) = l.split(",") # l = "Keeyong,M" -> [ 'keeyong', 'M' ] records.append([name, gender]) logging.info("Transform ended") return records def load(**context): logging.info("load started") schema = context["params"]["schema"] table = context["params"]["table"] records = context["task_instance"].xcom_pull(key="return_value", task_ids="transform") """ records = [ [ "Keeyong", "M" ], [ "Claire", "F" ], ... ] """ # BEGIN과 END를 사용해서 SQL 결과를 트랜잭션으로 만들어주는 것이 좋음 cur = get_Redshift_connection() try: cur.execute("BEGIN;") cur.execute(f"DELETE FROM {schema}.name_gender;") # DELETE FROM을 먼저 수행 -> FULL REFRESH을 하는 형태 for r in records: name = r[0] gender = r[1] print(name, "-", gender) sql = f"INSERT INTO {schema}.name_gender VALUES ('{name}', '{gender}')" cur.execute(sql) cur.execute("COMMIT;") # cur.execute("END;") except (Exception, psycopg2.DatabaseError) as error: print(error) cur.execute("ROLLBACK;") raise logging.info("load done") dag = DAG( dag_id = 'name_gender_v4', start_date = datetime(2023,4,6), # 날짜가 미래인 경우 실행이 안됨 schedule = '0 2 * * *', # 적당히 조절 max_active_runs = 1, catchup = False, default_args = { 'retries': 1, 'retry_delay': timedelta(minutes=3), # 'on_failure_callback': slack.on_failure_callback, } ) extract = PythonOperator( task_id = 'extract', python_callable = extract, params = { 'url': Variable.get("csv_url") }, dag = dag) transform = PythonOperator( task_id = 'transform', python_callable = transform, params = { }, dag = dag) load = PythonOperator( task_id = 'load', python_callable = load, params = { 'schema': 'keeyong', ## 자신의 스키마로 변경 'table': 'name_gender' }, dag = dag) extract >> transform >> load -
task decorator 적용 버전.
from airflow import DAG from airflow.models import Variable from airflow.providers.postgres.hooks.postgres import PostgresHook from airflow.decorators import task from datetime import datetime from datetime import timedelta import requests import logging def get_Redshift_connection(autocommit=True): hook = PostgresHook(postgres_conn_id='redshift_dev_db') conn = hook.get_conn() conn.autocommit = autocommit return conn.cursor() @task def extract(url): logging.info(datetime.utcnow()) f = requests.get(url) return f.text @task def transform(text): lines = text.strip().split("\n")[1:] # 첫 번째 라인을 제외하고 처리 records = [] for l in lines: (name, gender) = l.split(",") # l = "Keeyong,M" -> [ 'keeyong', 'M' ] records.append([name, gender]) logging.info("Transform ended") return records @task def load(schema, table, records): logging.info("load started") cur = get_Redshift_connection() """ records = [ [ "Keeyong", "M" ], [ "Claire", "F" ], ... ] """ # BEGIN과 END를 사용해서 SQL 결과를 트랜잭션으로 만들어주는 것이 좋음 try: cur.execute("BEGIN;") cur.execute(f"DELETE FROM {schema}.name_gender;") # DELETE FROM을 먼저 수행 -> FULL REFRESH을 하는 형태 for r in records: name = r[0] gender = r[1] print(name, "-", gender) sql = f"INSERT INTO {schema}.name_gender VALUES ('{name}', '{gender}')" cur.execute(sql) cur.execute("COMMIT;") # cur.execute("END;") except (Exception, psycopg2.DatabaseError) as error: print(error) cur.execute("ROLLBACK;") logging.info("load done") with DAG( dag_id='namegender_v5', start_date=datetime(2022, 10, 6), # 날짜가 미래인 경우 실행이 안됨 schedule='0 2 * * *', # 적당히 조절 max_active_runs=1, catchup=False, default_args={ 'retries': 1, 'retry_delay': timedelta(minutes=3), # 'on_failure_callback': slack.on_failure_callback, } ) as dag: url = Variable.get("csv_url") schema = 'jaeho' ## 자신의 스키마로 변경 table = 'name_gender' lines = transform(extract(url)) # 간단하게 서로 인자, 결과값 등을 공유함. load(schema, table, lines)
실행 데모 (웹 UI 버전)
git clone https://github.com/learndataeng/learn-airflow로 소스 파일 다운로드.cp -r learn-airflow/dags/* dags로 다운로드한 레포의 dags 폴더의 파일들을 airflow-setup 폴더에 있는 dags 폴더로 복사. (현재 디렉토리: airflow-setup)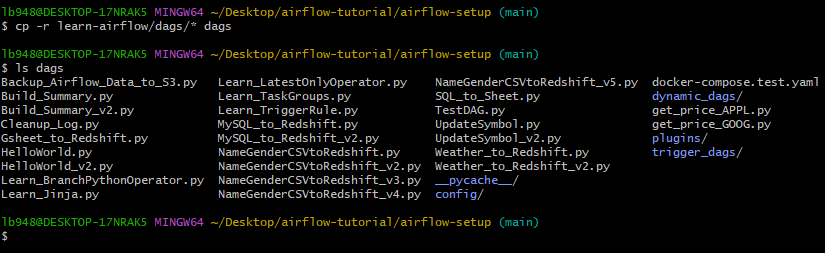
- http://localhost:8080 에 접속.(도커 엔진을 켜야 함.)
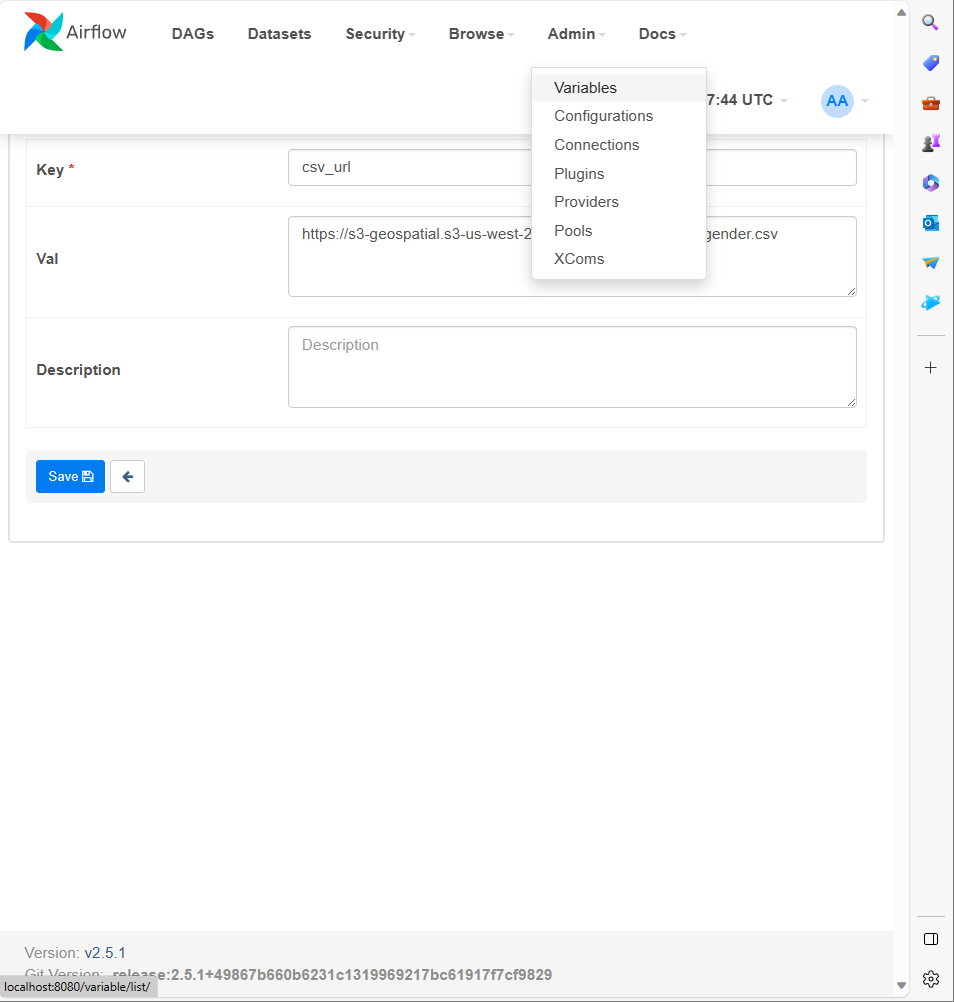
- Admin의 Variable에서 Variable 지정.
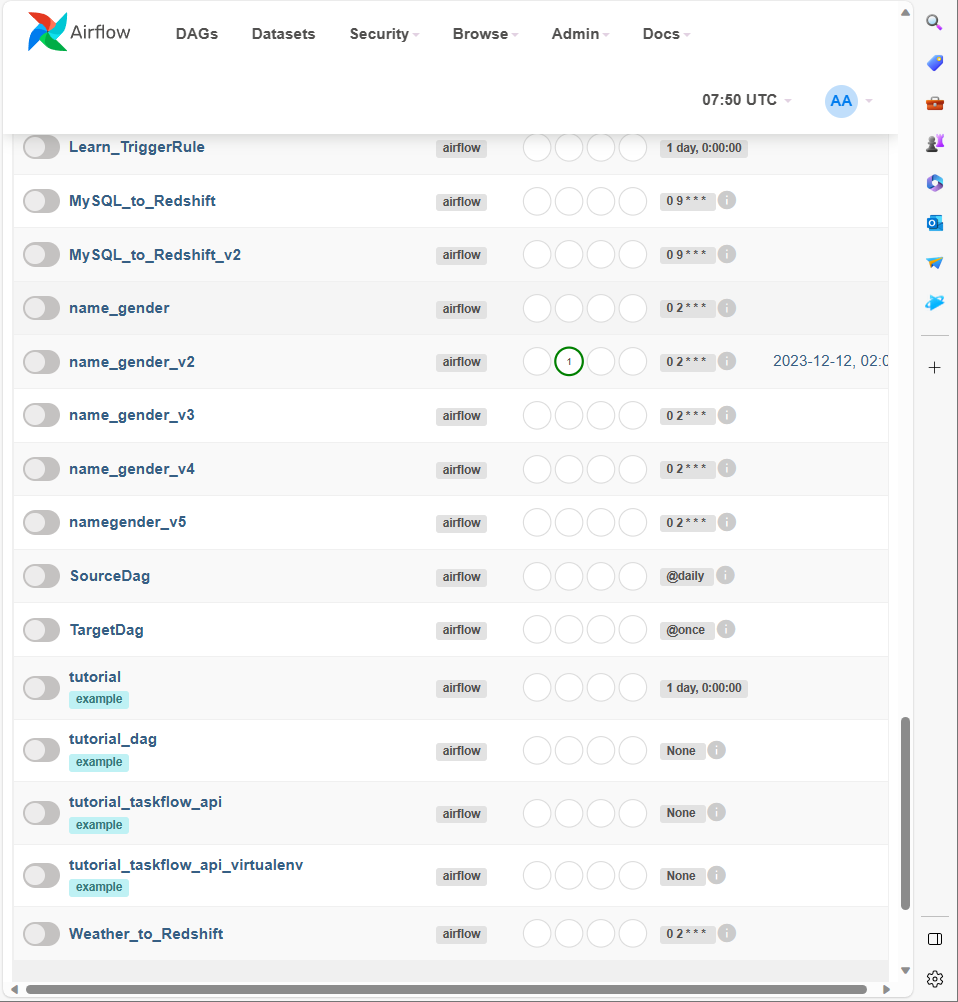
- Dags에서 namegender가 추가된 것을 확인할 수 있음. (이를 활성화하면 코드가 실행됨.)
실행 데모 (커맨드 라인 버전)
-
docker ps로 airflow-scheduler 컨테이너 아이디 확인 및 복사.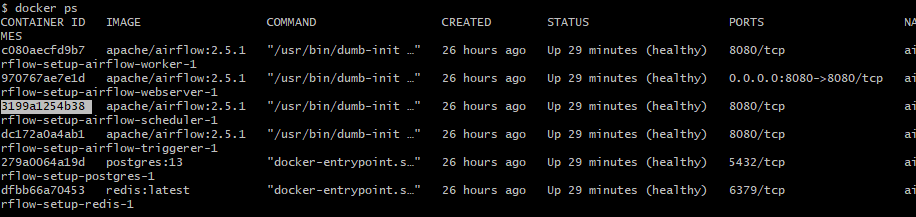
-
docker exec -it 3199a1254b38 sh로 스케쥴러로 로그인.- 만약
the input device is not a TTY. If you are using mintty, try prefixing the command with 'winpty'에러 발생 시, https://wotres.tistory.com/entry/docker-error-%ED%95%B4%EA%B2%B0%EB%B2%95-the-input-device-is-not-a-TTY-If-you-are-using-mintty-try-prefixing-the-command-with-winpty 참고.

- 만약
-
airflow dags list로 dags 리스트 조회.
-
airflow tasks list namegender_v5로 테스크 조회.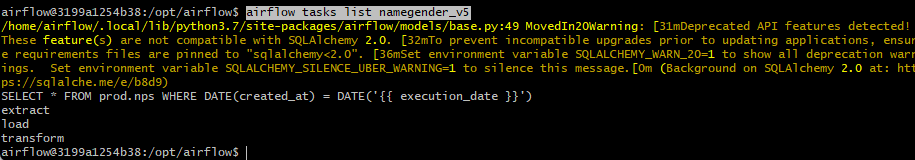
-
airflow variables list로 variable 리스트 조회.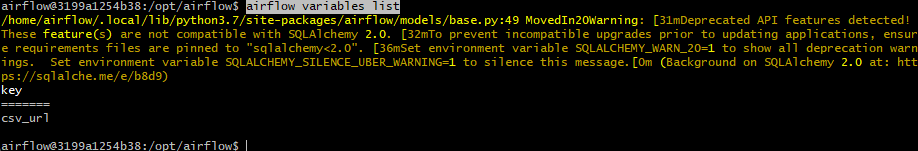
-
airflow variables get csv_url로 특정 variable의 정보 조회.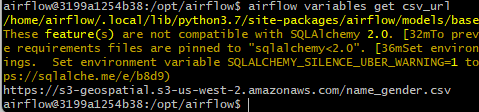
자주 나오는 질문
- PostgresHook의 autocommit 파라미터 관련.
- default: false, false인 경우 BEGIN의 의미 X.- DAG에서 task를 어느 정도로 분리할 지.
- 오래 걸리는 DAG일 경우에는 재실행이 쉽도록 다수의 task로 나누기, 간단하다면 소수의 task에 작업을 모두 할당하기.- Variable vs. 코드로 관리:
- 매우 중요한 코드라면 코드로 놔두고, 그렇지 않다면 Variable로 관리.
- Airflow 관련 기타 정보 : https://hongcana.tistory.com/122
3. Yahoo Finance API DAG 작성
Full Refresh로 구현
1. Yahoo Finance API를 호출하여 애플 주식 정보 수집(지난 30일).
2. Redshift 상의 테이블로 1에서 받은 레코드들을 적재.
- api -> extract/transform -> load -> stock_info
-
UpdateSymbol.py 코드
from airflow import DAG from airflow.decorators import task from airflow.providers.postgres.hooks.postgres import PostgresHook from datetime import datetime from pandas import Timestamp import yfinance as yf import pandas as pd import logging def get_Redshift_connection(autocommit=True): hook = PostgresHook(postgres_conn_id='redshift_dev_db') conn = hook.get_conn() conn.autocommit = autocommit return conn.cursor() @task def get_historical_prices(symbol): # 미국 주식의 경우 symbol이 존재. ex) 구글 : GOOG ticket = yf.Ticker(symbol) data = ticket.history() # pandas df 형식으로 반환 받음. records = [] for index, row in data.iterrows(): date = index.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S') records.append([date, row["Open"], row["High"], row["Low"], row["Close"], row["Volume"]]) return records @task def load(schema, table, records): logging.info("load started") cur = get_Redshift_connection() try: cur.execute("BEGIN;") cur.execute(f"DROP TABLE IF EXISTS {schema}.{table};") cur.execute(f""" CREATE TABLE {schema}.{table} ( date date, "open" float, high float, low float, close float, volume bigint );""") # DELETE FROM을 먼저 수행 -> FULL REFRESH을 하는 형태 for r in records: sql = f"INSERT INTO {schema}.{table} VALUES ('{r[0]}', {r[1]}, {r[2]}, {r[3]}, {r[4]}, {r[5]});" print(sql) cur.execute(sql) cur.execute("COMMIT;") # cur.execute("END;") except Exception as error: print(error) cur.execute("ROLLBACK;") raise logging.info("load done") with DAG( dag_id = 'UpdateSymbol', start_date = datetime(2023,5,30), catchup=False, tags=['API'], schedule = '0 10 * * *' ) as dag: results = get_historical_prices("AAPL") load("jaeho", "stock_info", results)
절차는 다음과 같음.
- airflow-scheduler로 로그인.
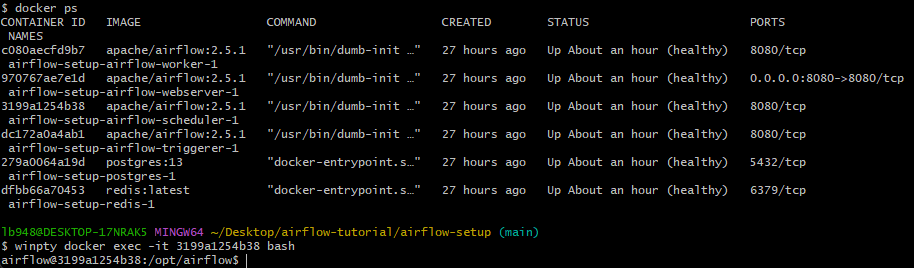
- docker에서 yahoo fianance 라이브러리 설치.
pip install yfinance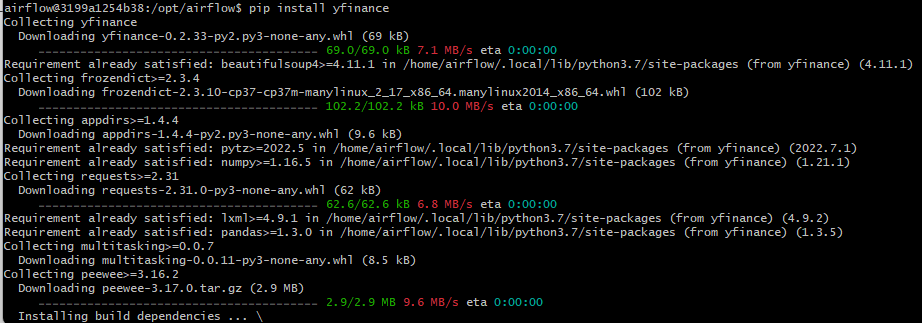
- 현재 디렉토리인 /opt/airflow에서 UpdateSymbol이라는 DAG 이름 복사.
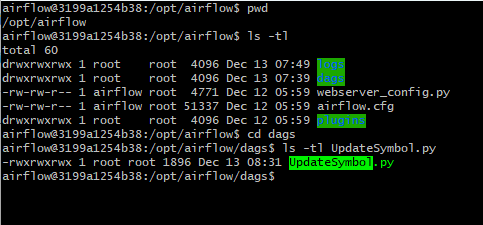
- 해당 DAG의 task 목록 조회.
airflow tasks list UpdateSymbol
원인을 모르겠으나 강의와 달리 본 컴퓨터에서는 실행이 안 됨..(airflow.exceptions.AirflowException: Dag 'UpdateSymbol' could not be found; either it does not exist or it failed to parse.) airflow dags test UpdateSymbol 2023-05-30으로 DAG 실행.docker exec --user root -it {컨테이너 아이디} sh로 root 유저로도 접속 가능.
Incremental Update 추가
-
앞과 유사하나, 테이블을 삭제하지 않고 적재 및 중복 제거 후 테이블 재로드.
-
매일 하루치의 데이터가 늘어남.
-
트랜잭션 형태로 Incremental Update 구현.
-
원본 테이블 레코드를 복사하여 TEMP라는 임시 테이블에 저장. (CTAS)
-
임시 테이블에 API로부터 읽어온 레코드 적재.
-
원본 테이블 삭제 및 새로 생성.
-
원본 테이블에 임시 테이블 내용 복사. (SELECT DISTINCT* 로 중복 제거)
from airflow import DAG from airflow.decorators import task from airflow.providers.postgres.hooks.postgres import PostgresHook from datetime import datetime from pandas import Timestamp import yfinance as yf import pandas as pd import logging def get_Redshift_connection(autocommit=True): hook = PostgresHook(postgres_conn_id='redshift_dev_db') conn = hook.get_conn() conn.autocommit = autocommit return conn.cursor() @task def get_historical_prices(symbol): ticket = yf.Ticker(symbol) data = ticket.history() records = [] for index, row in data.iterrows(): date = index.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S') records.append([date, row["Open"], row["High"], row["Low"], row["Close"], row["Volume"]]) return records def _create_table(cur, schema, table, drop_first): if drop_first: # drop_first를 쓰는 이유: Incremental Update의 경우, 원본 테이블이 유지되어야 하지만, 처음 생성되는 경우에는 원본 테이블이 없기 때문에. cur.execute(f"DROP TABLE IF EXISTS {schema}.{table};") cur.execute(f""" CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS {schema}.{table} ( date date, "open" float, high float, low float, close float, volume bigint );""") @task def load(schema, table, records): logging.info("load started") cur = get_Redshift_connection() try: cur.execute("BEGIN;") # 원본 테이블이 없으면 생성 - 테이블이 처음 한번 만들어질 때 필요한 코드 _create_table(cur, schema, table, False) # 임시 테이블로 원본 테이블을 복사 cur.execute(f"CREATE TEMP TABLE t AS SELECT * FROM {schema}.{table};") for r in records: sql = f"INSERT INTO t VALUES ('{r[0]}', {r[1]}, {r[2]}, {r[3]}, {r[4]}, {r[5]});" print(sql) cur.execute(sql) # 원본 테이블 생성 _create_table(cur, schema, table, True) # 임시 테이블 내용을 원본 테이블로 복사 cur.execute(f"INSERT INTO {schema}.{table} SELECT DISTINCT * FROM t;") cur.execute("COMMIT;") # cur.execute("END;") except Exception as error: print(error) cur.execute("ROLLBACK;") raise logging.info("load done") with DAG( dag_id = 'UpdateSymbol_v2', start_date = datetime(2023,5,30), catchup=False, tags=['API'], schedule = '0 10 * * *' ) as dag: results = get_historical_prices("AAPL") load("jaeho", "stock_info_v2", results)
-