Ad-hoc polymorphism
애드훅 다형성이라 부르는 것은 함수 오버로딩이라고도 한다.
함수 오버로딩은 함수 이름은 같지만, 다른 매개변수를 받는 걸 의미한다. C 에서는 있을 수 없지만 C++ 에서는 가능하다.
예시
- Sample.class.hpp
hpp 파일의 멤버 함수를 보면 이름이 같은 함수지만 매개 변수의 타입이 다른 걸 확인할 수 있다.
#ifndef SAMPLE_CLASS_H
# define SAMPLE_CLASS_H
class Sample
{
private:
public:
Sample(void);
~Sample(void);
void bar(char const c) const;
void bar(int const n) const;
void bar(float const z) const;
void bar(Sample const & i) const;
};
#endif- Sample.class.cpp
각각은 매개 변수로 받아온 값을 출력한다.
#include <iostream>
#include "Sample.class.hpp"
Sample::Sample( void ) {
std::cout << "Constructor called" << std::endl;
return;
}
Sample::~Sample(void) {
std::cout << "Destructor called" << std::endl;
return;
}
void Sample::bar(char const c) const {
std::cout << "Called with char overload : " << c << std::endl;
return;
}
void Sample::bar(int const n) const {
std::cout << "Called with int overload : " << n << std::endl;
return;
}
void Sample::bar(float const z) const {
std::cout << "Called with float overload : " << z << std::endl;
return;
}
void Sample::bar(Sample const & i) const {
(void)i;
std::cout << "Called with Smaple class overload" << std::endl;
return;
}- main.cpp
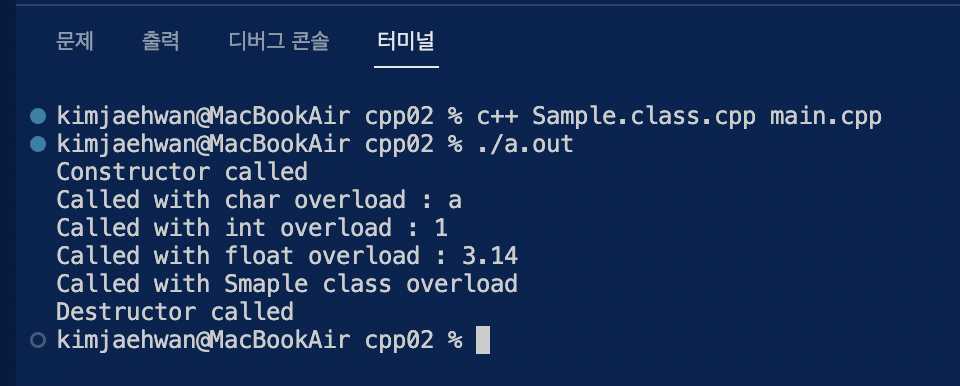
매개 변수에 알맞은 타입만 들어가면, 에러가 발생하지 않고 작동하는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
#include <iostream>
#include "Sample.class.hpp"
int main(void) {
Sample test;
test.bar('a');
test.bar(1);
test.bar((float)3.14);
test.bar(test);
}