1. 동기와 비동기
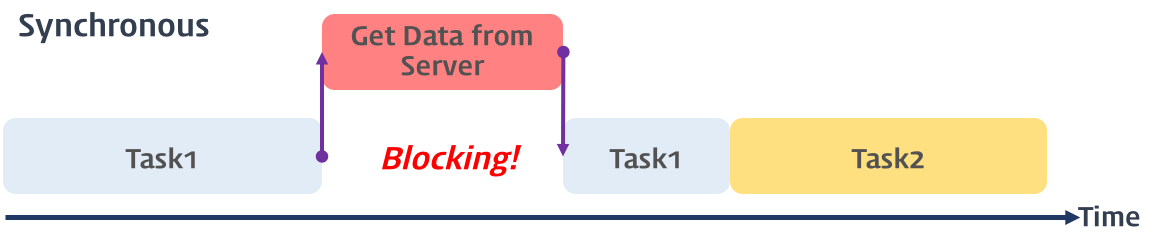
동기(synchronous)
- 태스크가 순차적으로(직렬적으로) 실행됨. 하나의 작업이 끝나야 다음 작업 수행 가능.
- 태스크가 끝날 때가지 대기하기 때문에 비효울적
console.log('A');
console.log('B');
//실행결과
A
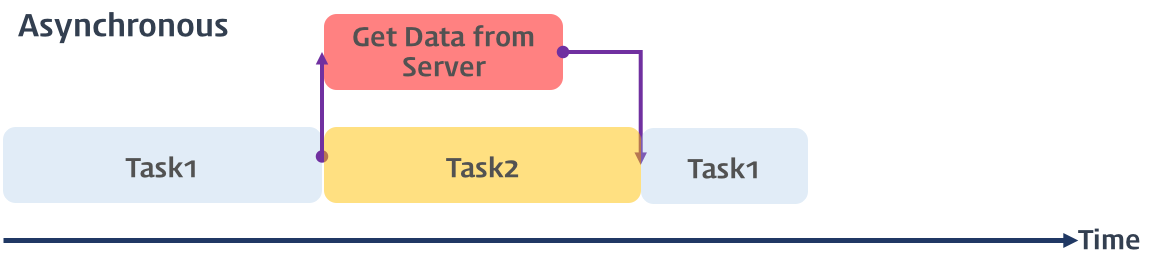
B비동기
- 태스크가 병렬적으로 실행됨.
- 어떤 작업을 요청한 후, 완료될 때까지 기다리지 않고 다음 작업을 먼저 실행함. 결과는 나중에 받음.
console.log('A');
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('B');
}, 1000);
console.log('C');
//
A
C
(1초 후) B2. 비동기 처리의 도구들
setTimeout, XMLHttpRequest, fetch, EventListener, WebSocket 등은 대표적인 비동기 함수
과거 콜백함수를 이용하여 비동기 작업을 처리.
콜백 지옥으로 인해 가독성 저하 및 에러 처리 어려움 등으로 유지보수가 힘들다.
login(user, (userInfo) => {
getProfile(userInfo.id, (profile) => {
getPosts(profile.id, (posts) => {
console.log(posts);
});
});
});이를 개선하기 위해 Promise → async/await 등장
3. Promise란?
- ES6에서는 비동기 처리를 위해 새롭게 프로미스(Promise)를 도입.
- 프로미스는 미래에 결과를 반환할 비동기 작업의 상태와 결과를 표현하는 객체
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// 비동기 작업
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('성공!');
}, 1000);
});
promise
.then(result => console.log(result)) // → 성공!
.catch(error => console.error(error))
.finally(() => {
console.log('항상 실행됨');
});Promise는 비동기 처리가 성공 여부에 따라 다양한 상태(state)를 가진다.
pending: 비동기 처리가 아직 수행되지 않은 상태fulfilled: 비동기 처리가 수행된 상태 (성공)rejected: 비동기 처리가 수행된 상태 (실패)settled: 비동기 처리가 수행된 상태 (성공 또는 실패)
Promise 호출 과정
-
Promise 객체 생성
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => { // 비동기 작업 수행 });이 시점에서 promise 객체는 pending 상태입니다.
resolve(value)를 호출하면 fulfilled 상태로 전이
reject(reason)을 호출하면 rejected 상태로 전이
-
비동기 작업 수행 (예: setTimeout, fetch 등)
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => { setTimeout(() => { resolve('작업 성공'); }, 1000); });resolve()나 reject()는 작업이 끝났을 때 “결과”를 전달하는 역할
여기선 1초 뒤 resolve()가 실행되므로 1초 후에 fulfilled 상태가 됨
-
.then()으로 성공 처리 연결
promise.then(result => { console.log(result); // → "작업 성공" });promise가 fulfilled 상태로 바뀌면, 등록된 .then() 콜백이 호출됨. then 메소드는 Promise를 반환.
result는 resolve()에서 전달한 값
-
.catch()으로 에러 처리 연결
promise .then(result => { console.log(result); }) .catch(error => { console.error('에러 발생:', error); });reject()가 호출되었거나 .then() 내부에서 에러가 나면 .catch()가 실행됨. catch 메소드는 Promise를 반환.
error는 reject()에서 전달한 값
-
.finally으로 성공여부 상관없이 항상실행
.catch(error => { console.error('에러 발생:', error); }) .finally(() => { console.log('항상 실행됨'); });결과에 상관없이 항상 실행됨
finally()는 값을 전달하지 않음 (다음 then()으로는 이전 then()의 결과가 넘어감)
프로미스는 후속 처리 메소드인 then, catch, finally 메소드를 체이닝(chainning)하여 여러 개의 프로미스를 연결하여 사용할 수 있다. 이런 방식을 이용해 콜백 헬을 해결한다.
Promise 중간 디버그 흐름
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
console.log('🟡 Promise 시작'); // 즉시 실행됨
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('🟢 비동기 완료 → resolve 호출');
resolve('완료');
}, 1000);
});
console.log('🟠 .then 등록 전');
promise.then(res => {
console.log('🔵 then 실행:', res);
});
console.log('🔴 .then 등록 완료');
//출력
🟡 Promise 시작
🟠 .then 등록 전
🔴 .then 등록 완료
🟢 비동기 완료 → resolve 호출
🔵 then 실행: 완료4. Async / Await
async await 이해
async/await는 Promise 기반 비동기 코드를 동기식처럼 읽기 쉽게 작성할 수 있게 해줍니다.
async function 함수명() {
await 비동기_처리_메서드_명();
}async 함수란?
- async 함수는 항상 프라미스를 반환한다. 일반 값을 반환하면 자동으로 Promise.resolve(value)로 감싸진다.
- 아래 예시의 함수를 호출하면 result가 1인 이행 프라미스가 반환된다.
async function example() {
return 1;
}
example().then(console.log); // 1await란?
- async 함수 내부에서만 사용 가능하다
- await promise 형태로 사용하며, Promise가 처리될 때까지 기다렸다가 결과를 반환
- 프라미스가 처리되길 기다리는 동안엔 엔진이 다른 작업이 수행 가능하다.
async function delay() {
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 1000));
console.log('1초 후 실행');
}async await를 이용한 성공 에러처리
await를 통해 then을 사용하지 않고 결과 값을 얻을 수 있고, catch대시 try…catch구문을 이용해 에러처리가 가능하다.
async function f() {
try {
let response = await fetch('http://유효하지-않은-주소');
} catch(err) {
alert(err); // TypeError: failed to fetch
}
}
f();에러가 발생하면 제어 흐름이 catch 블록으로 넘어간다. 또한, 여러 줄의 코드를 try로 감쌀 수 있다.
await time() 으로 5초 대기
console.log('a');
await time();
console.log('b');이렇게 하려면 time()이 Promise를 반환해야 await이 효과가 있음.
function time() {
return new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 5000));
}
async function run() {
console.log('a');
await time(); // 5초 기다림
console.log('b');
}
run();
//출력
a
(5초 후)
b출처
