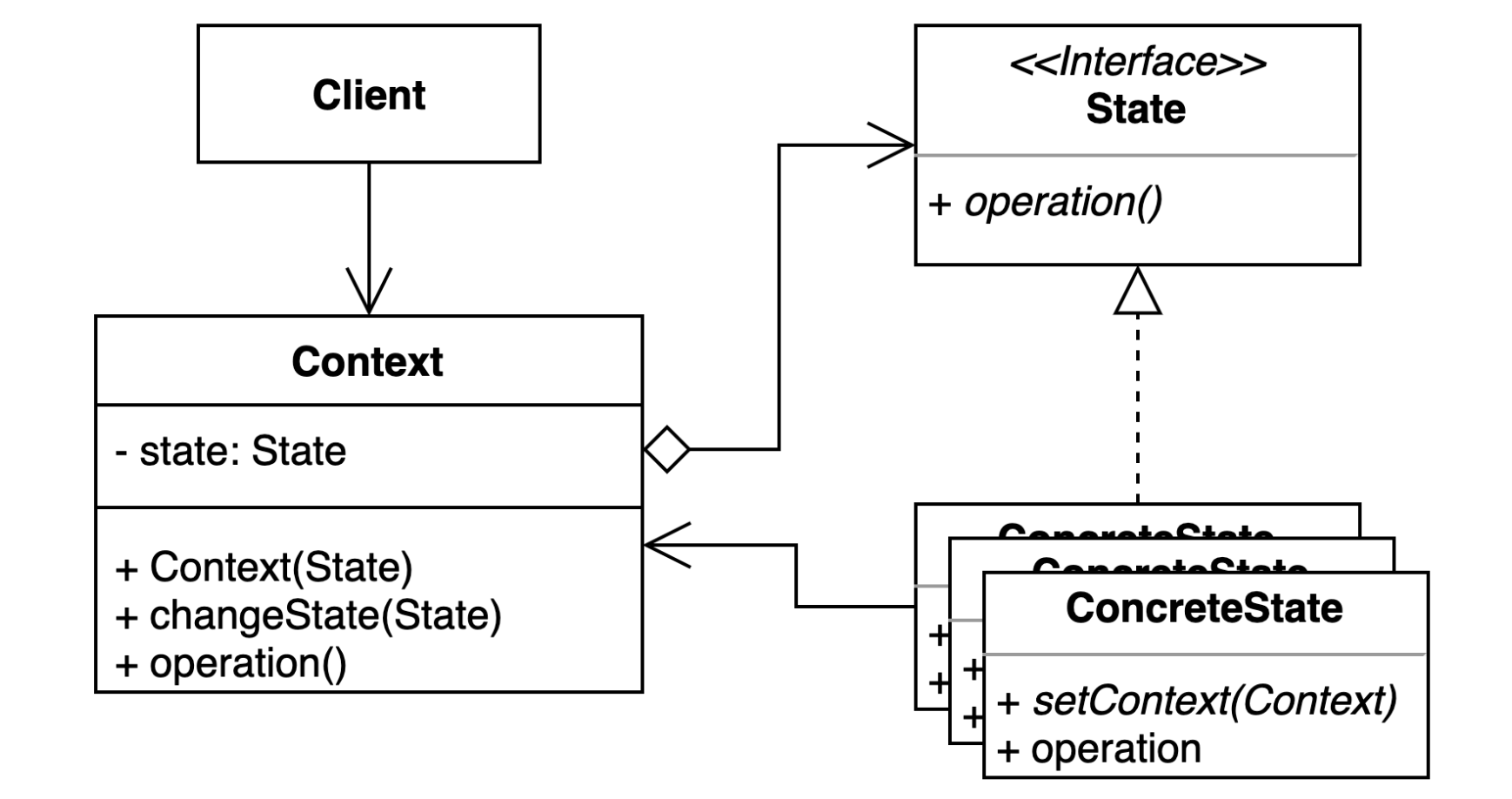
1. 상태 (State) 패턴 : 객체 내부 상태 변경에 따라 객체의 행동이 달라지는 패턴.
상태에 특화된 행동들을 분리해 낼 수 있으며, 새로운 행동을 추가하더라도 다른 행동에 영향을 주지 않는다.
Before
1) OnlineCourse
State열거형:DRAFT,PUBLISHED,PRIVATE의 상태를 관리.- 상태별 동작:
addReview: 상태에 따라 리뷰 작성 가능 여부를 결정.addStudent: 상태에 따라 학생 등록 가능 여부를 결정.
public class OnlineCourse {
public enum State {
DRAFT, PUBLISHED, PRIVATE
}
private State state = State.DRAFT;
private List<String> reviews = new ArrayList<>();
private List<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();
public void addReview(String review, Student student) {
if (this.state == State.PUBLISHED) {
this.reviews.add(review);
} else if (this.state == State.PRIVATE && this.students.contains(student)) {
this.reviews.add(review);
} else {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("리뷰를 작성할 수 없습니다.");
}
}
public void addStudent(Student student) {
if (this.state == State.DRAFT || this.state == State.PUBLISHED) {
this.students.add(student);
} else if (this.state == State.PRIVATE && availableTo(student)) {
this.students.add(student);
} else {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("학생을 해당 수업에 추가할 수 없습니다.");
}
if (this.students.size() > 1) {
this.state = State.PRIVATE;
}
}
public void changeState(State newState) {
this.state = newState;
}
public State getState() {
return state;
}
public List<String> getReviews() {
return reviews;
}
public List<Student> getStudents() {
return students;
}
private boolean availableTo(Student student) {
return student.isEnabledForPrivateClass(this);
}
}2) Student
- 학생 이름과 프라이빗 코스 접근 권한 관리.
- 특정 코스 접근 가능 여부를
isEnabledForPrivateClass로 확인.
public class Student {
private String name;
public Student(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
private List<OnlineCourse> privateCourses = new ArrayList<>();
public boolean isEnabledForPrivateClass(OnlineCourse onlineCourse) {
return privateCourses.contains(onlineCourse);
}
public void addPrivateCourse(OnlineCourse onlineCourse) {
this.privateCourses.add(onlineCourse);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}3) Client
- 코스 상태 변경과 학생/리뷰 추가를 테스트하는 메인 클래스.
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student = new Student("whiteship");
OnlineCourse onlineCourse = new OnlineCourse();
Student keesun = new Student("keesun");
keesun.addPrivateCourse(onlineCourse);
onlineCourse.addStudent(student);
onlineCourse.changeState(OnlineCourse.State.PRIVATE);
onlineCourse.addStudent(keesun);
onlineCourse.addReview("hello", student);
System.out.println(onlineCourse.getState());
System.out.println(onlineCourse.getStudents());
System.out.println(onlineCourse.getReviews());
}
}문제점
-
코드 복잡도 증가:
- 상태별 동작이
OnlineCourse내부에 몰려 있어 코드가 비대해지고 복잡해짐. - 예를 들어,
addReview메서드:public void addReview(String review, Student student) { if (this.state == State.PUBLISHED) { this.reviews.add(review); } else if (this.state == State.PRIVATE && this.students.contains(student)) { this.reviews.add(review); } else { throw new UnsupportedOperationException("리뷰를 작성할 수 없습니다."); } }
- 상태별 동작이
-
캡슐화 부족:
- 상태별 로직이 분산되지 않고
OnlineCourse에 몰려 응집도가 낮음.
- 상태별 로직이 분산되지 않고
-
확장성 문제:
- 새로운 상태를 추가하거나 변경하면, 기존 코드를 수정해야 하므로 유지보수가 어려움.
After

바뀐점
-
상태 인터페이스 (
State) 도입:addReview와addStudent를State인터페이스로 분리하여 상태별 행동 정의.
-
상태별 클래스:
Draft,Published,Private클래스로 상태별 행동을 캡슐화.- 각 상태는 고유한 동작을 정의하고, 상태 전환도 담당.
-
상태 전환:
- 상태 전환은
changeState메서드를 통해 동적으로 변경.
- 상태 전환은
-
캡슐화 강화:
OnlineCourse는 상태 전환과 상태 실행을 위임하며, 코드가 단순해짐.
State 인터페이스
- 상태별 행동을 정의하는 인터페이스.
public interface State {
void addReview(String review, Student student);
void addStudent(Student student);
}Draft 상태
- 초기 상태로, 리뷰 작성 불가.
- 학생이 2명 이상이 되면
Private상태로 전환.
public class Draft implements State {
private OnlineCourse onlineCourse;
public Draft(OnlineCourse onlineCourse) {
this.onlineCourse = onlineCourse;
}
@Override
public void addReview(String review, Student student) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("드래프트 상태에서는 리뷰를 남길 수 없습니다.");
}
@Override
public void addStudent(Student student) {
this.onlineCourse.getStudents().add(student);
if (this.onlineCourse.getStudents().size() > 1) {
this.onlineCourse.changeState(new Private(this.onlineCourse));
}
}
}Published 상태
- 리뷰 작성과 학생 추가 모두 가능.
public class Published implements State {
private OnlineCourse onlineCourse;
public Published(OnlineCourse onlineCourse) {
this.onlineCourse = onlineCourse;
}
@Override
public void addReview(String review, Student student) {
this.onlineCourse.getReviews().add(review);
}
@Override
public void addStudent(Student student) {
this.onlineCourse.getStudents().add(student);
}
}Private 상태
- 리뷰 작성은 등록된 학생만 가능.
- 등록은 특정 조건(
isAvailable)을 만족해야 가능.
public class Private implements State {
private OnlineCourse onlineCourse;
public Private(OnlineCourse onlineCourse) {
this.onlineCourse = onlineCourse;
}
@Override
public void addReview(String review, Student student) {
if (this.onlineCourse.getStudents().contains(student)) {
this.onlineCourse.getReviews().add(review);
} else {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("프라이빗 코스를 수강하는 학생만 리뷰를 남길 수 있습니다.");
}
}
@Override
public void addStudent(Student student) {
if (student.isAvailable(this.onlineCourse)) {
this.onlineCourse.getStudents().add(student);
} else {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("프라이빗 코스를 수강할 수 없습니다.");
}
}
}3) OnlineCourse
- 상태 변경과 실행을 상태 객체에 위임.
public class OnlineCourse {
private State state = new Draft(this);
private List<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();
private List<String> reviews = new ArrayList<>();
public void addStudent(Student student) {
this.state.addStudent(student);
}
public void addReview(String review, Student student) {
this.state.addReview(review, student);
}
public State getState() {
return state;
}
public List<Student> getStudents() {
return students;
}
public List<String> getReviews() {
return reviews;
}
public void changeState(State state) {
this.state = state;
}
}상태 패턴 장단점
장점
• 상태에 따른 동작을 개별 클래스로 옮겨서 관리할 수 있다.
• 기존의 특정 상태에 따른 동작을 변경하지 않고 새로운 상태에 다른 동작을 추가할 수 있다.
• 코드 복잡도를 줄일 수 있다.
단점
• 복잡도가 증가한다.
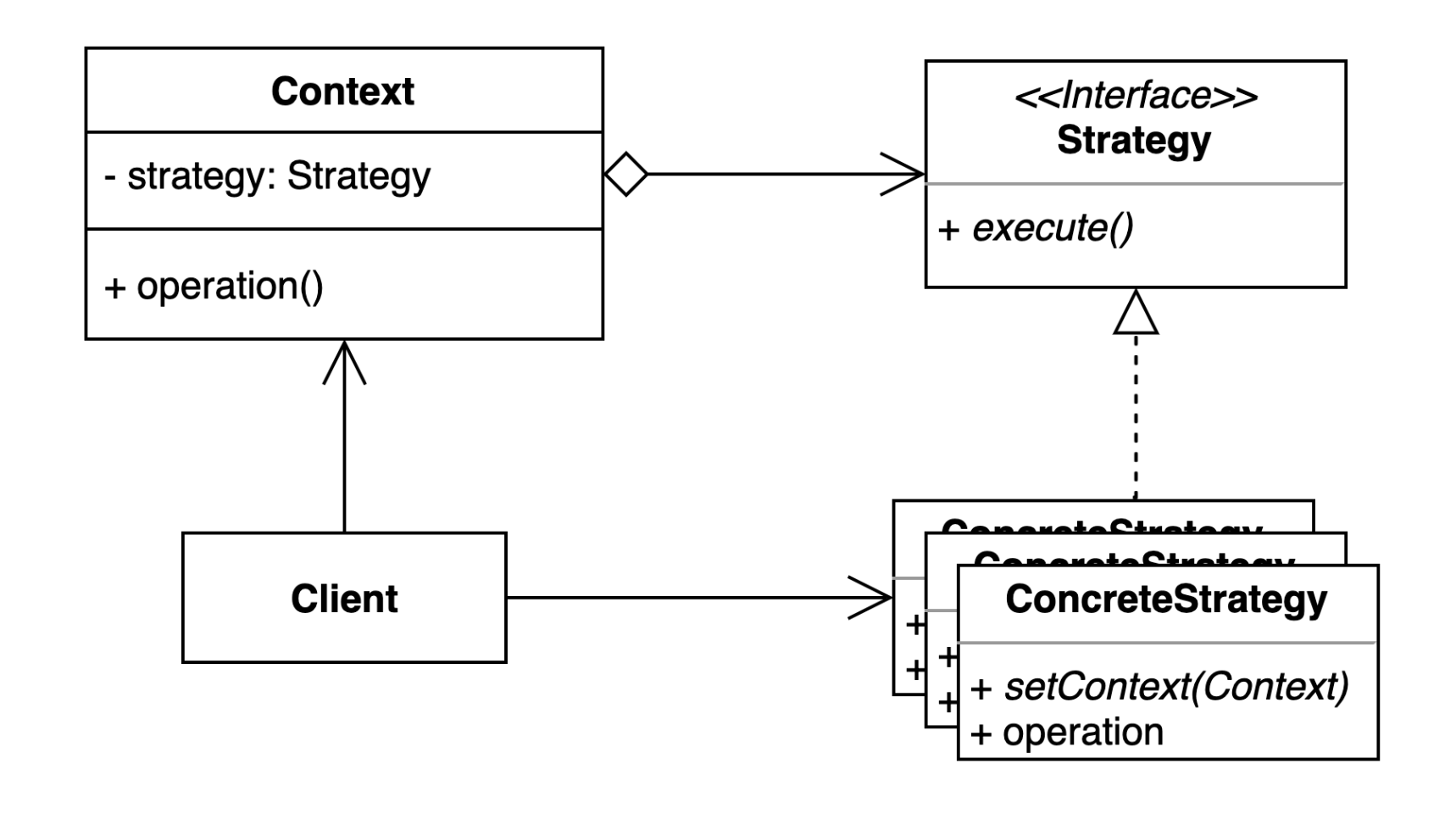
2. 전략 (Strategy) 패턴 : 여러 알고리듬을 캡슐화하고 상호 교환 가능하게 만드는 패턴.
• 컨텍스트에서 사용할 알고리듬을 클라이언트가 선택한다.
Before 코드
BlueLightRedLight 클래스
- 특정 속도(
speed)에 따라blueLight()와redLight()메서드의 출력이 달라진다. - 속도에 따른 동작은
if-else조건문으로 구현되어 있다.
public class BlueLightRedLight {
private int speed;
public BlueLightRedLight(int speed) {
this.speed = speed;
}
public void blueLight() {
if (speed == 1) {
System.out.println("무 궁 화 꽃 이");
} else if (speed == 2) {
System.out.println("무궁화꽃이");
} else {
System.out.println("무광꼬치");
}
}
public void redLight() {
if (speed == 1) {
System.out.println("피 었 습 니 다.");
} else if (speed == 2) {
System.out.println("피었습니다.");
} else {
System.out.println("피어씀다");
}
}
}
문제점
-
조건문 남용:
- 속도가 증가하거나 새로운 속도에 따른 동작이 추가될 경우,
if-else조건문이 계속 늘어나 코드가 복잡해진다. - 유지보수가 어려워진다.
- 속도가 증가하거나 새로운 속도에 따른 동작이 추가될 경우,
-
확장성 부족:
- 새로운 속도나 동작을 추가하려면 기존 코드를 수정해야 한다.
- 이는 개방-폐쇄 원칙(OCP)을 위반한다.
-
행동과 속도의 결합:
- 속도에 따른 동작이
BlueLightRedLight클래스 내부에 결합되어 있어 재사용성이 떨어진다.
- 속도에 따른 동작이
After
바뀐 점
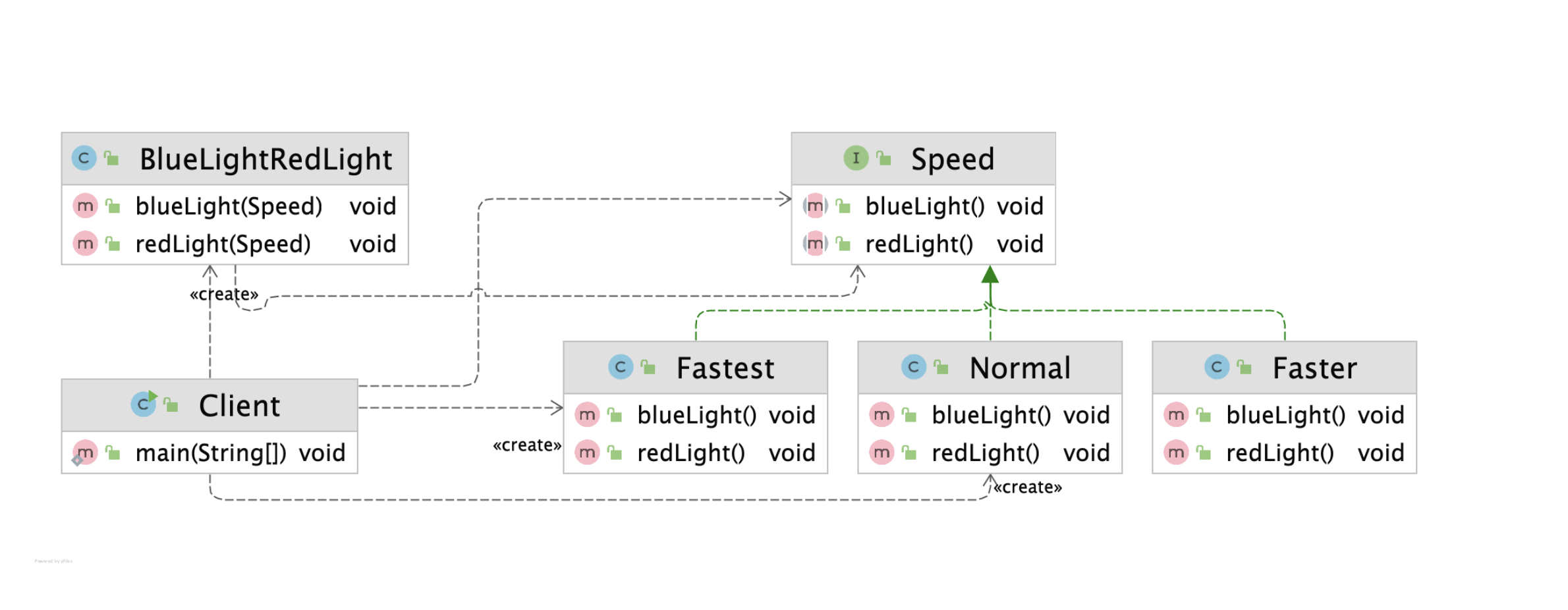
- 각 속도에 따른 동작(
Normal,Faster,Fastest)을Speed인터페이스로 추상화했다. BlueLightRedLight는 전략 실행을 담당하는 컨텍스트(Context)로, 알고리즘 실행만 책임지고 특정 알고리즘(속도 동작)을 알지 못한다.
코드 분석
Speed인터페이스- 각 속도의 행동(알고리즘)을 추상화한다.
- 각 구현체(
Normal,Faster,Fastest)는 속도별 동작을 정의한다.
public interface Speed {
void blueLight();
void redLight();
}
- 속도별 구현체
- 각 클래스(
Normal,Faster,Fastest)는Speed인터페이스를 구현하며, 속도에 따른 동작을 정의한다.
- 각 클래스(
public class Normal implements Speed {
@Override
public void blueLight() {
System.out.println("무 궁 화 꽃 이");
}
@Override
public void redLight() {
System.out.println("피 었 습 니 다.");
}
}
public class Faster implements Speed {
@Override
public void blueLight() {
System.out.println("무궁화꽃이");
}
@Override
public void redLight() {
System.out.println("피었습니다.");
}
}
public class Fastest implements Speed{
@Override
public void blueLight() {
System.out.println("무광꼬치");
}
@Override
public void redLight() {
System.out.println("피어씀다.");
}
}BlueLightRedLight클래스- 컨텍스트 역할을 한다.
Speed인터페이스를 사용하여 동작을 실행하며, 특정 구현체에 의존하지 않는다.- 새로운 동작을 추가하려면
Speed구현체만 만들면 된다.
public class BlueLightRedLight {
public void blueLight(Speed speed) {
speed.blueLight();
}
public void redLight(Speed speed) {
speed.redLight();
}
}- Client 클래스
Client에서 익명 클래스를 활용하여 동적으로 새로운 동작을 정의할 수도 있다.
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlueLightRedLight game = new BlueLightRedLight();
game.blueLight(new Normal());
game.redLight(new Fastest());
game.blueLight(new Speed() {
@Override
public void blueLight() {
System.out.println("blue light");
}
@Override
public void redLight() {
System.out.println("red light");
}
});
}
}로직 실행 순서
1) BlueLightRedLight가 blueLight(Speed speed) 호출.
2) 전달받은 Speed 구현체의 blueLight() 실행.
(결과 출력: 예: Normal 실행 시 무 궁 화 꽃 이 출력.)
3) 클라이언트에서 동적으로 다른 전략(Faster, Fastest) 실행.
4) 런타임 중 익명 클래스를 활용해 새로운 동작 추가.
바뀐점
-
조건문 제거:
if-else조건문이 사라지고, 각 동작이Speed구현체로 분리되었다.- 코드 가독성과 유지보수성이 향상되었다.
-
확장성 향상:
- 새로운 속도 동작을 추가하려면
Speed인터페이스를 구현하는 클래스만 추가하면 된다. - 기존 코드를 수정할 필요가 없으므로 OCP(개방-폐쇄 원칙)를 만족한다.
- 새로운 속도 동작을 추가하려면
-
유연한 전략 선택:
- 런타임에 전략(속도 동작)을 쉽게 교체하거나 확장할 수 있다.
-
컨텍스트 단순화:
BlueLightRedLight클래스는 특정 동작을 실행할 책임만 가지며, 구체적인 구현에 대해 알지 못한다.
전략 패턴 장단점
장점
- 새로운 전략을 추가하더라도 기존 코드를 변경하지 않는다.
- 상속 대신 위임을 사용할 수 있다.
- 런타임에 전략을 변경할 수 있다.
단점
- 복잡도가 증가한다.
- 클라이언트 코드가 구체적인 전략을 알아야 한다.
전략 패턴, 실무에서는?
1. 자바(Java)에서의 활용
Comparator인터페이스:- 정렬 방식을 동적으로 선택하거나 교체 가능하도록 설계된 전략 패턴의 예.
예제 코드
public class StrategyInJava {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> numbers = new ArrayList<>();
numbers.add(10);
numbers.add(5);
System.out.println("Before Sorting: " + numbers);
// 전략 설정: Comparator.naturalOrder()
Collections.sort(numbers, Comparator.naturalOrder());
System.out.println("After Sorting: " + numbers);
}
}설명
- 전략 패턴 적용:
Collections.sort()는Comparator객체를 받아 정렬 전략을 실행.
- 전략 교체 가능:
- 다양한 정렬 방식(오름차순:
naturalOrder, 내림차순:reverseOrder, 사용자 정의)을 런타임에서 선택 가능.
- 다양한 정렬 방식(오름차순:
2. 스프링(Spring)에서의 활용
ApplicationContext:- 스프링 IoC 컨테이너의 여러 구현체(
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext,FileSystemXmlApplicationContext,AnnotationConfigApplicationContext)가 전략으로 작동.
- 스프링 IoC 컨테이너의 여러 구현체(
PlatformTransactionManager:- JDBC, JPA, Hibernate 등 다양한 트랜잭션 관리 전략을 제공.
예제 코드
public class StrategyInSpring {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 다양한 ApplicationContext 구현체
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext();
ApplicationContext applicationContext1 = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext();
ApplicationContext applicationContext2 = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
// 스프링에서 사용하는 다양한 전략 인터페이스
BeanDefinitionParser parser;
PlatformTransactionManager platformTransactionManager;
CacheManager cacheManager;
}
}설명
-
컨텍스트의 전략적 역할:
ApplicationContext인터페이스를 구현한 다양한 구현체를 사용하여 애플리케이션 환경에 맞는 IoC 컨테이너를 선택 가능.
-
트랜잭션 관리 전략:
PlatformTransactionManager를 통해 JDBC, JPA 등 특정 기술에 종속되지 않고 트랜잭션 관리.
-
캐싱 전략:
CacheManager를 사용해 다양한 캐싱 기술(EhCache, ConcurrentMapCache 등)을 적용.
