실행 중인 하나의 프로그램을 프로세스라고 부른다.
✏️ 스레드란
스레드란, 프로세스 내부에서 코드의 실행 흐름이다.
-
프로세스가 두 가지 이상의 작업을 처리하기 위해 멀티 스레드를 사용한다.
-
멀티 프로세스와 멀티 스레드는 다른 개념이다. 멀티 프로세스는 서로 다른 프로그램을 동시에 여러개 실행하는 것이고, 멀티 스레드는 하나의 프로세스에서 여러 실행 흐름을 생성하는 것이다.
-
멀티 프로세스는 서로 독립적이지만, 멀티 스레드는 서로 종속적이다.
✏️ 메인 스레드
자바의 모든 애플레케이션은 메인 스레드가 main() 메소드를 실행하면서 시작한다.
- 메인 스레드에서 작업 스레드를 여러개 만들어서 병렬로 코드를 실행할 수 있다.
- 실행 중인 스레드가 하나라도 있다면, 메인 스레드가 종료되더라도 프로세스는 종료되지 않는다.
✏️ 스레드의 생성과 실행
자바에서 스레드는 객체로 생성된다.
■ java.lang.Thread 클래스의 인스턴스 생성
Thread thread = new Thread(Runnable target);- Runnable은 인터페이스로, run() 메소드가 선언되어 있다.
- Runnable 인터페이스를 구현하는 구현객체는 run() 메소드를 재정의하여 작업 스레드가 실행할 코드를 작성해야 한다.
- ⚠️ Runnable 구현 객체를 생성했다고 해서 스레드가 만들어 진 것은 아니다. 구현 객체를 인수로 하여 Thread 생성자를 호출했을 때 스레드가 만들어진다.
// Runnable 인터페이스의 구현 클래스 Task
public class Task implments Runnable{
@Override
public void run(){
System.out.println("new thread");
}
}// 메인 스레드
public class Execute{
public static void main(String[] args){
Runnable task = new Task(); // 구현 객체를 생성 후 task에 저장
Thread thread = new Thread(task);
thread.start(); // run() 메소드 실행
System.out.println("main thread");
}
}또는, 다음과 같이 익명 객체로 생성할 수도 있다.
// 메인 스레드
public class Execute{
public static void main(String[] args){
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable(){
@Override
public void run(){
System.out.println("new thread");
}
});
thread.start();
System.out.println("main thread");
}
}■ Thread 클래스의 자식 클래스로 인스턴스 생성
Thread 클래스의 인스턴스를 생성하는 경우, Runnable의 구현 객체로 작업 스레드의 실행 코드를 작성했다.
Thread 클래스를 상속하는 자식 클래스를 만들어서 run() 메소드를 재정의 하면 똑같은 결과를 얻을 수 있다.
// Thread 클래스의 자식 클래스 Task
public class Task extends Thread{
@Override
public void run(){
System.out.println("new thread");
}
}// 메인 스레드
public class Execute{
public static void main(String[] args){
Thread thread = new Task();
thread.start(); // run() 메소드 실행
System.out.println("main thread");
}
}마찬가지로, 위의 코드도 익명 자식 객체를 이용해서 간단하게 바꿀 수 있다.
public class Execute{
public static void main(String[] args){
Thread thread = new Thread(){
@Override
public void run(){
System.out.println("new thread");
}
};
thread.start(); // run() 메소드 실행
System.out.println("main thread");
}
}✏️ 스레드의 이름
개발자가 직접 생성한 스레드는 자동적으로 Thread-n 이라는 이름으로 설정된다.
■ 다른 이름으로 설정
thread.setName("newName");■ 스레드의 이름 알아내기
thread.getName();
// 참조 변수가 없는 경우
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
thread.getName();✏️ 동기화 메소드
멀티 스레드는 객체를 공유해서 작업해야 하는 경우가 있다.
➜ 간섭이 발생할 수 있다.
예를 들어, A 스레드가 memory 필드를 100으로 바꾸고 5초간 sleep 한 후 memory의 값을 출력하려고 한다. A 스레드가 sleep 하는 동안 B 스레드가 memory 필드를 50으로 바꾼다면, A 스레드는 50을 출력하게 된다.
위의 문제를 해결하기 위한 것이 "동기화"이다.
단 하나의 스레드만 실행할 수 있는 코드 영역을 임계 영역이라 한다.
임계 영역을 지정하기 위한 것이 동기화 메소드이다.
// 동기화 메소드는 synchronized 키워드로 선언할 수 있다.
public synchronized void method(){ }
// 메소드 전체가 임계 영역이다.A 스레드가 객체의 동기화 메소드를 실행하면, B는 해당 객체의 일반 메소드만 접근 가능하다. 객체에 존재하는 다른 동기화 메소드에도 접근이 불가능하다.
// 공유 객체 Shared
public class Shared{
private int memory;
public synchronized void setMemory(int memory){
this.memory = memory;
//5초간 sleep
try{
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch(InterruptedException e) {}
// memory 값 출력
System.out.println(this.memory);
}
}// 작업 스레드 A
public class ThreadA extends Thread{
Shared shared = new Shared();
@Override
public void run(){
System.out.println("ThreadA runs");
shared.setMemory(100); // 동기화 메소드를 실행하여 객체를 잠금
}
}// 작업 스레드 B
public class ThreadB extends Thread{
Shared shared = new Shared();
@Override
public void run(){
System.out.println("ThreadB runs");
shared.setMemory(50);
}
}// 메인 스레드
public class mainThread{
public static void main(String[] args){
Thread threadA = new ThreadA();
Thread threadB = new ThreadB();
threadA.start(); // 100 출력
threadB.start(); // 50 출력
}
}✏️ 스레드의 상태
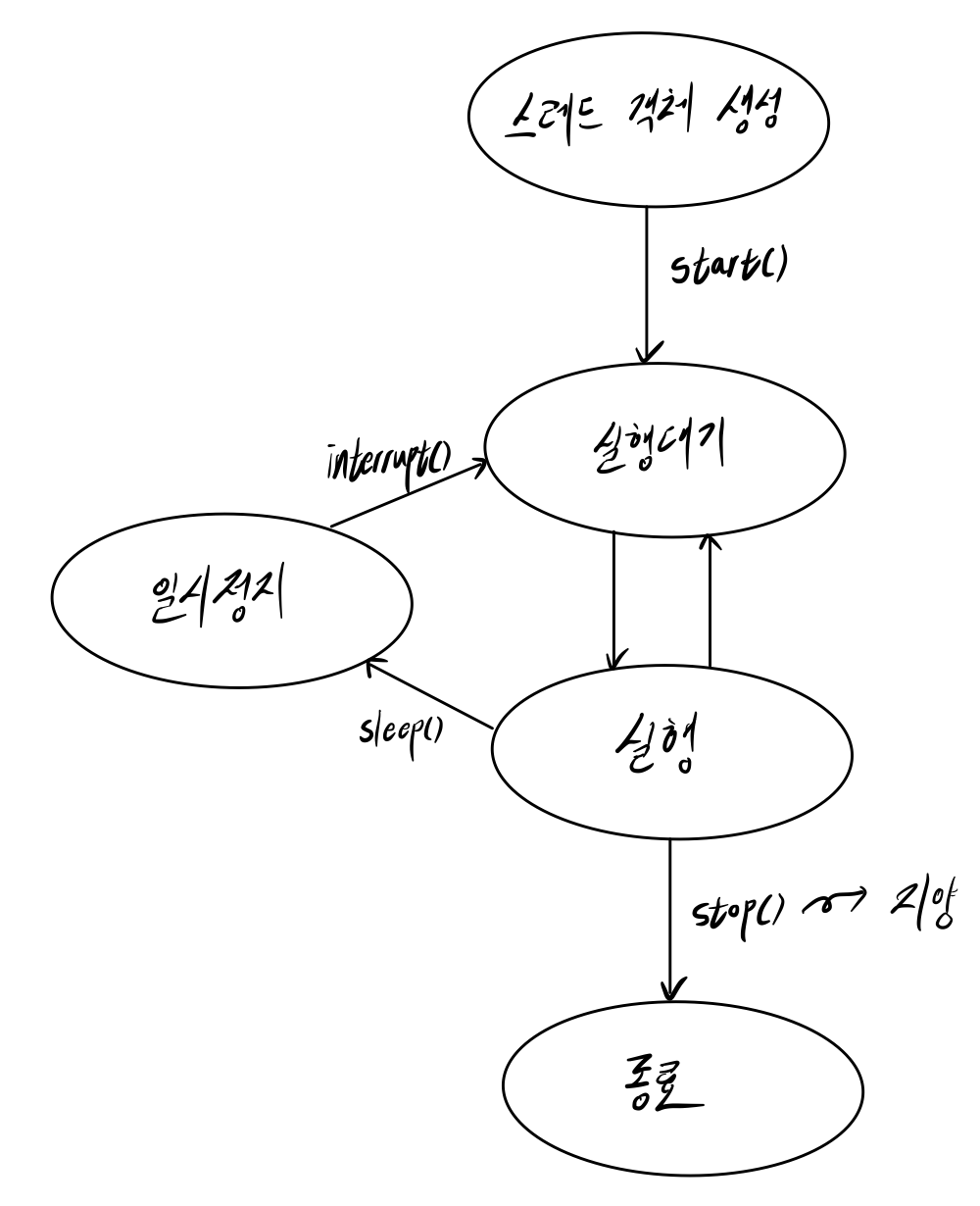
■ 실행대기
- 실행을 기다리는 상태
■ 실행
- run() 메소드를 실행하는 상태
- 실행대기 상태와 실행 상태를 번갈아가면서 run() 코드를 조금씩 실행한다.
■ 일시정지
- 스레드가 일시정지된 상태.
- 일시정지 후에는 자동으로 실행대기 상태로 돌아간다. 실행 상태로는 바로 돌아갈 수 없다.
- 일시정지 상태에서 interrupt() 메소드가 실행되면, 바로 실행대기 상태로 돌아간다.
// 작업 스레드 A
public class ThreadA extends Thread{
try{
while(true){
System.out.println("실행중");
Thread.sleep(1); // sleep중 interrupt() 실행 시, InterruptedException이 발생하여 catch로 넘어감
}
} catch(InterruptedException e){ }
} public class MainThread{
public static void main(String[] args){
Thread threadA = new ThreadA();
thread.start();
//mainThread를 1초간 정지
try{Thread.sleep(1000);} catch(InterruptedExeption e){ }
//sleep중인 threadA를 대기상태로 변환
threadA.interrupt();
}
} ⚠️ 실행대기/실행 상태에서 interrupt() 메소드가 실행되면, 예외가 발생하지 않는다.
미래에 일시 정지 상태가 되면, 그때 InterruptedExcpetion이 발생한다.
✏️ 데몬 스레드
데몬 스레드는 주 스레드의 작업을 돕는 스레드이다.
- ex. 워드프로세서(주 스레드), 자동저장(데몬 스레드)
- 데몬 스레드는 주 스레드가 종료되면 같이 종료된다.
//setDaemon(true)로 해당 스레드를 데몬 스레드로 설정 가능하다.
thread.setDaemon(true);
thread.start();⚠️ 데몬 스레드는 start() 메소드 전에 반드시 setDaemon() 메소드가 실행되어야 한다!!
REFERENCE
혼자 공부하는 자바
