1) JSP란?
실습코드
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>sum10</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
int total = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= 10; i++){
total += i;
}
%>
1부터 10까지의 합 : <%=total %>
</body>
</html><% %>안에 java 코드를 사용할 수 있다.
<%=total%> === out.print(total)
2) JSP 라이프싸이클
jsp 라이프사이클
public void _jspInit() {
}
public void _jspDestroy() {
}
public void _jspService(final javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest request, final javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse response)
throws java.io.IOException, javax.servlet.ServletException {
.....
try {
.....
out.write("\n");
out.write("<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC \"-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN\" \"http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd\">\n");
out.write("<html>\n");
out.write("<head>\n");
out.write("<meta http-equiv=\"Content-Type\" content=\"text/html; charset=UTF-8\">\n");
out.write("<title>sum10</title>\n");
out.write("</head>\n");
out.write("<body>\n");
out.write("\n");
int total = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= 10; i++){
total = total + i;
}스크립틀릿 부분이라고 java 코드를 입력한 부분은 다음과 같이 입력되어 있다.
int total = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= 10; i++){
total = total + i;
}표현식으로 출력한 부분은 다음과 같다.
out.print(total );🔍 JSP의 실행순서
1.브라우저가 웹서버에 JSP에 대한 요청 정보를 전달한다.
2.브라우저가 요청한 JSP가 최초로 요청했을 경우만 JSP로 작성된 코드가 서블릿으로 코드로 변환한다. 👀(java 파일 생성)
3.서블릿 코드를 컴파일해서 실행가능한 bytecode로 변환한다. 👀(class 파일 생성)
4.서블릿 클래스를 로딩하고 인스턴스를 생성한다.
5.서블릿이 실행되어 요청을 처리하고 응답 정보를 생성한다.
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
hello
<%
System.out.println("_jspService()");
%>
<%!
public void jspInit() {
System.out.println("jspInit()!");
}
public void jspDestroy() {
System.out.println("jspDestroy()");
}
%>
</body>
</html>
- 서블릿 라이프 싸이클 - init(), service(), destroy()
- JSP 라이프 싸이클 - _jspInit(), _jspService(), _jspDestroy()
3) JSP 문법
🔍 스크립트 요소의 이해
JSP 페이지에서는 선언문(Declaration), 스크립트릿(Scriptlet), 표현식(Expression) 이라는 3가지의 스크립트 요소를 제공

📍 선언문
- 선언문 : <%! %>
- 선언문은 JSP 페이지 내에서 필요한 멤버변수나 메소드가 필요할 때 선언해 사용하는 요소
- 선언문의 문법
- <%! 문장 %>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
id : <%=getId() %>
</body>
</html>
<%!
String id = "u001"; //멤버변수 선언
public String getId( ) { //메소드 선언
return id;
}
%>📍 스크립트릿
- 스크립트릿 : <% %>
- 가장 일반적으로 많이 쓰이는 스크립트 요소
- 주로 프로그래밍의 로직을 기술할 때 사용
- 스크립트릿에서 선언된 변수는 지역변수
- 스크립트릿의 문법
- <% 문장%>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
for(int i = 1; i <= 5; i++){
%>
<H<%=i %>> 아름다운 한글 </H<%=i %>>
<%
}
%>
</body>
</html>
코드에서 아름다운한글 부분을 보면 <% } %> 이런 식으로 따로 줄수도 있으며, html 태그도 위처럼 같이 사용할 수 있다.
📍 표현식(Expression)
- 표현식 : <%=%>
- JSP 페이지에서 웹 브라우저에 출력할 부분을 표현 (즉, 화면에 출력하기 위한 것)
- 스크립트릿내에서 출력할 부분은 내장객체인 out 객체의 print() 또는 println() 메소드를 사용해서 출력
- 표현식의 문법
- <%=문장%>
🔍주석(Comment)
1. HTML 주석
- HTML 주석은
<!--로 시작해서 -->로 끝나는 형태 - HTML 주석은 HTML주석을 사용한 페이지를 웹에서 서비스할 때 화면에 주석이 내용이 표시되지는 않으나 , [소스보기]수행하면 HTML주석의 내용이 화면에 표시.
HTML주석의 예시
<!-- html 주석입니다. -->2. JSP주석
- JSP 페이지에서만 사용되며
<%--로 시작해서 --%>로 끝나는 형태 - JSP 주석은 해당 페이지를, 웹 브라우저를 통해 출력 결과로서 표시하거나, 웹 브라우저 상에서 💡소스 보기를 해도 표시 되지 않음. 또한 JSP주석 내에 실행코드를 넣어도 그 코드는 실행되지 않는다.
JSP주석의 예시
<%-- JSP 주석입니다. --%>3. 자바주석
- 자바 주석은
//, /**/을 사용해서 작성. //은 한 줄짜리 주석을 작성할 때 사용되고,/**/은 여러 줄의 주석을 작성할 때 사용- 스크립트릿이나 선언문에서 사용되는 주석으로, 자바와 주석 처리 방법이 같음
자바주석의 예시
//주석
/*주석
여러 줄에 걸친 주석이다.
*/
4) JSP 내장객체
🔍 JSP 내장 객체란?
- JSP를 실행하면 서블릿 소스가 생성되고 실행된다.
- JSP에 입력한 대부분의 코드는 생성되는 서블릿 소스의
_jspService()메소드 안에 삽입되는 코드로 생성된다.
-_jspService()에 삽입된 코드의 윗부분에 미리 선언된 객체들이 있는데, 해당 객체들은 jsp에서도 사용 가능하다. - 💡
response,request,application,session,out과 같은 변수를 내장객체라고 한다.
🔍 내장 객체의 종류
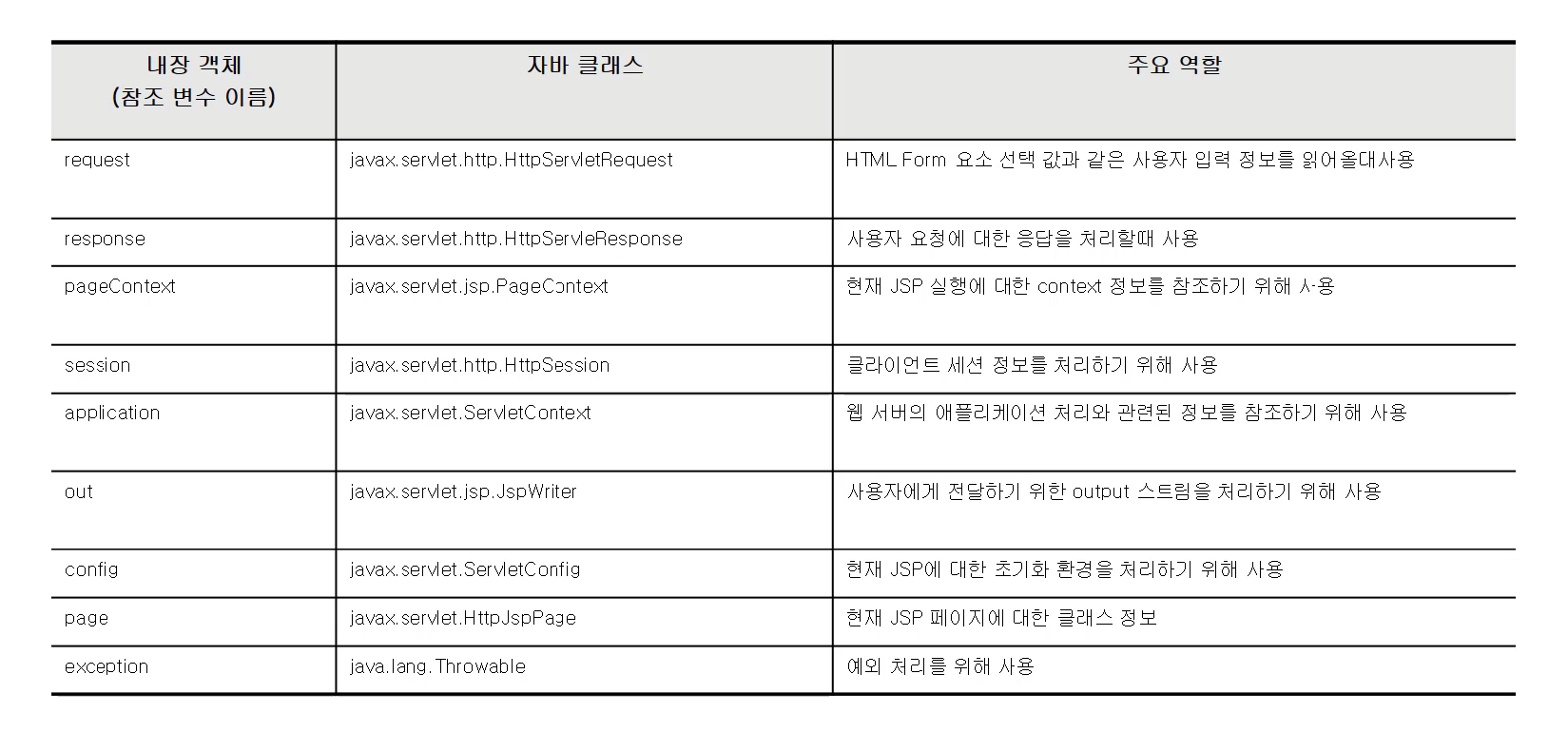
<body>
<%
StringBuffer url = request.getRequestURL();
out.println("url : " + url.toString());
out.println("<br>");
%>request와 out은 내장 객체 이므로 변수를 선언 하지 않아도 오류없이 사용할 수 있다.
