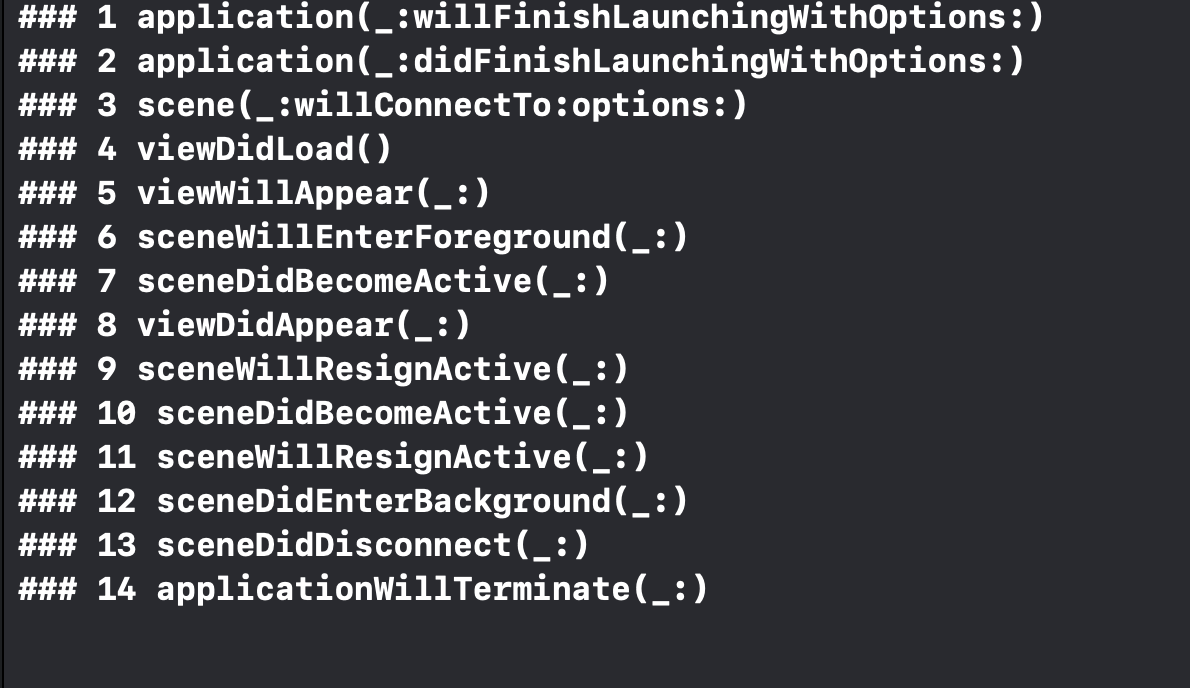
✅목록
- AppDelegate
- SceneDelegate
- View LifeCycle
- 코드 출력
1. AppDelegate
- App의 데이터 구조 초기화
- App의 Scene에 대한 Configuration( 환경설정 )
- App 밖에서 오는 알림에 대응( ex: 배터리 부족, 다운로드 완료 )
- App 자체를 targeting하는 이벤트에 대응( 특정 View, ViewController, Scene ❌ )
- 실행시 요구되는 Service 등록( ex: Apple Push Notification Center )
- SceneSession을 통해 Scene에 대한 정보를 업데이트 받는다.
import UIKit
// App 단위의 설정을 관리하거나 Event에 대응
@main
class AppDelegate: UIResponder, UIApplicationDelegate {
// 2
// App 자체에 대한 각종 setup을 진행. launch시 호출
func application(_ application: UIApplication, didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplication.LaunchOptionsKey: Any]?) -> Bool {
// Override point for customization after application launch.
LifeCycle.addCount()
print("### \(LifeCycle.count) \(#function)")
return true
}
func application(_ application: UIApplication, willFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplication.LaunchOptionsKey: Any]? = nil) -> Bool {
LifeCycle.addCount()
print("### \(LifeCycle.count) \(#function)")
return true
}
func applicationWillEnterForeground(_ application: UIApplication) {
// Application이 Foreground로 진입하는 상태
LifeCycle.addCount()
print("### \(LifeCycle.count) \(#function)")
}
func applicationWillResignActive(_ application: UIApplication) {
// Application이 Background로 진입하는 과정 중 일부로,
// Active상태를 벗어날 때를 의미한다. 이때, inActive상태를 거쳐간다.
LifeCycle.addCount()
print("### \(LifeCycle.count) \(#function)")
}
func applicationDidEnterBackground(_ application: UIApplication) {
// Application이 Background로 진입하는 상태.
// 앱이 종료된 것은 아니며, 메모리를 차지하고 있다. 마무리 작업을 한다.
// 전화가 올 때처럼 interrupt에 의해 Background로 진입할 수 있다.
LifeCycle.addCount()
print("### \(LifeCycle.count) \(#function)")
}
func applicationDidBecomeActive(_ application: UIApplication) {
// Background상태에서 다시 Active상태가 될 때를 의미한다.
// 이때, inActive상태를 거쳐간다.
LifeCycle.addCount()
print("### \(LifeCycle.count) \(#function)")
}
func applicationWillTerminate(_ application: UIApplication) {
// Background상태에서 메모리를 반납하고 종료된다.
// 너무 오래 Background상태에서만 머물고 있으면 OS에 의해 Terminate 된다.
LifeCycle.addCount()
print("### \(LifeCycle.count) \(#function)")
}
// MARK: UISceneSession Lifecycle
// App launch가 아닌, 새로운 scene/window를 제공할 때 불리는 메소드.
func application(_ application: UIApplication, configurationForConnecting connectingSceneSession: UISceneSession, options: UIScene.ConnectionOptions) -> UISceneConfiguration {
// Called when a new scene session is being created.
// Use this method to select a configuration to create the new scene with.
return UISceneConfiguration(name: "Default Configuration", sessionRole: connectingSceneSession.role)
}
// 사용자가 scene을 폐기할 때 호출되는 메소드
func application(_ application: UIApplication, didDiscardSceneSessions sceneSessions: Set<UISceneSession>) {
// Called when the user discards a scene session.
// If any sessions were discarded while the application was not running, this will be called shortly after application:didFinishLaunchingWithOptions.
// Use this method to release any resources that were specific to the discarded scenes, as they will not return.
}
}2. SceneDelegate
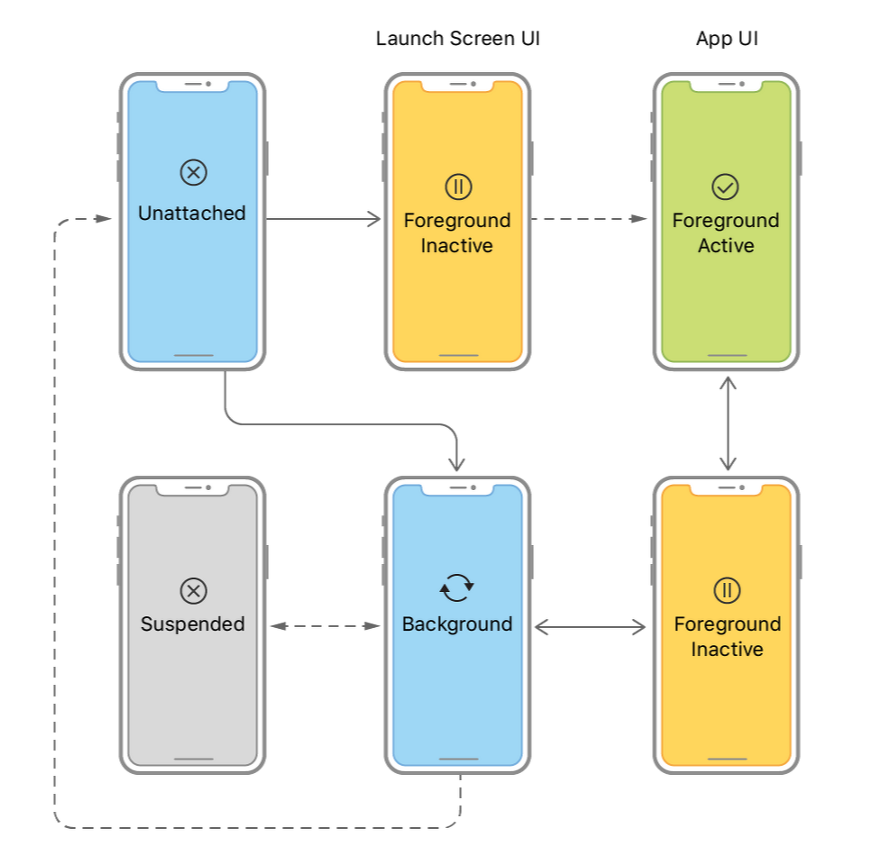
- UI의 상태를 알 수 있는 UILifeCycle을 관리하는 역할
- Unattached: scene이 연결되지 않은(unattached) 상태
- Foreground: 사용자가 ‘현재 집중’하고 있는 앱 상태
- Inactivive: App이 실행중이며 이벤트를 받지 않은 상태
- Active: App이 실행중이며 이벤트를 받은 상태
- Background : 사용자에게 보이지 않지만 여전히 실행 중 상태
- Suspended: Background에 있고, 실행되는 code가 없는 상태
- Not Running : 실행되지 않은 상태
import UIKit
// Scene LifeCycle을 관리
class SceneDelegate: UIResponder, UIWindowSceneDelegate {
var window: UIWindow?
/*
Unattached : scene이 연결되지 않은(unattached) 상태
Active : App이 실행중이며 이벤트를 받은 상태
Inactivive : App이 실행중이며 이벤트를 받지 않은 상태
Suspended : Background에 있고, 실행되는 code가 없는 상태
*/
func scene(_ scene: UIScene, willConnectTo session: UISceneSession, options connectionOptions: UIScene.ConnectionOptions) {
guard let _ = (scene as? UIWindowScene) else { return }
LifeCycle.addCount()
print("### \(LifeCycle.count) \(#function)")
// = 새로운 UIWindow를 생성하여 scene에 연결하고, rootViewController를 설정.
// Storyboard를 사용하면 자동으로 초기화 되며, 그렇지 않을 때는 이곳에서 추가 설정이 필요.
// 보통 code로 UI를 짤 때, 첫 view를 만들 때 쓰임.
}
func sceneWillEnterForeground(_ scene: UIScene) {
LifeCycle.addCount()
print("### \(LifeCycle.count) \(#function)")
// = scene이 background → foreground(혹은 처음 active)로 전환될 때 호출되는 메소드.
// background상태로 돌입할 때의 변화들을 다시 원상복귀 시키는 작업을 한다.
}
func sceneDidBecomeActive(_ scene: UIScene) {
LifeCycle.addCount()
print("### \(LifeCycle.count) \(#function)")
// = inactive → active상태로 scene이 돌입할 때 호출되는 메소드
// scene이 inactive되면서 멈춰있었던 작업들은 다시 시작하는 작업을 한다.
}
func sceneWillResignActive(_ scene: UIScene) {
LifeCycle.addCount()
print("### \(LifeCycle.count) \(#function)")
// = scene이 active → inactive 상태로 빠질 때 호출된다
// 추가로, 이러한 전환은 interrupt에 의해 일어날 수 있다(ex) 전화가 왔을 때)
}
func sceneDidEnterBackground(_ scene: UIScene) {
LifeCycle.addCount()
print("### \(LifeCycle.count) \(#function)")
// = scene이 foreground → background 상태로 돌입할 때 호출된다.
// data를 저장하고, 공유 중이던 자원을 돌려주거나
// 다시 scene이 foreground로 돌입할 때 필요한 data들을 처리하는 작업을 한다.
}
func sceneDidDisconnect(_ scene: UIScene) {
LifeCycle.addCount()
print("### \(LifeCycle.count) \(#function)")
// = scene이 폐기되거나 background상태에 들어갈 때 호출되는 메소드.
// scene이 사용하던 자원을 돌려주는 작업을 한다.
// scene은 폐기될 필요가 없다면 다시 연결될 수 있다.(disconnect는 app 종료와는 다른 개념임.)
}
}3. View LifeCycle
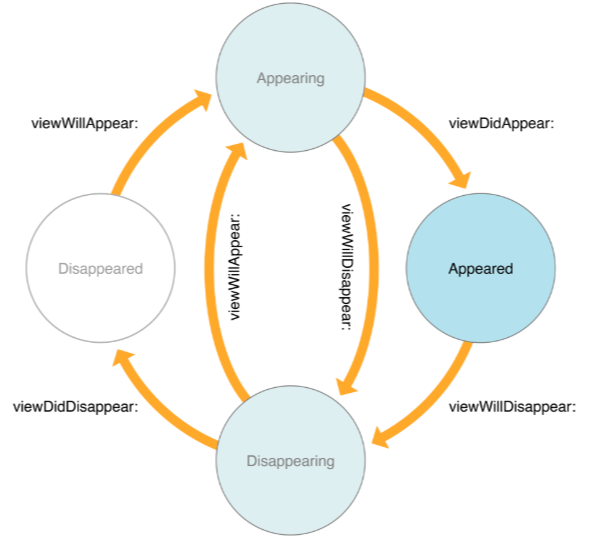
import UIKit
class ViewController: UIViewController {
/*
Appearing : 보여지는 상태
Appeared : 보여진(완료된) 상태
Disappearing : 사라지는 상태
Disappeared : 사라진(완료된) 상태
*/
// 처음 생성될 때 한 번만 호출
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
LifeCycle.addCount()
print("### \(LifeCycle.count) \(#function)")
}
// 화면에 보여지기 시작할 때
override func viewWillAppear(_ animated: Bool) {
LifeCycle.addCount()
print("### \(LifeCycle.count) \(#function)")
}
// 화면에 보여진 후(View 계층에 추가된 후)
override func viewDidAppear(_ animated: Bool) {
LifeCycle.addCount()
print("### \(LifeCycle.count) \(#function)")
}
// 화면에서 사라지기 시작할 때(View 계층에 제거되기 전)
override func viewWillDisappear(_ animated: Bool) {
LifeCycle.addCount()
print("### \(LifeCycle.count) \(#function)")
}
// 화면에서 사라진 뒤(View 계층에서 제거된 후)
override func viewDidDisappear(_ animated: Bool) {
LifeCycle.addCount()
print("### \(LifeCycle.count) \(#function)")
}
}4. 코드 출력
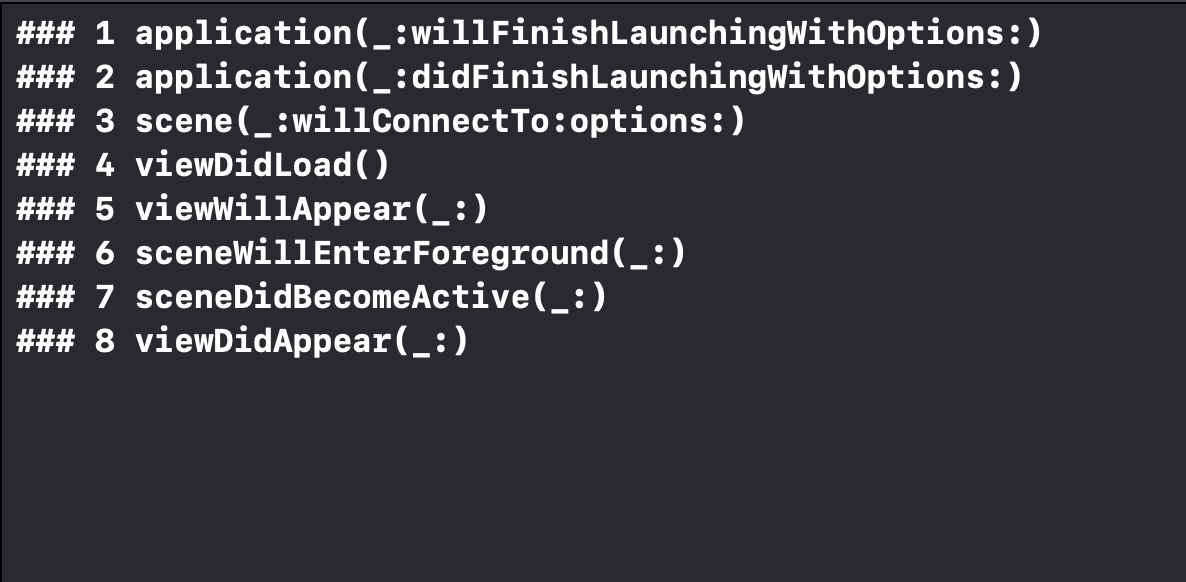
-
첫 화면이 나타날 때 콘솔 출력
-
BackGround로 진입할 때 콘솔 출력
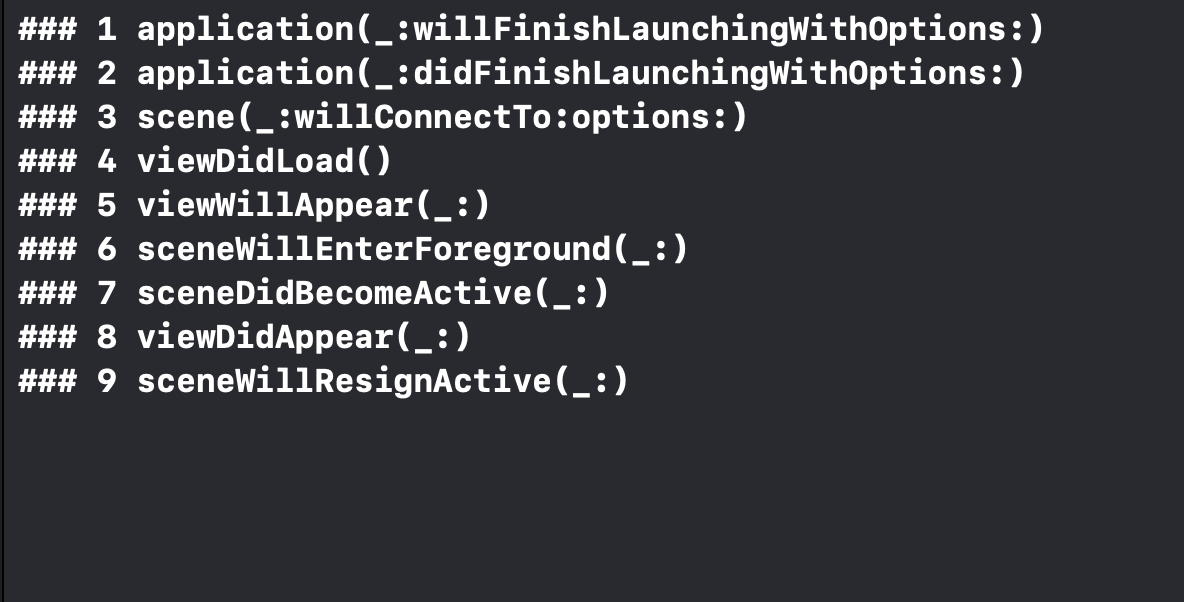
-
다시 ForeGround로 진입할 때 콘솔 출력
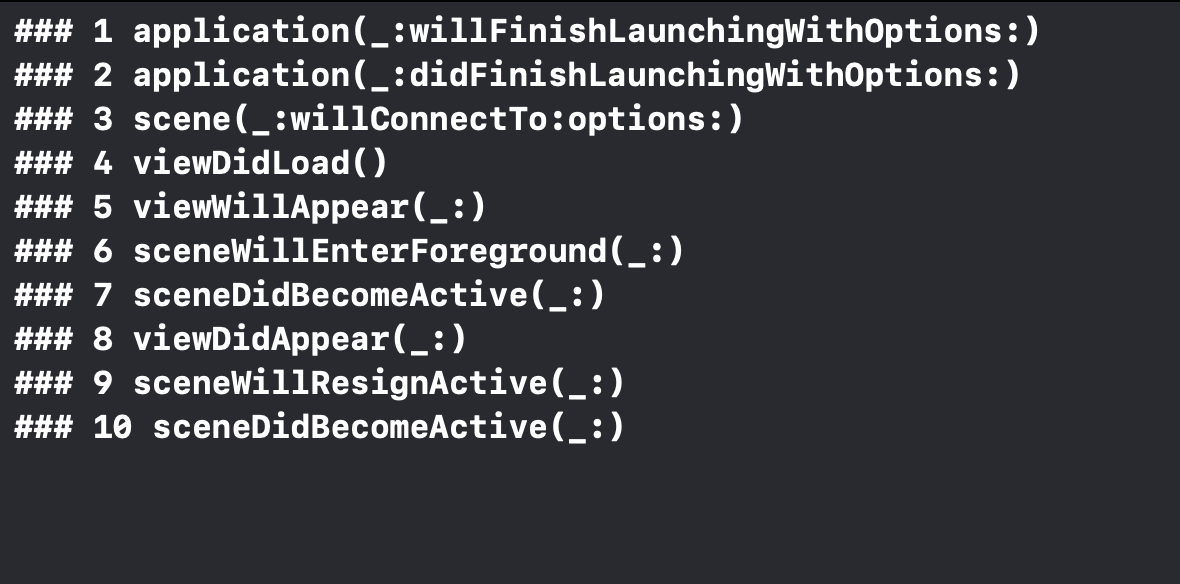
-
앱이 종료될 때 콘솔 출력