Microsoft Azure is a cloud computing platform with an ever-expanding set of services to help building solutions to meet one's business goals.
AZ-900 Domain Area
- Describe cloud concepts 25-30%
- Describe Azure architecture and services 35-40%
- Describe Azure management and governance 30-35%
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services over the internet.
(Virtual Machine, storage, databases, networking ... - IT infrastructure)
+++ expand to (IoT, Machine Learning, Artificial Intelligence)
Shared responsibility model
The shared responsibility model is heavily tied into the cloud service types (covered later in this learning path):
infrastructure as a service (IaaS),
platform as a service (PaaS),
and software as a service (SaaS).

You(Customer)’ll always be responsible for:
- The information and data stored in the cloud
- Devices that are allowed to connect to your cloud (cell phones, computers, and so on)
- The accounts and identities of the people, services, and devices within your organization
The cloud provider is always responsible for:
- The physical datacenter
- The physical network
- The physical hosts
Your service model will determine responsibility for things like:
- Operating systems
- Network controls
- Applications
- Identity and infrastructure
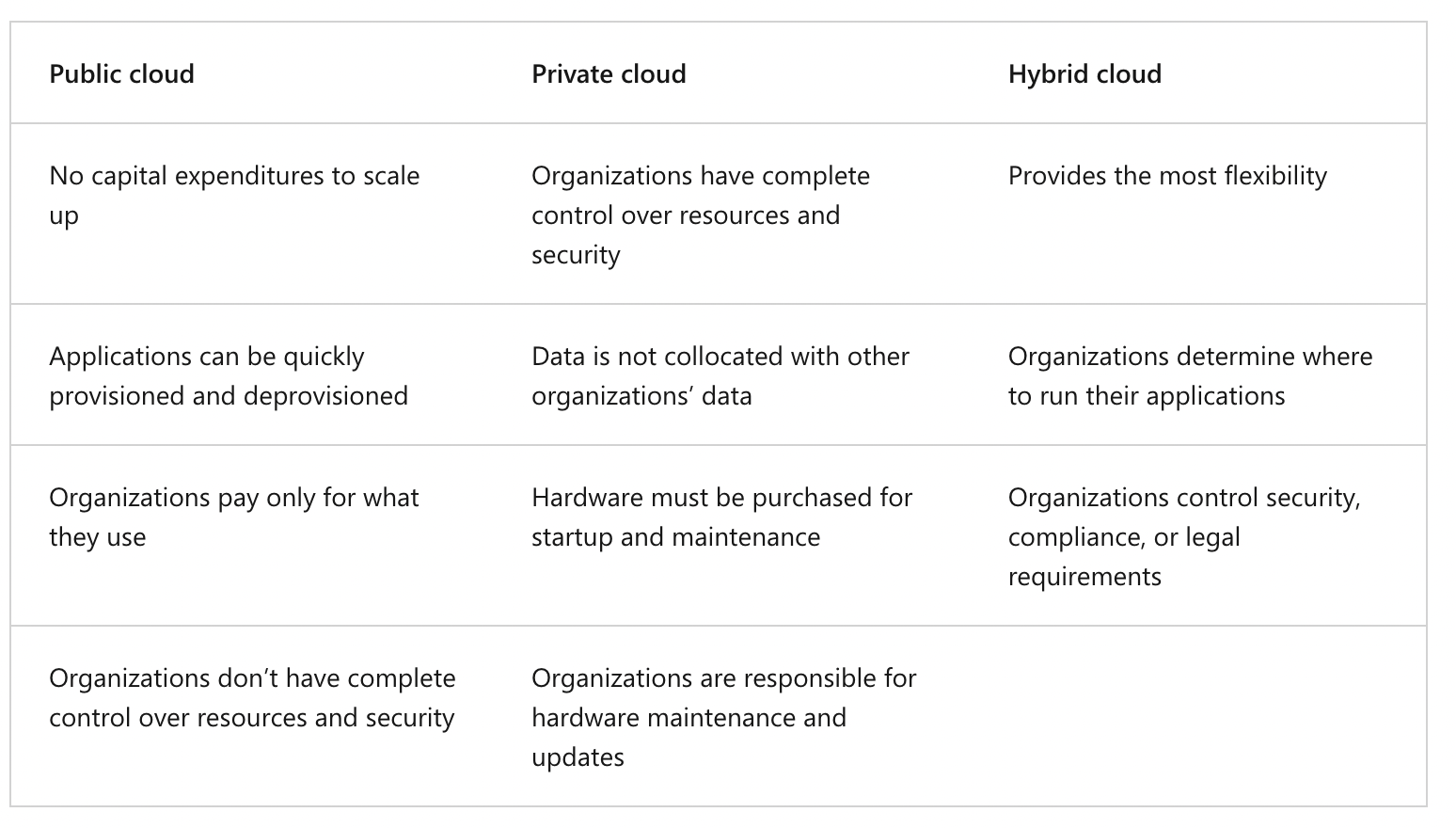
Cloud models
The cloud models define the deployment type of cloud resources.
The three main cloud models are: private, public, and hybrid.
- Private Cloud
• Organizations create a cloud environment in their datacenter.
• Organization is responsible for operating the services they provide.
• Does not provide access to users outside of the organization. - Public Cloud
• Owned by cloud services or hosting provider.
• Provides resources and services to multiple organizations and users.
• Accessed via secure network connection (typically over the internet). - Hybrid Cloud
• Combines Public and Private clouds to allow applications to run in the most appropriate location.
• Which cloud model uses some datacenters focused on providing cloud services to anyone that wants them, and some data centers that are focused on a single customer?

Q. Which cloud model allows an organization to shut down its data center if it hosts its infrastructure there?
A. Public CloudAn organisation can close its DC by hosting its infrastructure in a public cloud. The public cloud is defined as computing services offered by third-party providers over the public Internet, making them available to anyone who wants to use or purchase them. The private cloud is defined as computing services offered either over the Internet or a private internal network and only to select users instead of the general public. A private cloud can be deployed on-premise or in a third-party hosted environment. A hybrid cloud combines the use of both public and private clouds.
Q. A company has distributed its workload on both the Azure Cloud and some on-premises servers. What type of architecture is this?
A. Hybrid Cloud
the consumption-based model
two types of expenses to consider.
Capital expenditure (CapEx)
and operational expenditure (OpEx).
Capital Expenditure (CapEx)
• The one-time, up-front spending of money on physical infrastructure
• Costs from CapEx have a value that reduces over time
ex) A new building, repaving the parking lot, building a datacenter, or buying a company vehicle
Operational Expenditure (OpEx)
• Spend on products and services as needed, payas-you-go
• Get billed immediately
ex) Renting a convention center, leasing a company vehicle, or signing up for cloud services
Cloud service providers operate on a consumption-based model, which means
that end users only pay for the resources that they use.
the benefits of using cloud services
Cloud Benefits
- High Availability(HA)
• it’s important the resources are available when needed.
• Azure is a highly available cloud environment with uptime guarantees depending on the service. These guarantees are part of the service-level agreements (SLAs).
• Ability of a system to remain operational to users during planned or unplanned outages(중단).
- Scalability
• The ability to scale Vertically (up or down), and horizontally (in or out)
• Vertical scaling is focused on increasing or decreasing the capabilities of resources.
• Horizontal scaling is adding or subtracting the number of resources.
- Elasticity
• The ability to scale automatically
- Reliability
• Reliability is the ability of a system to recover from failures and continue to function
• With a decentralized design, the cloud enables you to have resources deployed in regions around the world.
- Predictability
• Predictability can be focused on performance predictability or cost predictability.
- Security
• you can find a cloud solution that matches your security needs.
- Governance
• By establishing a good governance footprint early, you can keep your cloud footprint updated, secure, and well managed.
- Manageability
• Management of the cloud speaks to managing your cloud resources.
