Process
실행중인 프로그램을 의미 (a program in execution)
- 프로그램을 실행하면 OS로부터 실행에 필요한 자원(메모리)를 할당받아 프로세스가 된다.
- 프로세스는 자원(프로그램을 수행하는 데 필요한 데이터와 메모리)과 쓰레드로 구성된다.
- 모든 프로세스에는 최소 1개 이상의 쓰레드가 존재한다.
- 프로세스가 둘 이상의 쓰레드를 가질 경우 multi-threaded process라고 부른다.
싱글쓰레드 = 자원 + 쓰레드
멀티쓰레드 = 자원 + 쓰레드 + 쓰레드 + ...
Thread
- 프로세스의 자원을 이용해서 실제로 작업을 수행하는 것
※ 경량 프로세스(LWP, light-weight process)라고 부르기도 한다. - 한 번 종료된 쓰레드는 다시 실행할 수 없다.
→ 하나의 쓰레드에 대해 start()를 두 번 이상 호출하면 IllegalThreadStateException이 발생한다. - 모든 쓰레드는 독립적인 작업을 수행하기 위한 자신만의 호출스택을 필요로 한다.
→ call stack은 thread가 생성될 때마다 생성되고, 종료시 함께 소멸된다.
→ 생성된 call stack들은 스케줄러가 정한 순서에 의해 번갈아 가며 실행된다.
→ 실행중인 user thread가 하나도 없다면 프로그램은 종료된다.📌 java에서 main 메서드를 실행하기 위해서도 main 쓰레드가 필요하다. 프로그램이 실행되면 main 쓰레드가 기본적으로 생성되고, main 쓰레드가 main 메서드를 호출함으로써 작업이 수행될 수 있다.
Thread 활용하기
Thread는 Thread 클래스를 상속 받거나 Runnable인터페이스를 implement 함으로써 구현할 수 있다.
1. Thread 클래스의 상속
class MyThread extends Thread { public void run() {...} }2. Runnable 인터페이스 구현
class MyThread implements Runnable { public void run() {...} }-
Runnable 인터페이스를 사용하면 재사용성(reusability)이 높고 코드의 일관성을 유지할 수 있다.
Runnable 인터페이스: 추상메서드인 run()만 정의되어 있는 인터페이스이다.
public interface Runnable { public abstract void run(); }
- Runnable 인터페이스를 구현한 클래스의 인스턴스를 생성하고, 그 인스턴스를 Thread 클래스 생성자의 매개변수로 제공해야 한다.
Thread thread = new Thread(new ThreadExample());
실습 코드
public class ThreadExample implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
// static Thread currentThread(): 현재 실행중인 쓰레드의 참조를 반환
// String getName(): 쓰레드의 이름을 반환
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
}
class Main {
public static void main (String[] args) {
Thread threadA =new Thread(new ThreadExample());
Thread threadB =new Thread(new ThreadExample());
Thread threadC =new Thread(new ThreadExample());
threadA.start(); // start(): 쓰레드 실행
threadB.start();
threadC.start();
}
}실행결과
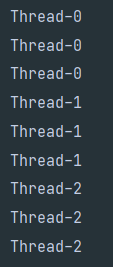
위의 코드에서 start()가 아닌 run()을 호출한다면, 생성된 쓰레드가 실행되는 것이 아니라 클래스에 선언된 메서드가 호출된다.
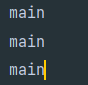
따라서 새로운 쓰레드가 작업하는데 필요한 call stack을 생성한 다음에 run()을 호출하기 위해서는 쓰레드를 실행시키는 명령어인 start()를 사용해야 한다.
Source
- 자바의 정석 (남궁성 저)
