
Promise란?
비동기를 간편하게 처리하는 데 도움을 주는 오브젝트이다. 들어가기에 앞서, 다음 개념을 보자.
- Producing code: 정보를 전달하는 코드. ex) 네트워크에서 사용자 데이터를 로드하는 코드
- Consuming code: producing code가 전달한 정보를 받는 코드. ex) 로드된 사용자 데이터를 받는 코드
- Promise: producing code와 consumer code를 연결하는 자바스크립트 객체. promise는 subscribed code(consumer) 에게 모든 정보가 전달될 것이라는 '약속'을 함.
Promise 객체의 생성자를 보자.
let promise = new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
//executor
}여기서 resolve와 reject는 자바스크립트 자체에서 제공되는 콜백들이다. executor가 결과를 받아오면, 다음 중 한 가지를 호출한다.
resolve(value)- 성공시reject(errror)- 실패시
Promise를 만드는 순간 이 콜백 중 하나가 바로 실행된다.
When new Promise is constructed, the executor runs automatically.
new Promise 생성자에 의해 만들어진 promise 객체는 다음과 같은 properties 를 가지고 있다.
state: 'pending' → either 'fulfilled'(성공시) or 'rejected'(실패시)result: 'undefined → either 'value'(성공시) or 'error'(실패시)
ex)
let promise = new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
//the function is executed automatically when the promise is construnctored
setTimeout(() => resolve("done"),1000);
}state: "pending" → "fulfilled"
result: undefined → "done"
이번에는 에러가 발생하여 reject되는 Promise 를 만들어 보자.
let promise = new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
//the function is executed automatically when the promise is construnctored
setTimeout(() => reject(new Error("Error!")),1000);
}state: "pending" → "rejected"
result: undefined → error
Consumers: then, catch, finally
Consumer 함수들은 .then, .catch, .finally를 사용해 subscribed 될 수 있다.
promise
.then(result => console.log(result), //when the promise is resolved
error => console.log(error)//when the promise is rejected
)
.catch(error => {
console.log(error);
})
.finally(() => {
// always execute at last
// finally is a good handler for performing cleanup, e.g. stopping our loading indicators as they are not needed anymore
console.log('finally');
})
then, catch, finally는 위 예시처럼 chaining될 수도 있고, 따로따로 사용할 수도 있다.
Example: loadScript
callback 기반으로 짜여진 다음 코드를 보자.
function loadScript(src, callback) {
let script = document.createElement('script');
script.src = src;
script.onload = () => callback(null, script);
script.onerror = () => callback(new Error(`Script load error for ${src}`));
document.head.append(script);
}이를 Promise를 사용해 바꿔보자.
function loadScript(src) {
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject)){
let script = document.createElement('script');
script.src = src;
script.onload = () => resolve(script) ;
script.onerror = () => reject(new Error(`Script load error for ${src}`));
document.head.append(script);
});
}let promise = loadScript("https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/lodash.js/4.17.11/lodash.js");
promise.then(
script => alert(`${script.src} is loaded`),
error => alert('Error')
);
promise.then(script => alert('Another handler...'));마음의 평화가 찾아온다!✨
Promises chaining
ex)
const fetchNumber = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => resolve(1),1000);
})
fetchNumber
.then(num => num*2)
.then(num => num*3)
.then(num => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => resolve(num-1),1000);
})
})
.then(num => console.log(num));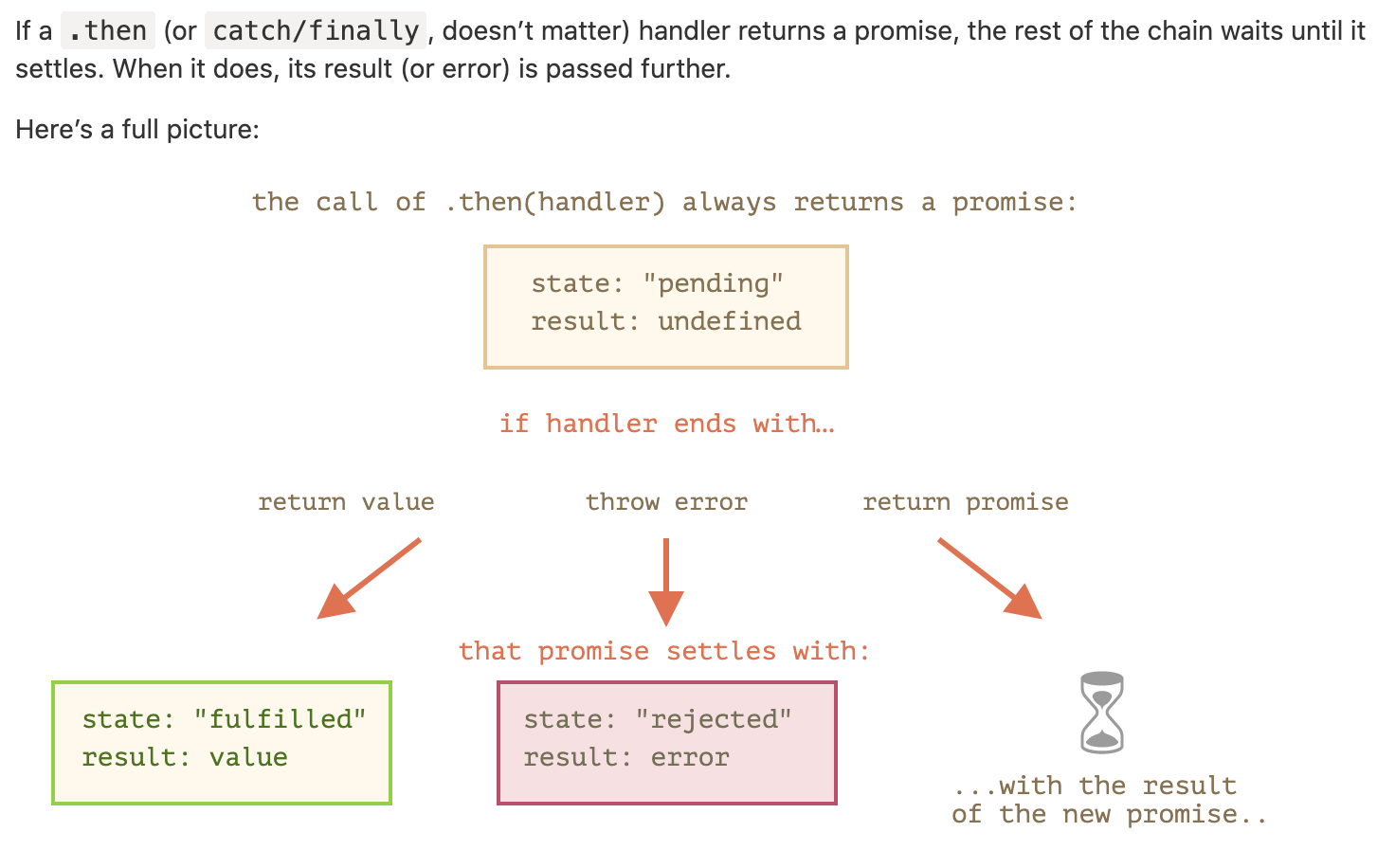
.jpeg)