퍼지스트링이란
1. Fuzzy string
근접 문자열 매칭 (Approximate String Matching)
- 유사한 문자열을 찾는 기술
- 근접 문자열 매칭의 응용 사례 : Query spell-checking
- 오류가 포함된 사용자 질의를 자동으로 교정하여 제시해 주는 기능 (예를 들어, 구글의 "이것을 찾으셨나요?")
-
기본 형식 : 불러오기
require 'fuzzystringmatch' jarow=FuzzyStringMatch::JaroWinkler.create( :native) p jarow.getDistance("jones", "johnson") 'jones'와 'johnson'의 단어 유사도 차이를 알 수 있음. jarow.getDistance( "al", "al" ) => 1.0 irb(main):004:0> jarow.getDistance( "dixon", "dicksonx" ) jarow.getDistance( "dixon", "dicksonx" ) => 0.8133333333333332
-
fuzzystring의 원리를 코드 구현
import numpy as np def levenshtein_ratio_and_distance(s, t, ratio_calc = False): """ levenshtein_ratio_and_distance: Calculates levenshtein distance between two strings. If ratio_calc = True, the function computes the levenshtein distance ratio of similarity between two strings For all i and j, distance[i,j] will contain the Levenshtein distance between the first i characters of s and the first j characters of t """ # Initialize matrix of zeros rows = len(s)+1 cols = len(t)+1 distance = np.zeros((rows,cols),dtype = int) # Populate matrix of zeros with the indeces of each character of both strings for i in range(1, rows): for k in range(1,cols): distance[i][0] = i distance[0][k] = k # Iterate over the matrix to compute the cost of deletions,insertions and/or substitutions for col in range(1, cols): for row in range(1, rows): if s[row-1] == t[col-1]: cost = 0 # If the characters are the same in the two strings in a given position [i,j] then the cost is 0 else: # In order to align the results with those of the Python Levenshtein package, if we choose to calculate the ratio # the cost of a substitution is 2. If we calculate just distance, then the cost of a substitution is 1. if ratio_calc == True: cost = 2 else: cost = 1 distance[row][col] = min(distance[row-1][col] + 1, # Cost of deletions distance[row][col-1] + 1, # Cost of insertions distance[row-1][col-1] + cost) # Cost of substitutions if ratio_calc == True: # Computation of the Levenshtein Distance Ratio Ratio = ((len(s)+len(t)) - distance[row][col]) / (len(s)+len(t)) return Ratio else: # print(distance) # Uncomment if you want to see the matrix showing how the algorithm computes the cost of deletions, # insertions and/or substitutions # This is the minimum number of edits needed to convert string a to string b return "The strings are {} edits away".format(distance[row][col]) -
partial_ratio
from thefuzz import fuzz,process s1="Just a test" s2="Just a test and some more" print(fuzz.partial_ratio(s1,s2)) 100 -
token_sort_ratio 예시
- token_sort_ratio는 단어를 토큰화해서 정렬했을때 ratio
from thefuzz import fuzz,process s1="Hello World is what I want to tell you" s2="What I want to tell you is Hello World" print(fuzz.ratio(s1,s2)) print(fuzz.partial_ratio(s1,s2)) print(fuzz.token_sort_ratio(s1,s2)) 61 61 100 -
token_set_ratio 예시
- token_set_ratio는 단어를 list에서 set을 했을 때처럼 uniq하게 요소를 만들어서 비교를 함.
from thefuzz import fuzz,process s1="Hello World" s2="Hello Hello World World World" print(fuzz.ratio(s1,s2)) print(fuzz.partial_ratio(s1,s2)) print(fuzz.token_sort_ratio(s1,s2)) print(fuzz.token_set_ratio(s1,s2)) 55 64 55 100 [](https://www.notion.so/8fcecbb95e65428c9353d1caa382a690) -
process.extract,process.extractOne 예시
- token_set_ratio는 단어를 list에서 set을 했을 때처럼 uniq하게 요소를 만들어서 비교를 함.
from thefuzz import fuzz,process things =["Programming Language","Native Language","React Native","Some Stuff","Hello World","Coding and Stuff"] print(process.extract("lang",things,limit=2)) print(process.extractOne("lang",things) # 여기에는 limit를 적어주지 않는다. 왜냐하면 One이 limit=1이기 때문 [('Programming Language',90),('Native Language',90)] ('Native Language',90) -
process.extract,process.extract 예시2
from thefuzz import fuzz,process books =[ "The Python Bible Volume 1 - Beginner","The Python Bible Volume 2 - Intermediate","The Python Bible Volume 3 - Data Science","The Python Bible Volume 4 - Matching Learning","The Python Bible Volume 5 - Finance","The Python Bible Volume 6 - Neural Net"] print(process.extract("python data science",books,limit=3)) [("The Python Bible Volume 1 - Beginner",86),(,"The Python Bible Volume 2 - Intermediate",86)] ('The Python Bible Volume 3 - Data Sciencee',100)
2. **Levenshtein (Edit) distance**
-
**Levenshtein에 대해서**
Levenshtein distance 는 한 string s1을 s2
로 변환하는 최소 횟수를 두 string 간의 거리로 정의합니다.
- PARTY와 PARK가 있다고 가정했을 때
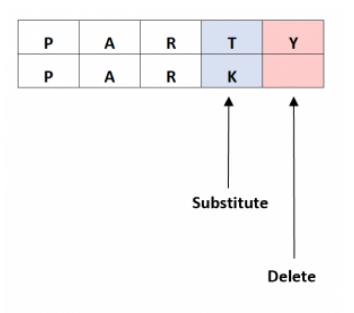
두 단어 간 Levenshtein에서의 거리는 이와 같이 Subtitute와 Delete가 된다.
from Levenshtein import distance as lev lev('party', 'park')위의 lev의 결과 값은 2가 된다.
-
리스트 안에서 요소간의 distance값을 바로 돌린 경우
#define arrays a = ['Mavs', 'Spurs', 'Lakers', 'Cavs'] b <- ['Rockets', 'Pacers', 'Warriors', 'Celtics'] #calculate Levenshtein distance between two arrays for i,k in zip(a, b): print(lev(i, k))- The Levenshtein distance between ‘Mavs’ and ‘Rockets’ is 6.
- The Levenshtein distance between ‘Spurs’ and ‘Pacers’ is 4.
- The Levenshtein distance between ‘Lakers’ and ‘Warriors’ is 5.
- The Levenshtein distance between ‘Cavs’ and ‘Celtics’ is 5.
