[JS 자료구조] 이진 힙(Binary Heap)과 우선순위 큐(Priority Queue)

이진 힙(Binary Heap)과 우선순위 큐(Priority Queue)
이진 힙 소개
-
일단 힙(Heap)이라는 단어가 매우 생소하므로, 이에 대하여 익숙해질 필요가 있다. Heap의 사전적 의미는
무엇인가 차곡차곡 쌓여있는 더미를 의미한다. 건초 더미, 모래 더미, 산 더미처럼 말이다. 이를 통해, 자료 구조에서 힙(Heap)은 모래 더미처럼 삼각형으로 쌓여 있는 구조임을 추측할 수 있다.

-
참고로
메모리 영역 Heap과자료구조 Heap은 서로 상관관계가 없다.메모리 영역 Stack은자료구조 Stack를 사용하기에Stack이라고 불리는 것과 달리,메모리 영역 Heap은자료구조 Heap을 사용하지 않는다. 단지, 영단어 힙(heap)은 '무엇인가 차곡차곡 쌓여있는 더미'라는 뜻을 지니고 있어, 사용 가능한 메모리 풀을 관용적으로 ‘Heap’이라고 불렀다고 한다.
https://softwareengineering.stackexchange.com/questions/186705/why-is-the-main-memory-for-object-allocation-called-the-heap
Several authors began about 1975 to call the pool of available memory a "heap." But in the present series of books, we will use that word only in its more traditional sense related to priority queues. (The Art of Computer Programming - Fundamental Algorithms, 3rd ed., p. 435)
몇몇 저자들은 1975년경에 사용 가능한 메모리 풀을 "힙"이라고 부르기 시작했습니다.그러나 현재 시리즈의 책에서는 우선 순위 대기열과 관련된 보다 전통적인 의미로만 이 단어를 사용할 것입니다. (컴퓨터 프로그래밍의 기술 - 기본 알고리즘, 3판, 435페이지)
-
힙(Heap)도 트리 자료 구조의 일종이다. 힙이 다른 트리와는 달리 데이터가 한 쪽으로 쏠리지 않고 모래 더미처럼 삼각형의 형태를 유지할 수 있는 이유는, 부모 노드가 항상 자식 노드들보다 크거나(최대이진힙) 작아야(최소이진힙) 한다는 규칙이 있고 형제 노드들 간의 관계에는 그러한 규칙이 없기 때문이다.
-
힙에도 여러 종류가 있는데 이번 포스팅에서는 그 중에서도 이진 힙(Binary Heap)에 집중해서 살펴보려고 한다.
-
이진 힙
- 이진 힙은 이진탐색트리(BST)와 아주 유사하지만, 다음과 같은 몇 가지 규칙이 다르다.
- 최대 이진 힙(MaxBinaryHeap)에서는 부모 노드가 항상 자식 노드들보다 커야 한다.
- 최소 이진 힙(MinBinaryHeap)에서는 부모 노드가 항상 자식 노드들보다 작아야 한다.
- 이진 힙에서 부모와 자식 노드 간의 관계는 위와 같이 크거나 작아야 하지만, 형제 노드들 간의 관계에는 그러한 규칙이 없다.
- 이진 힙은 언제가 가능한 가장 적은 최적의 공간만을 차지한다.
- 이진 힙은 이진탐색트리(BST)와 아주 유사하지만, 다음과 같은 몇 가지 규칙이 다르다.
아래 이미지와 같은 트리가 최대 이진 힙(MaxBinaryHeap) 이다. 부모 노드들이 항상 자식 노드들보다 크며, 형제 노드들 간에는 특별한 순서가 없다.
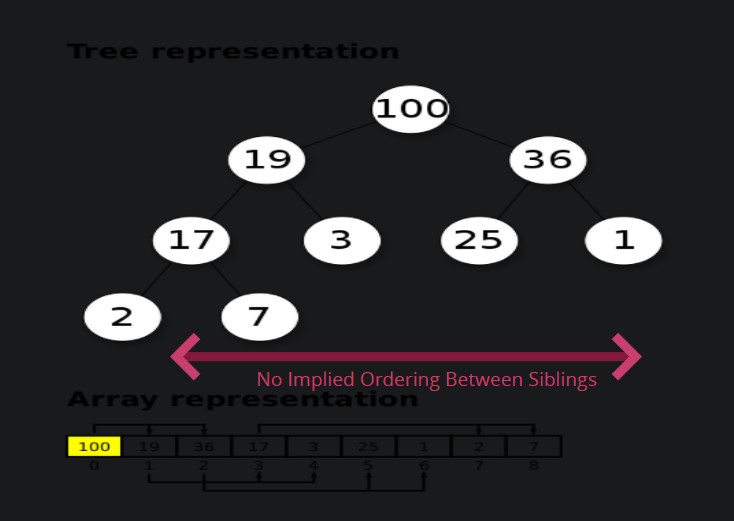
- 그리고 반대로 최소이진힙(MinBinaryHeap)은 아래 이미지와 같다.
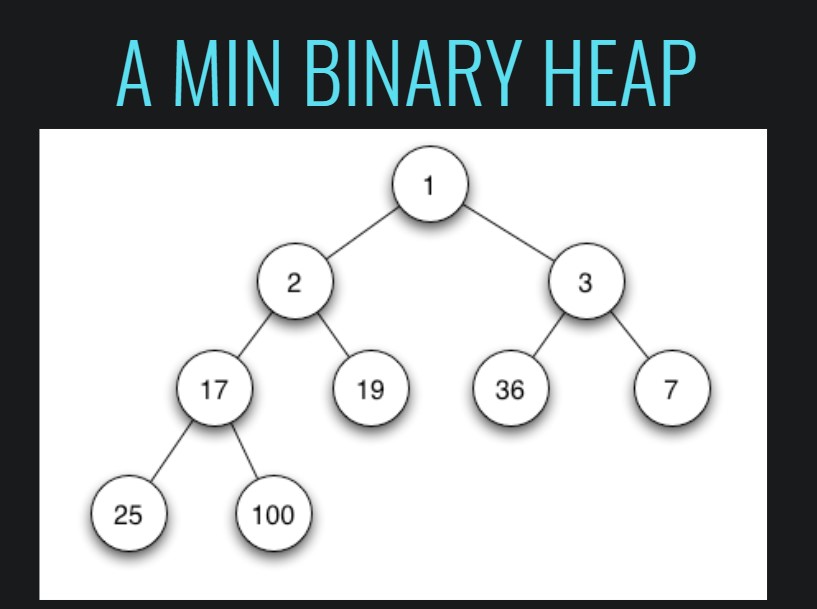
- 이진 힙을 왜 배워야 할까?
이진 힙은 자료구조에서 자주 사용되는우선순위 큐(Priority Queues)를 코딩할 때 사용된다.이진 힙은그래프 순회(Graph Traversal)알고리즘 등에서도 자주 사용된다.
이진 힙 - 부모와 자식이 서로의 위치 찾는 규칙
- 이진 힙과 이진탐색트리의 차이점을 이해하자. 둘은 비슷해보이지만 다르다.
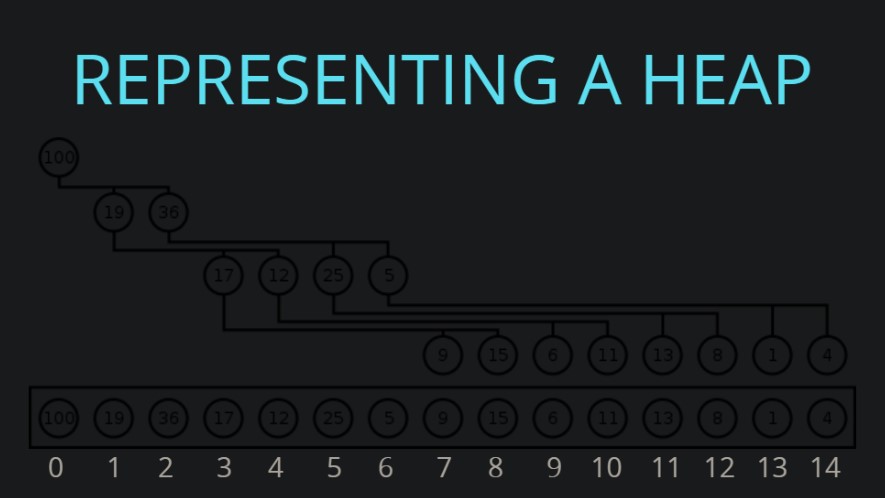
- 어떤 요소(인덱스 n)에 대한 child들의 인덱스는 각각 다음과 같다는 규칙이 있다. 예를 들어, 3 인덱스에 대한 left child의 인덱스는 7(=23+1)이며, right child의 인덱스는 8(=23+2)이다.
- 부모의 위치(n)를 가지고 자식의 위치 찾기
left child인덱스 : 2n+1right child인덱스 : 2n+2
- 부모의 위치(n)를 가지고 자식의 위치 찾기
- 반대로 child 노드의 인덱스를 가지고 parent 노드의 인덱스를 찾을 수도 있다.
- 자식의 위치(n)를 가지고 부모의 위치 찾기
parent인덱스 : Math.floor((n-1)/2)
- 자식의 위치(n)를 가지고 부모의 위치 찾기
이진 힙 클래스 정의 - 생성자
- 배열을 이용할 수 있다.
- 본 포스팅에서는 이진 힙 중
최대이진힙(MaxBinaryHeap)클래스만 만들어보므로, 이하 메서드는 모두 최대이진힙의 메서드이다.
class MaxBinaryHeap {
constructor() {
this.values = [];
}
}이진 힙 Insert 메서드
- 메서드 로직
- 제일 밑에 요소를 넣는다.
this.values.push(element); - 그 요소가 알아서 제 자리로 가도록 비눗방울처럼 띄어 올린다.
this.bubbleUp();
- 제일 밑에 요소를 넣는다.
- 아래 이미지는
[41,39,33,18,27,12]이진 힙 데이터에55를 Insert했을 때 발생하는 과정을 시각화한 것이다.
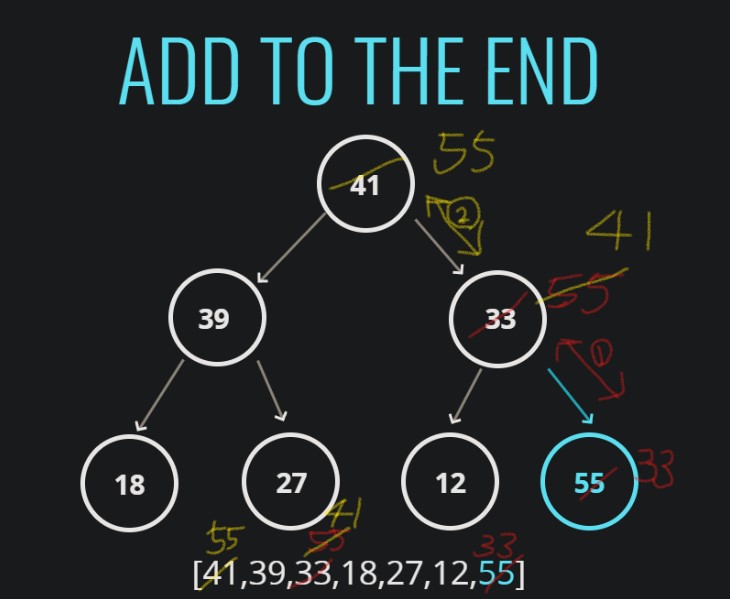
- 이진 힙 Insert 메서드 자바스크립트 코드
insert(element) {
// 삽입하려는 요소를 기존 배열의 끝에 push한다.
this.values.push(element);
// bubbleUp 메서드 호출
this.bubbleUp();
}
bubbleUp() {
// 삽입한 요소의 현재 인덱스를 idx 변수로 정의한다.
let idx = this.values.length - 1;
// idx는 element의 인덱스이며, idx가 0이 되기 전까지 반복문을 돌린다.
// 인덱스 0이 되면 삽입한 요소가 이미 root 자리에 도착했다는 것이므로 더 올라갈 곳이 없다.
while (idx > 0) {
// 삽입한 요소와 비교해야 하는 부모 요소를 찾아서 변수로 할당한다.
// 위에서 살펴본 자식의 위치로 부모 위치 찾는 공식(n-1/2)을 사용한다.
const parentIdx = Math.floor((idx - 1) / 2);
// 삽입한 요소보다 비교하려는 부모 요소가 같거나 크면 자리를 바꿀 필요가 없으므로 반복문 깨기
if (this.values[idx] <= this.values[parentIdx]) break;
// 삽입한 요소보다 비교하려는 부모 요소가 작으면 자리를 서로 바꿔준다.
this.values[parentIdx] = this.values[idx];
// 자리를 바꿨으니 인덱스도 서로 바꾼다.
idx = parentIdx;
}
}이진 힙 ExtractMax 메서드
- 최대이진힙에서 root(가장 큰 값)를 제거하는 메서드다. 이진힙을 기반으로 한 우선순위 큐에서 최우선순위를 가져오고 제거할 때 사용하는 알고리즘이다.
- 메서드 로직
- root를 제거한다.
- root 자리에 가장 최근에 추가한 요소를 옮겨 넣는다.
- root 자리에 옮겨진 요소가 제 자리를 찾아서 내려가도록 조절한다.
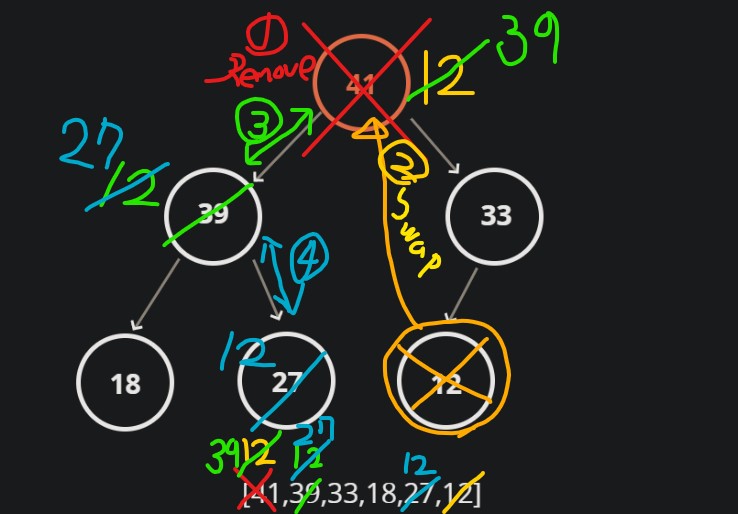
- 아래 이미지는
[41,39,33,18,27,12]이진 힙에서 ExtractMax()를 했을 때, 발생하는 과정을 시각화한 것이다.- (1) 먼저 41을 제거하고 이를 나중에 리턴한다.
- (2) 가장 최근에 추가된(가장 뒤에 있는) 12를 root 자리로 옮겨 넣는다.
- (3) root 자리에 올라선 12가 그 자리에 걸맞은 자격이 있는지 바로 아래 child 중 값이 큰 녀석인 39와 크기를 비교하고, 12가 더 작으므로 12와 39가 자리를 서로 바꾼다.
- (4) 한 단계 아래로 내려간 12가 다시 그 아래 child 중 값이 큰 녀석인 27과 크기를 비교하고, 12가 더 작으므로 12와 27이 자리를 서로 바꾼다.
- 12 아래에 더 이상 하위 child가 없으므로 반복문 종료하고, 제거했던 41을 return한다.
- 이진 힙 ExtractMax 메서드 자바스크립트 코드
extractMax() {
// 이진 힙의 max와 end 변수 정의
const max = this.values[0];
const end = this.values.pop();
// pop한 후에 남은 요소가 있으면
if (this.values.length > 0) {
// root 자리에 가장 최근에 삽입됐던 end를 넣고
this.values[0] = end;
// root 자리에 올라간 end의 sinkDown()을 시작한다.
this.sinkDown();
}
// pop한 후에 남은 요소가 없으면 바로 return하고 종료한다.
return max;
}
sinkDown() {
let idx = 0;
const length = this.values.length;
while (true) {
// sinkDown할 주인공 element 변수 설정
const element = this.values[idx];
// 부모 위치로부터 자식 위치 찾는 공식을 이용해서 left, right 자식의 위치를 구한다.
const leftChildIdx = 2 * idx + 1;
const rightChildIdx = 2 * idx + 2;
let leftChild;
let rightChild;
let swap = null;
// 찾은 자식의 인덱스가 실제로 존재할 때에만, 그 값을 변수로 할당한다.
// 먼저 leftChild 변수가 element와 비교해서 더 크면, 그 인덱스를 swap에 할당한다.
if (leftChildIdx < length) {
leftChild = this.values[leftChildIdx];
if (leftChild > element) {
swap = leftChildIdx;
}
}
// rightChild도 위에서 leftChild에게 한 것처럼, 비교하고 swap에 할당하려고 하는데,
// leftChildIdx가 존재하지 않아서 swap이 여전히 null일 수 있으므로
// 그러한 경우를 고려하여 조건을 추가한다.
// swap이 null이고 rightChild가 element보다 크거나,
// swap에 값(leftChildIdx)이 있고 rightChild가 leftChild보다 큰 경우에,
// 그 인덱스를 swap에 할당한다.
if (rightChildIdx < length) {
rightChild = this.values[rightChildIdx];
if ((swap === null && rightChild > element) || (swap !== null && rightChild > leftChild)) {
swap = rightChildIdx;
}
}
// 만약 여전히 swap이 null이면 element는 이미 제 자리에 있는 것이므로 반복문을 break
if (swap === null) break;
// 그렇지 않고 swap 값이 있다면, element와 swap할 대상의 자리를 서로 바꾼다.
[this.values[idx], this.values[swap]] = [this.values[swap], this.values[idx]];
// while문의 다음 턴에서 사용할 element의 새 인덱스를 swap으로 재할당해서 최신화해준다.
idx = swap;
}
}우선순위 큐(Priority Queue)
- 우선순위 큐는 각각의 요소가 개별 우선순위를 갖는 자료구조다. 높은 우선순위를 가진 요소는 낮은 우선순위를 가진 요소보다 앞에 온다.
- 우선순위 큐가 보통 힙(Heap)을 사용하기 때문에, 이 둘이 같거나 관계가 있다고 생각할 수도 있으나, 우선순위 큐와 힙(Heap)은 상관관계가 없다. 우선순위 큐는 단지 추상적인 개념에 불과하며, 힙 외에 배열이나 리스트 등의 다른 방식(물론 느릴 수는 있음)으로도 구현할 수 있다.
- 하지만 힙(Heap)이 더 좋은 성능(삽입, 제거 모두 O(log n))을 갖기 때문에, 힙으로 우선순위 큐를 구현해보자.
- 이번에는
최소이진힙으로 구현하고 value 외에도 priority 클래스를 함께 담기 위해 Node 클래스를 사용한다. 코드는 아래와 같다. 로직은 위의 이진힙과 거의 같고, 다른 점은 주석을 달았다.
- 이번에는
class Node { // value 외에도 priority 클래스를 함께 담기 위해 Node 클래스를 사용한다.
constructor(val, priority) {
this.val = val;
this.priority = priority;
}
}
class PriorityQueue {
constructor() {
this.values = [];
}
enqueue(val, priority) { // 이진 힙에서 만든 Insert 메서드에서 이름을 바꿨다.
const newNode = new Node(val, priority);
this.values.push(newNode);
this.bubbleUp();
}
bubbleUp() {
let idx = this.values.length - 1;
while (idx > 0) {
const parentIdx = Math.floor((idx - 1) / 2);
if (this.values[idx].priority >= this.values[parentIdx].priority) break;
[this.values[idx], this.values[parentIdx]] = [this.values[parentIdx], this.values[idx]];
idx = parentIdx;
}
}
dequeue() { // 이진 힙에서 만든 extractMax 메서드에서 이름을 바꿨다.
const min = this.values[0];
const end = this.values.pop();
if (this.values.length > 0) {
this.values[0] = end;
this.sinkDown();
}
return min;
}
sinkDown() {
let idx = 0;
const length = this.values.length;
const element = this.values[0];
while (true) {
const leftChildIdx = 2 * idx + 1;
const rightChildIdx = 2 * idx + 2;
let leftChild;
let rightChild;
let swap = null;
if (leftChildIdx < length) {
leftChild = this.values[leftChildIdx];
// 최소이진힙이라 최대이진힙과 달리 부등호 방향이 반대고, 비교하는 값은 priority 프로퍼티다.
if (leftChild.priority < element.priority) {
swap = leftChildIdx;
}
}
if (rightChildIdx < length) {
rightChild = this.values[rightChildIdx];
if ((swap === null && rightChild.priority < element.priority) || (swap !== null && rightChild.priority < leftChild.priority)) {
swap = rightChildIdx;
}
}
if (swap === null) break;
this.values[idx] = this.values[swap];
this.values[swap] = element;
idx = swap;
}
}
}이진 힙 성능
- 시간복잡도
- 삽입 :
- 제거 :
- 탐색 :
- 이진 힙은 최대이진힙이든 최소이진힙이든 삽입과 삭제에 있어서 성능이 아주 좋다. 이진 힙 구조 특성상 데이터가 한 쪽으로 쏠리지 않으므로, 언제나 삽입과 제거에 있어서 평균적인 의 시간복잡도를 갖는다.
- 하지만 이진 힙은 탐색에서는 시간복잡도가 좋은 편이 아니므로 탐색에 대한 최적화가 필요하다면 다른 자료구조를 고려하는 것이 낫다.
- 탐색에서 O(N)의 시간복잡도가 나오는 이유는, 이진 힙의 형제 노드 사이에 순서가 정해져 있지 않기 때문에, 무언가를 찾으려면 왼쪽과 오른쪽을 항상 모두 뒤져야 하기 때문이다.
결론
- 이진 힙은 힙의 한 종류이며, 힙은 트리의 한 종류이다.
- 이진 힙은 그 자체로도 유용하지만, 우선순위 큐와 같은 다른 데이터 구조를 코딩하는 데에도 유용하다.
- 이진 힙은 크게 최대이진힙과 최소이진힙으로 나뉜다.
- 최대이진힙에서는 모든 부모가 두 자식보다 크다.
- 최소이진힙에서는 모든 부모가 두 자식보다 작다.
- 이진 힙은 왼쪽에서부터 오른쪽으로 채워나가기 때문에, 한 쪽으로 치우친 트리는 나오지 않고 피라미드 모양에 가깝게 유지한다.
- 약간의 수학공식을 활용하면, 노드의 포인터 같은 것 없이도 배열만을 가지고 힙을 구현할 수도 있다. 물론 직접 클래스를 만들고 노드를 활용하여 힙을 만들 수도 있다.
