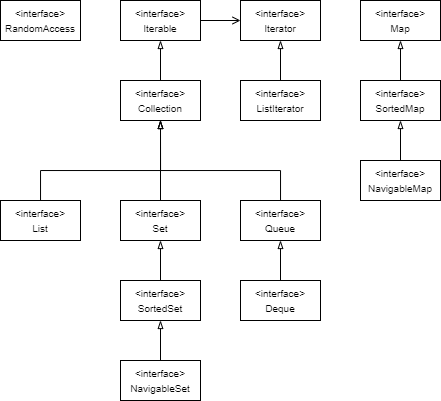
List 순차 컬렉션.
ArrayList 내부 배열 관리
LinkedList 연결리스트
Set 특정 위치에 삽입하지 않음, 중복 허용하지 않음
Deque 큐와 스택으로 활용
Collection 인터페이스 자체에 addAll, removeIf 같은 몇몇 기본 알고리즘들이 구현되어있음
Collections 유틸리티 클래스에는 그밖에 다양한 종류의 컬렉션에 동작하는 여러 알고리즘들이 있음
반복자 (Iterator)
Collection<String> collection = Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c");
Iterator<String> iterator = collection.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}for (String element : collection) {
System.out.println(element);
}아래 for 문은 위처럼 동작함
집합
정렬된 순서로 집합을 순회하려면 TreeSet 사용
TreeSet을 사용하는 집합의 요소 타입은 Comparable 인터페이스를 구현하거나 생성자에 Comparator를 전달해야함
맵
key, value
Map<String, Integer> counts = new HashMap<>();
counts.put("Alice", 1); // insert
counts.put("Alice", 2); // update
int count = counts.get("Alice"); // get. returns null if key not found
int count = counts.getOrDefault("Alice", 0); // get 0 if key not found
counts.merge(word, 1, Integer::sum);Set<K> keySey()
Set<Map, Entry<K, V>> entrySet()
Collection<K> values()위 메서드들로 맵의 키, 값, 엔트리의 뷰를 얻을 수 있다.
반환된 맵 데이터는 사본이 아니고 해당 맵에 연결되어있음
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entey : counts.entrySet()) {
String k = entry.getKey();
Integer v = entey.getValue();
// do something with k, v
}counts.forEach((k, v) -> {
// do something with k, v
});