Sliding Window
Concept
Sliding Window(슬라이딩 윈도우(는 문제를 풀기위해 window또는 range(범위)를 정의하여 input data를 이동하면서, 해당 윈도우의 데이터를 연산하는 방법이다. 이 방법은 subarray의 특정한 합계를 찾거나, 특정 문자를 포함하는 가장 긴 subarray를 착거나, 하는 등 고정 윈도우를 필요로하는 문제에서 요소들을 효과적으로 처리하기 위해 사용한다.
Sliding Window Technique is a method used to efficiently solve problems that involve defining a window or range in the input data (arrays or strings) and then moving that window across the data to perform some operation within the window. This technique is commonly used in algorithms like finding subarrays with a specific sum, finding the longest substring with unique characters, or solving problems that require a fixed-size window to process elements efficiently.
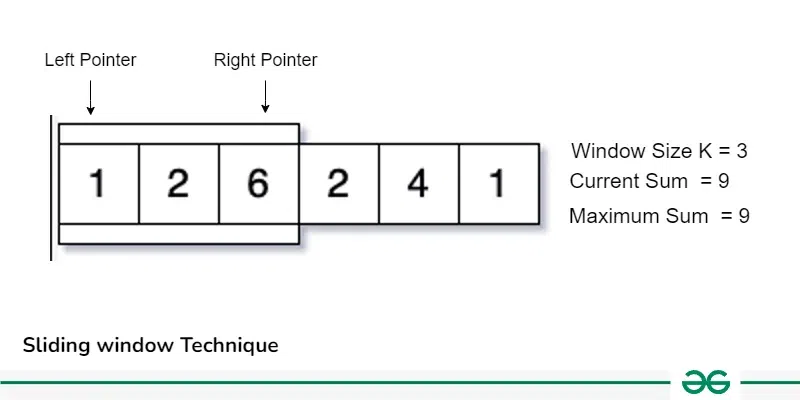
(자료: GeeksforGeeks)
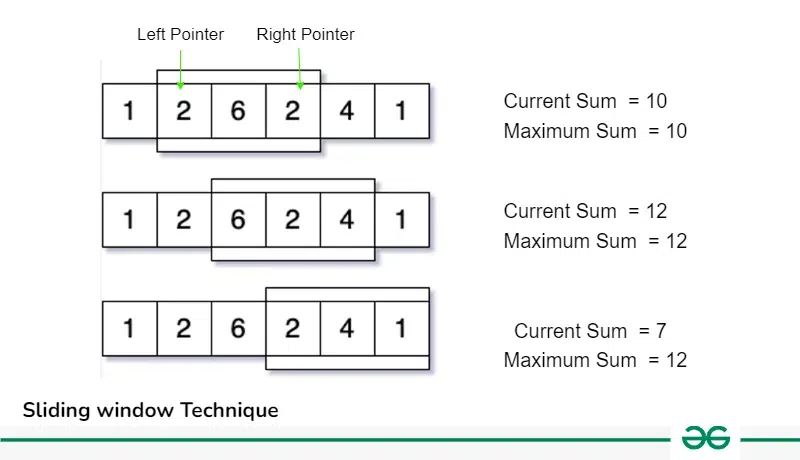
(자료: GeeksforGeeks)
Features
Process
Note that : an array of size
N, an integerK
윈도우 크기가 K, 이고, 윈도우를 이동하면서 최대 합계를 구하는 문제가 있다. 이 때, 처음부터 모든 값을 다시 다 더하는 것이 아니라, 윈도우를 이동하면서 왼쪽 포인터와 오른쪽 포인터를 이용하여 값을 더하고 빼는 방식을 통해서 한번만 연산하면, 시간 복잡도가 O(n^2)에서 O(1)이 될 수 있다.
Types of Sliding Window
Fixed Size
- 필요한 윈도우 윈도우 크기(size of the window)인 K를 찾한다.
- 첫 번쨰 윈도우의 결과를 계산한다.
i.e. 데이터 구조의 첫번 째 K개의 요소들(elements)을 포함한다. - 윈도우를 1씩 이동하면서 결과를 연산한다. (1 operation / 1 loop)
Variable Size
- 오른쪽 포인터를 하나씩 증가시키면서 조건이 참인지 확인한다.
- 어떤 단계에서든지 조건이 맞지 않는다면, 우리는 왼쪽 포인터를 증가시켜 윈도우의 크기를 줄인다.
- 다시 조건이 만족되면 오른쪽 포인터를 증가시키고 1단계를 따른다.
- 이 과정을 배열의 끝에 도달할 때까지 반복한다.
Code
C++
// O(n*k) solution for finding maximum sum of
// a subarray of size k
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int fixed_maxSum(vector<int> &arr, int n, int k)
{
if (n <= k)
{
cout << "Invalid";
return -1;
}
int max_sum = INT_MIN;
for (int i = 0; i < n - k + 1; i++)
{
int current_sum = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < k; j++)
current_sum = current_sum + arr[i + j];
max_sum = max(current_sum, max_sum);
}
return max_sum;
}
int variable_maxSum(vector<int> arr, int n, int k)
{
if (n <= k)
{
cout << "Invalid";
return -1;
}
int max_sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
max_sum += arr[i];
int window_sum = max_sum;
for (int i = k; i < n; i++)
{
window_sum += arr[i] - arr[i - k];
max_sum = max(max_sum, window_sum);
}
return max_sum;
}
int main()
{
cout << "==================Fized Sliding Window==================" << endl;
// case # 1
vector<int> arr = {1, 4, 2, 10, 2, 3, 1, 0, 20};
int k = 4;
int n = 9;
cout << sizeof(arr) <<endl; // 24
cout << sizeof(arr[0]) << endl; // 4
cout << fixed_maxSum(arr, n, k) << endl; // 24
// case # 2
n = 4;
k = 2;
arr.resize(n,0);
arr = {100, 200, 300, 400};
cout << fixed_maxSum(arr, n, k) << endl; // 700
// case # 3
n = 2;
k = 3;
arr.resize(n,0);
arr = {2, 3};
cout << fixed_maxSum(arr, n, k) << endl; // 39
cout << "==================Variable Sliding Window==================" << endl;
n = 9;
k = 4;
arr.resize(n,0);
arr = {1, 4, 2, 10, 2, 3, 1, 0, 20};
cout << variable_maxSum(arr, n, k) << endl; // 24
return 0;
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Aditya Kumar (adityakumar129)
// Revised by Jasmine(2024.July.)Reference
[1] https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/window-sliding-technique/
