Time Complexity & Space Complexity
컴퓨터사이언스에서는 문제를 해결하는 여러가지 알고리즘이 있는데, 어떤 것이 가장 최적인지 비교하기 위한 방법이 필요하다. 일반적으로 입력이 n일 때, 결과를 얻을 때까지의 연산시간이다.
- 기계와 configurations 과는 독립적
- 인풋에 대한 직접적인 관계를 보여줌
- 두 개의 알고리즘을 명확하게 구분할 수 있음
Time Complexity
컴퓨터과학에서 알고리즘의 시간복잡도는 입력을 나타내는 문자열 길이의 함수로서 작동하는 알고리즘을 취해 시간을 정량화하는 것이다. 알고리즘의 시간복잡도는 주로 빅-오 표기법(Big-O notation)을 사용하여 나타내며, Pan Bubilek의 빅-오 표기법은 계수와 낮은 차수의 항을 제외시키는 방법이다.
by wikipedia
Big-O notaion Time Complexity
| Notation | Name |
|---|---|
| constant | |
| double logarithmic | |
| logarithmic | |
| , c>1 | polylogarithmic |
| , 0<c<1 | fractional power |
| linear | |
| nlog-starn | |
| linearithmic, lolinear, quasilinear, nlogn | |
| quadratic | |
| polynomial or algeraic | |
| exponential | |
| factorial |
Big-O notation 비교
알고리즘 복잡도는 아래 그림과 같이 성능이 더 좋고, 나쁘게 비교될 수 있다.

General Time complexity grpah
| Input Length | Worst Accepted Time Complexity | Usually type of solutions |
|---|---|---|
| 10 -12 | Recursion and backtracking | |
| 15-18 | Recursion, backtracking, and bit manipulation | |
| 18-22 | Recursion, backtracking, and bit manipulation | |
| 30-40 | Meet in the middle, Divide and Conquer | |
| 100 | Dynamic programming, Constructive | |
| 400 | Dynamic programming, Constructive | |
| 2K | Dynamic programming, Binary Search, Sorting, Divide and Conquer | |
| 10K | Dynamic programming, Graph, Trees, Constructive | |
| 1M | Sorting, Binary Search, Divide and Conquer | |
| 100M | Constructive, Mathematical, Greedy Algorithms |
Types of Time complexity
시간 복잡도는 다양한 표기법이 있는데, Big-O(), Big-Omega(), Big-Theta()가 있다.
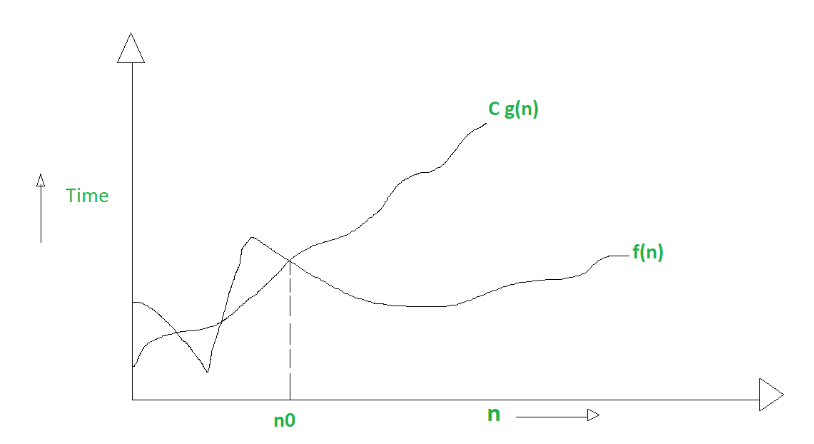
- Big O notation ():
<=
upper bound
the most amount of time required
the worst case performanc
asymptotic upper bound
Mathematically – Big Oh is :
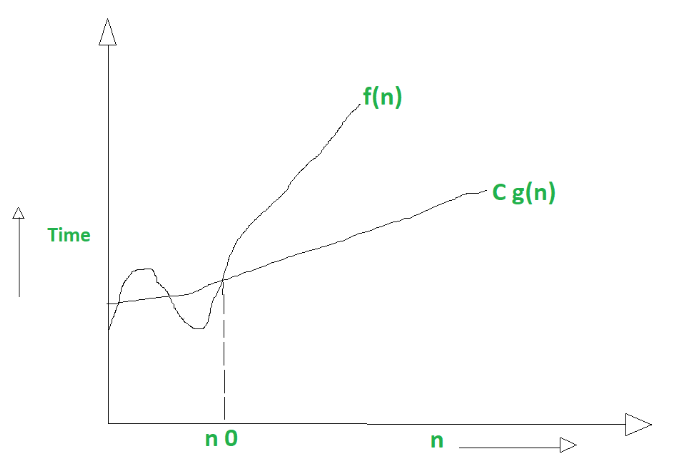
- Big Omega notation () :
>=
lower bound
the least amount of time required
the most efficient way possible, i.e. best case
asymptotic lower bound
Mathematically – Big Omega is :
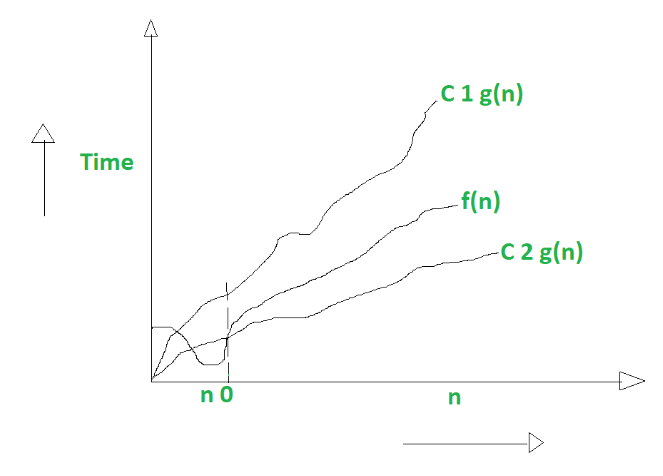
- Big Theta notation () :
==
tightest bound
the best of all the worst case times
Mathematically – Big Theta is :
※자료: geeksforgeeks.org
Reference
[1] https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/time-complexity-and-space-complexity/
[2] https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/understanding-time-complexity-simple-examples/
[3] https://ko.wikipedia.org/wiki/%EC%8B%9C%EA%B0%84_%EB%B3%B5%EC%9E%A1%EB%8F%84
[4] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Big_O_notation
[5] https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/difference-between-big-oh-big-omega-and-big-theta/
[6] https://medium.com/thedevproject/logarithm-complexity-vs-linear-complexity-f9871333756b
with
[Algorithm] Space Complexity (공간 복잡도 )
