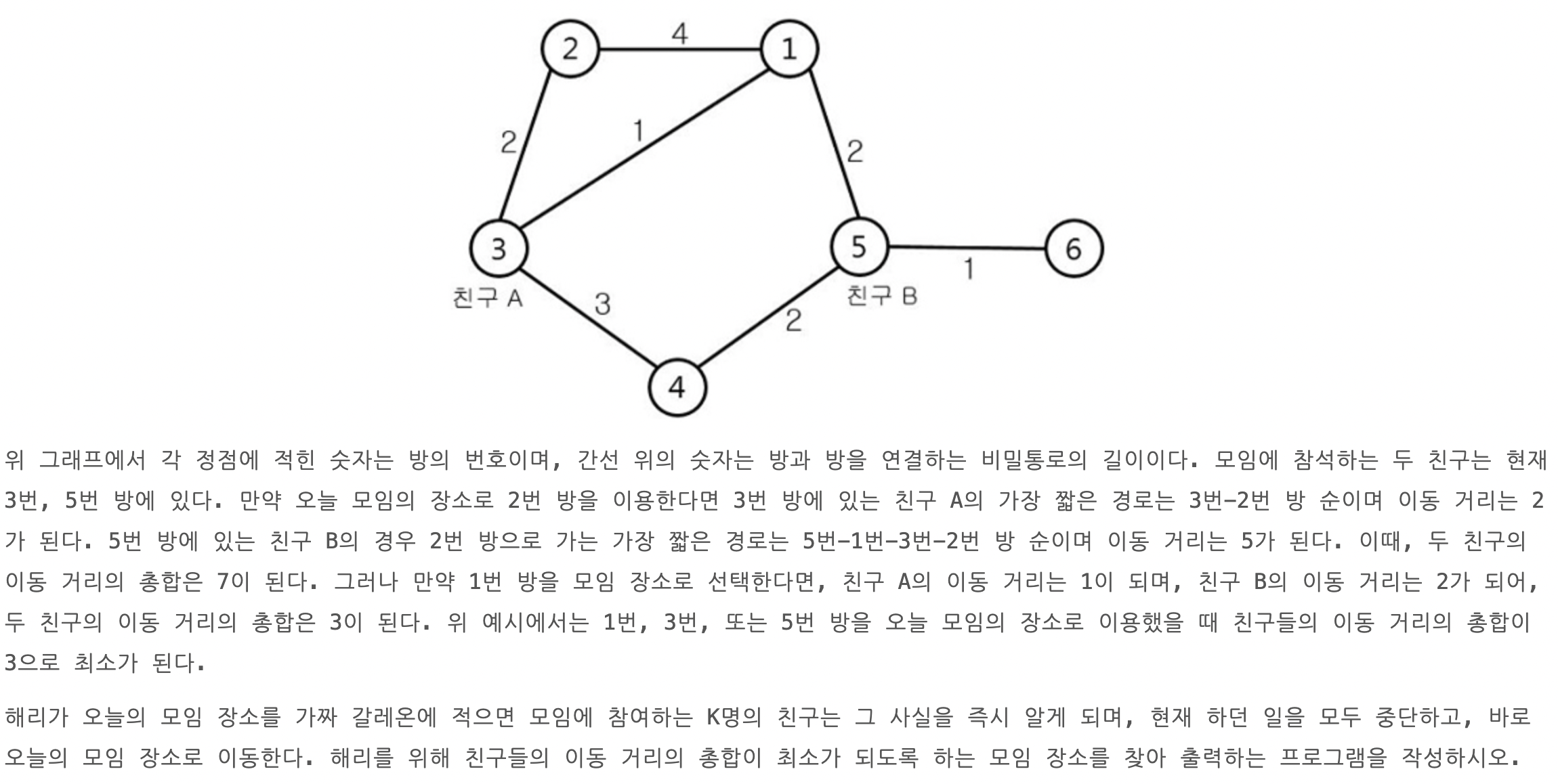
Intro


Solution
다익스트라 알고리즘을 알고 있다면 쉽게 풀 수 있다.
- 다익스트라 알고리즘을 이용해 모든 친구들의 이동 비용을 구하여 저장한다.
- N은 최대 100이므로 K * N은 최대 10000, 친구들의 이동 비용의 합을 도착지마다 구하여 비교하여도 시간 제한을 통과할 수 있다.
Code
import sys, heapq
input = sys.stdin.readline
def dijkstra(n, graph, start):
cost = [float('inf')] * (n+1)
cost[start] = 0
hq = [(cost[start], start)]
while hq:
t, x = heapq.heappop(hq)
if cost[x] != t: continue
for nt, nx in graph[x]:
if cost[nx] > t + nt:
cost[nx] = t + nt
heapq.heappush(hq, (cost[nx], nx))
return cost
def solve():
for _ in range(int(input())):
n, m = map(int, input().split())
graph = [[]*(n+1) for _ in range(n+1)]
for _ in range(m):
a, b, c = map(int, input().split())
graph[a].append((c, b))
graph[b].append((c, a))
answers = []
fnum = int(input())
frooms = [*map(int, input().split())]
for friend in frooms:
answers.append(dijkstra(n, graph, friend))
_min = float('inf')
for i in range(1, n+1):
tmp = 0
for j in range(fnum):
tmp += answers[j][i]
if tmp < _min:
_min = tmp
answer = i
print(answer)
solve()