React JS_goormedu
React 소개
A JavaScript library for building user interfaces: 화면을 만들기 위한 기능들을 모아놓은 것
장점
- 빠른 업데이트와 렌더링 속도: Virtual DOM을 사용하여 Browser DOM을 직접 수정하는 것이 아니라 업데이트할 최소한의 부분만을 찾아서 업데이트 한다
- Component-Based: 레고 블록을 조립하듯 컴포넌트들을 모아서 개발할 수 있다 -> Reusability -> 개발 속도가 빨라진다
- 페이스북에서 만들었기 때문에 하루아침에 사라질 확률이 낮다
- 활발한 지식 공유 & 커뮤니티
JSX 소개
A syntax extension to JavaScript: JavaScript + XML/HTML
const element = <h1>Hello, world!</h1>React에서 JSX를 쓰는 것이 필수가 아님
// JSX를 사용한 경우
class Hello extends React.Component {
render() {
return <div>Hello {this.props.toWhat}</div>;
}
}
ReactDOM.render(
<Hello toWhat="World" />
document.getElementById('root')
);
// JSX를 사용하지 않고 JS를 사용한 경우
class Hello extends React.Component {
render() {
return React.createElement('div', null, `Hello ${this.props.toWhat}`);
}
}
ReactDOM.render(
React.createElement(Hello, {toWhat: 'World'}, null),
document.getElementById('root')
);JSX는 객체를 나타냄
const element = React.createElement(
'h1',
{className: 'greeting'},
'Hello, world!'
);
// 위 코드의 결과로 아래와 같은 객체(React elements)가 만들어짐
const element = {
type: 'h1',
props: {
className: 'greeting',
children: 'Hello, world!'
}
};JSX의 장점
- 간결한 코드
- 가독성 향상 -> 버그를 발견하기 쉬움
- Injection Attack 방어
Rendering Elements
Element
- Elements are the smallest building blocks of React Apps.
- React elements are immutable: 생성된 후에는 children이나 attributes를 바꿀 수 없다
// Root DOM node
<div id="root"></div>
const element = <h1>Hello, world</h1>;
ReactDOM.render(element, document.getElementById('root'));리액트는 바뀐 부분만 계산을 해서 해당 부분만 새롭게 랜더링함
Components and Props
Components
- 리액트는 component-based library
- react component는 props라는 입력값을 받아서 React element라는 출력값을 낸다
Props - property를 줄여서 말함
- read-only(값을 변경할 수 없음): All React components must act like pure functions with respect to their props.
// PURE - input을 변경하지 않으며, 같은 input에 대해서 항상 같은 output을 리턴
function sum(a, b) {
return a+b;
}
// IMPURE - input을 변경함
function withdraw(account, amount) {
account.total -= amount;
}Component
- 항상 대문자로 시작해야 함, 소문자로 시작하면 리액트에서는 DOM tag로 인식함
- 최대한 작게 만들어서 재사용성을 높이자
- component 합성: component안에 또 다른 component를 쓸 수 있음
- Function component
function Welcome(props) {
return <h1> Hello, {props.name}</h1>
}- Class component
class Welcome extends React.Component {
render() {
return <h1> Hello, {props.name}</h1>
}
}State and Lifecycle
State
- React component에 대한 변경 가능한 데이터
- 사용자가 정의함
- JavaScript의 객체임
- 직접 수정하면 안됨, setState 함수를 통해서만 수정하자
class LikeButton extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
liked: false
};
}
render() {
if (this.state.liked) {
return 'You liked this.';
}
return e(
'button',
{ onClick: () => this.setState({ liked: true }) },
'Like'
);
}
}Lifecycle
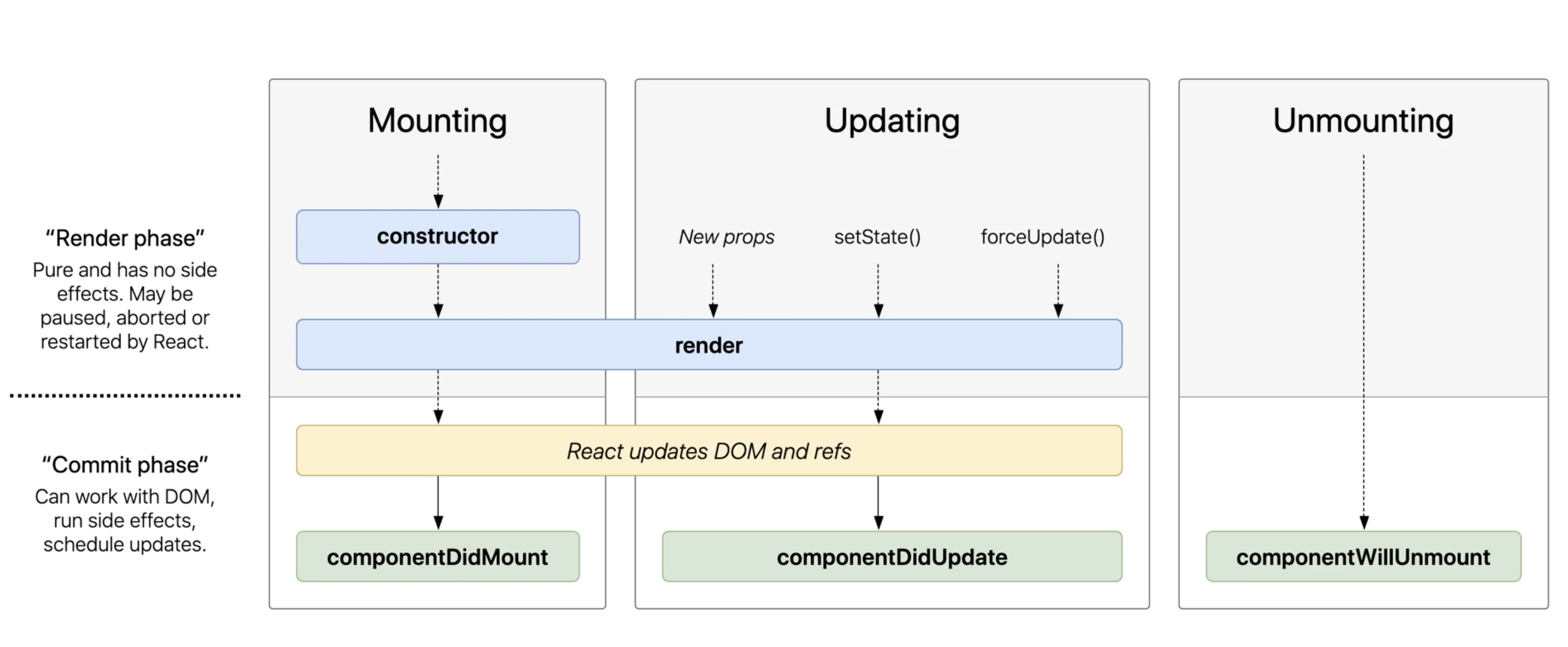
Copyright@Soaple
Handling Events
<button onClick={activeLasers}>
Activate Lasers
</button>Event Handler: 이벤트를 처리하는 함수, Event Listener라고도 함
class Toggle extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {isToggleOn: true};
// This binding is necessary to make 'this' work in the callback
this.handleClick = this.handleClick.bind(this);
}
handleClick() {
this.setState(state => ({
isToggleOn: !state.isToggleOn
}));
}
render() {
return (
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>
{this.state.isToggleOn ? 'ON' : 'OFF'}
</button>
)
}
}
// 또는
class LoggingButton extends React.Component {
// This syntax ensures 'this' is bound within handleCllick.
// Warning: this is *experimental* syntax.
handleClick = () => {
console.log('this is: ', this);
}
render() {
return (
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>
Click me
</button>
);
}
}Conditional Rendering
function Greeting(props) {
const isLoggedIn = props.isLoggedIn;
if (isLoggedIn) {
return <UserGreeting />;
}
return <GuestGreeting />;
}
ReactDOM.render (
<Greeting isLoggedIn={false} />, document.getElementById('root')
);
Inline condition
function MailBox(props) {
const unreadMessages = props.unreadMessage;
return (
<div>
<h1>Hello!</h1>
{unreadMessages.length > 0 &&
<h2>
You have {unreadMessages.length} unread messages.
</h2>
}
</div>
);
}If else condition
render() {
const isLoggedIn = this.state.isLoggedIn;
return (
<div>
The user is <b>{isLoggedIn ? 'currently' : 'not'}</b> logged in.
</div>
);
}null을 리턴하면 렌더링 되지 않음
function WarningBanner(props) {
if(!props.warn) {
return null;
}
return (
<div className="warning">
Warning!
</div>
);
}Lists and Keys
List
- JavaScript의 변수나 객체들을 하나의 변수로 묶어놓은 것
function NumberList(props) {
const numbers = props.numbers;
const listItems = number.map((number) =>
<li>{number}</li>
);
return (
<ul>{listItems}</ul>
);
}
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
ReactDOM.render(
<NumberList numbers={numbers} />, documeng.getElementById('root')
);Keys
- 아이템들을 구분하기 위한 고유한 문자열
- key의 값은 해당 element사이에서만 고유한 값이면 된다
key로 값을 사용하는 경우
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const listItems = numbers.map((number) =>
<li key={number.toString()}>
{number}
</li>
);key로 객체의 ID를 사용하는 경우
const todoItems = todos.map((todo) =>
<li key={todo.id}>
{todo.text}
</li>
);key로 index를 사용하는 경우 -> index는 고유한 key값은 아님
const todoItems = todos.map((todo, index) =>
// Only do this if items have no stable IDs
<li key={index}>
{todo.text}
</li>
);key는 props로 전달되지 않음
const content = posts.map((post) =>
<Post
// 아래에 있는 key는 Post에서 props.key 찍어봐도 안나옴
key={post.id}
// 그래서 id를 전달한다
id={post.id} />
);Forms
Controlled Components는 값이 react의 통제를 받는 Input form element를 의미함
handleChange(event) {
this.setState({value: event.target.value});
}
handleSubmit(event) {
alert('A name was submitted: ' + this.state.value);
event.preventDefault();
}
render() {
return (
<form onSubmit={this.handleSubmit}>
<label>
Name:
<input type='text' value={this.state.value} onChange={this.handleChange} />
</label>
<input type="submit" value="Submit" />
</form>
);
}File input tag는 값을 읽을 수만 있고 통제할 수 없기 때문에 Uncontrolled Components
Lifting State Up
Shared State
- state에 있는 데이터를 여러 개의 하위 컴포넌트에서 공통적으로 사용하는 경우
- 하위 컴포넌트들이 각자 state에 데이터를 가지고 있을 필요가 없음
Lifting State Up - sharing state is accomplished by moving it up to the closest common ancestor of the components that need it
- 하위 컴포넌트의 state를 공통 상위 컴포넌트로 올림
Composition vs. Inheritance
Composition
- 여러개의 컴포넌트를 합쳐서 새로운 컴포넌트를 만드는 것
- Containment: children이라는 prop을 사용해서 조합
function WelcomdDialog() {
return (
<FancyBorder color='blue'>
// 여기서부터
<h1 className="Dialog-title">
Welcome
</h1>
<p className="Dialog-message">
Thank you for visiting our spacecraft!
</p>
// 여기까지 FancyBorder 컴포넌트의 children으로 전달이 됨
</FancyBorder>
);
}- Specialization: 'WelcomeDialog'는 'Dialog'의 특별한 케이스
<Dialog
title="Welcome"
message="Thank you for visiting our spacecraft!"
</>Inheritance
- 다른 컴포넌트로부터 상속을 받아서 새로운 컴포넌트를 만드는 것
- At Facebook, we use React in thousands of components, and we haven't found any use cases where we would recommend creating component inheritance hierarchies. -> inheritance는 react에서 사용할 필요가 없다
참고자료
처음 만난 리액트 by goormedu
