Title
💡 연산자 / 조건문 / 반복문 1 + 백준 문제 풀이⏰ 연산자
⁉️연산자란 무엇일까?
💡 연산자 = 계산을 하기 위해 사용하는 기호- 간단히 말해 연산자란 연산을 실행는 +, - , * , / 등의 기호를 연산자라고 하며 연산의 대상을 피연산자라고 한다.
ex) x + y
다음에서 연산의 대상이 되는 x와 y는 피연산자, 더하기(+) 는 연산자라고 한다.
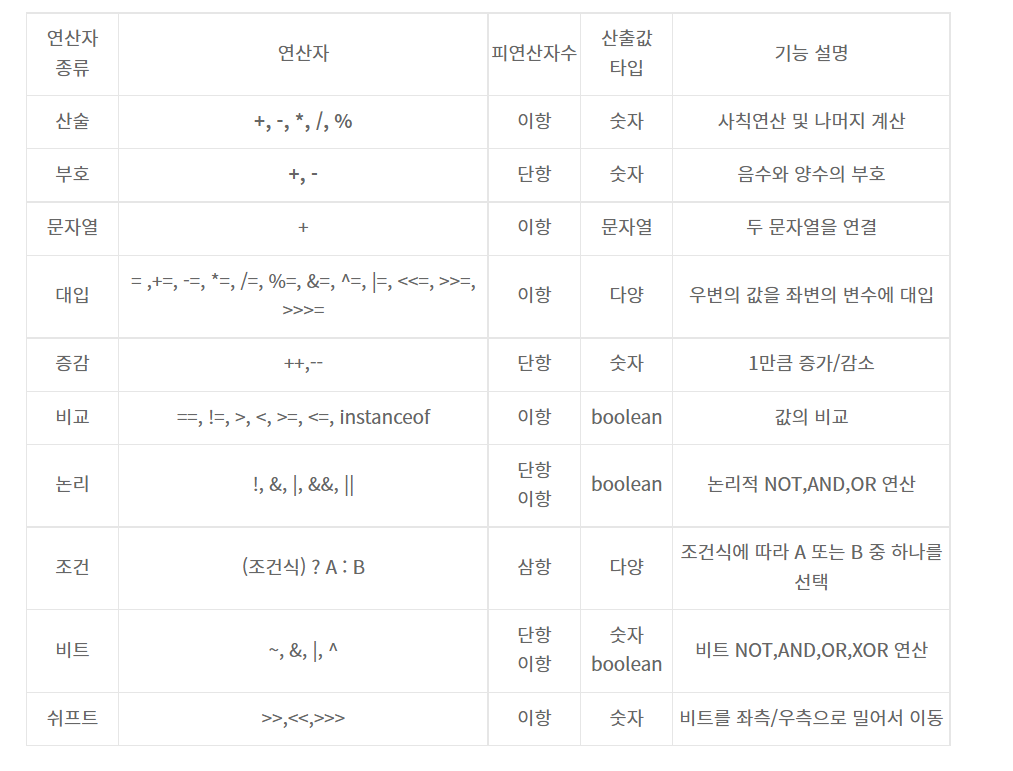
🏠 연산자의 종류
✏️ 이항 연산자란?
- 피 연산자가 2개인 연산자를 의미한다.
ex) x + y
다음에서 피 연산자는 2개( x와 y), 연산자는 + 이다.
따라서 위와 같은 식은 이항 연산자라고 한다.
✏️ 산술 연산자
💡 산술 연산자는 수학적인 계산에 사용되는 연산자
| 연산자 | 의미 |
|---|---|
| + | 더하기 |
| - | 빼기 |
| * | 곱하기 |
| / | 나누기 |
| % | 나머지 |
public static void main(String [] args) {
//산술 연산자 (덧셈)
int result = 1 +2; //result값은 3
System.out.println(result);
//산술 연산자 (뺄셈)
result = result -1;
System.out.println(result); //result값은 3 - 1 =2
//산술 연산자 (곱셈)
result = result *2;
System.out.prinltn(result); //result값은 2 * 2 = 4
//산술 연산자 (나누기)
result = result / 2;
System.out.prinltn(result); //result 값은 4 / 2 = 2
//산술 연산자 (나머지)
result = result + 8; //result 값은 10
result = result % 7; //result 값을 7로 나누기
System.out.println(result); //result값은 10 % 7 =3
}
}💡 연산자는 숫자와 숫자를 더할 때 사용되지만, 문자열과 문자열을 결합할 때도 사용된다.
public class Main {
public static viod main(String [] args) {
String firstStiring = " This is";
String secondString = " java programming";
String thirdString = firstString + secondString;
System.out.println(thirdString);
}
}출력 값
💡 This is java programming
✏️ 단항 연산자란?
- 피 연산자가 1개인 연산자를 의미한다.
💡 단항 연산자 = 연산자 피연산자 혹은 피연산자 연산자
ex) +1, -1, 1 ++, 1—**
| 연산자 | 의미 |
- : 양수를 표현한다.(대개 생략한다)
- : 음수를 의미한다
++ : 증가 연산자, 값을 1씩 증가한다.
— : 감소 연산자
public class Main {
public static viod main(String [] args) {
int i = 3;
//단항 연산자 (증가 연산자)
i++; //1을 증가한다.
System.out.println(i); // 4 출력
//단항 연산자 (증가 연산자)
++i;
System.out.println(i); // 5 출력
}
}자료 출처: https://www.opentutorials.org/course/1223/5331
✏️ 다양한 연산자의 종류
위의 예를 제외하고 연산자에는 수 많은 종류가 존재한다.
💡 각 연산자의 종류는 외우는 것이 아니라 하나하나 타자를 치면서 해당 기능을 배우면 된다!
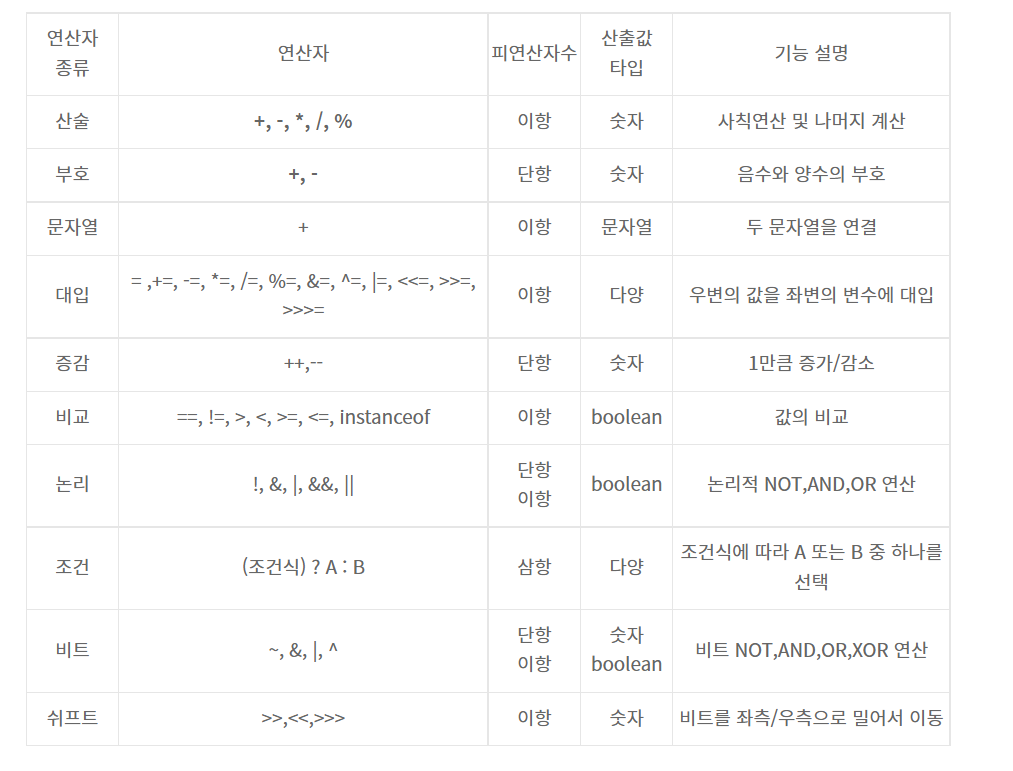
✏️ 연산자의 우선순위
💡 연산자의 우선순위는 전혀 외울 필요가 없다!!! 그냥 수학 공식에서 1순위: 괄호가 처진 수는 먼저 계산한다, 곱셈, 나누기가 덧셈, 뺄셈보다 먼저 실행된다! 이렇게만 간단히 확인만 하고 넘어가면 된다!!
우선순위와 결합방향은 외우는 것이 아니다!!
| 우선순위 | 연산자 | 결합방향 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | [ ] | → |
| () | ||
| . | ||
| 2 | ++ | ← |
| -- | ||
| +(양수) -(음수) | ||
| ~ | ||
| ! | ||
| (type) | ||
| new | ||
| 3 | * / % | → |
| 4 | +(더하기) -(빼기) | → |
| +(문자 결합 연산자) | ||
| 5 | << | → |
| >> | ||
| >>> | ||
| 6 | < <= | → |
| > >= | ||
| instanceof | ||
| 7 | == | → |
| != | ||
| 8 | & | → |
| & | ||
| 9 | ^ | → |
| ^ | ||
| 10 | ||
| 11 | && | → |
| 12 | ||
| 13 | ? : | ← |
| 14 | = | ← |
| *= /= += -= %=<<= >>= >>>=&= ^= | = |
🏠 조건문
✏️ 조건문이란?
💡 조건문이란 설정된 조건에 맞으면 실행되도록 하는 명령문이다.
✏️ if문

public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
if(true) { //참이라면
System.out.println(1); //1을 출력해라
System.out.println(2); //2을 출력해라
System.out.println(3); //3을 출력해라
System.out.println(4); //4을 출력해라 }
}
}- 다음과 같은 결과가 출력된다
출력문
1
2
3
4✏️ else문, else if 문
⏰else문
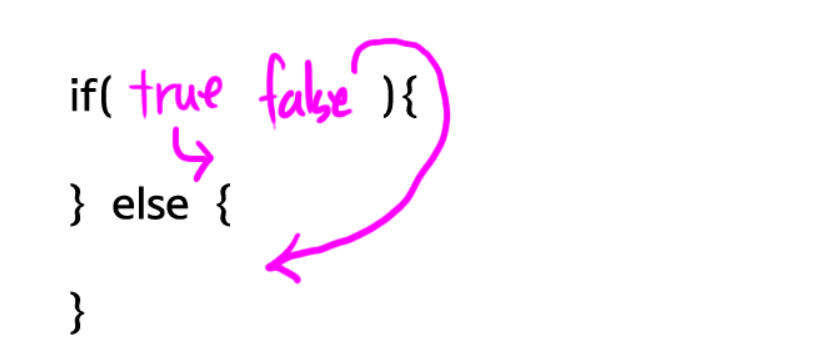
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
if(true) { //참이라면
System.out.println(1); //1을 출력해라
}else{ //거짓이라면
System.out.println(2); //2을 출력해라
}
}
}⏰else if문
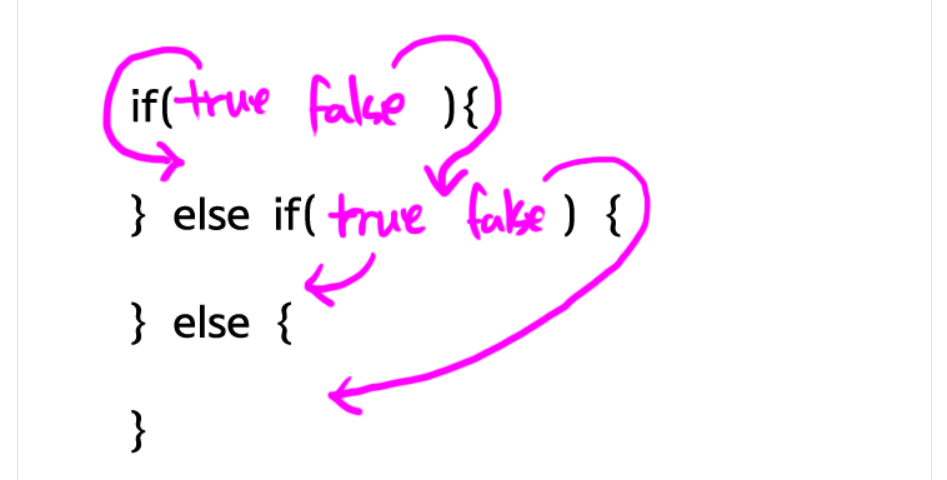
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
int a = 2;
if(a == 1) { //a가 1이라면
System.out.println(1); //1을 출력해라
else if (a == 2){// a가 1이 아닌 2 라면
System.out.println(2); //2을 출력해
}else{ //a가 1,2도 아니면 라면
System.out.println(3); //3을 출력해라
}
}
}✏️ Switch문
💡 Switch문은 조건이 많을 때 수 많은 if문을 사용하기 보다 효율적으로 실행하기 위해 사용하는 조건문이다.
형식
switch(입력변수) {
case 입력값1: // 변수 값이 1이라면
....
break; //실행 후 Switch문 실행 종료
case 입력값2: // 변수 값이 2이라면
....
break; //실행 후 Switch문 실행 종료
default: //모든 조건에 해당하지 않다면
...
break; //실행 후 Switch문 실행 종료
}예시
public class Sample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int month = 8; //8월달이라면
String monthString = "";
switch (month) {
case 1: monthString = "January";
break;
case 2: monthString = "February";
break;
case 3: monthString = "March";
break;
case 4: monthString = "April";
break;
case 5: monthString = "May";
break;
case 6: monthString = "June";
break;
case 7: monthString = "July";
break;
case 8: monthString = "August";
break;
case 9: monthString = "September";
break;
case 10: monthString = "October";
break;
case 11: monthString = "November";
break;
case 12: monthString = "December";
break;
default: monthString = "Invalid month";
break;
}
System.out.println(monthString); //8월달인 August출력
}
}출력문
💡 August참고 자료 : https://wikidocs.net/263
🏠 반복문
✏️ 반복문이란?
💡 반복문이란 설정된 조건에 맞으면 실행되도록 하는 명령문이다. 💡 “만약 ~라면 게속 ~해라”라는 의미이다.
✏️ While문
while(조건){ //만약 조건이라면 게속 ~해라
반복 실행 영역
}public class main{
public static void main(String[] args){
int treeHit = 0;
while (treeHit < 10) { //1~9번까지 게속해라
treeHit++;
System.out.println("나무를 " + treeHit + "번 찍었습니다.");
if (treeHit == 10) { //10이라면
System.out.println("나무 넘어갑니다.");
}
}
}출력 결과:
나무를 1번 찍었습니다.
나무를 2번 찍었습니다.
나무를 3번 찍었습니다.
나무를 4번 찍었습니다.
나무를 5번 찍었습니다.
나무를 6번 찍었습니다.
나무를 7번 찍었습니다.
나무를 8번 찍었습니다.
나무를 9번 찍었습니다.
나무를 10번 찍었습니다.
나무 넘어갑니다.⏰ 백준 문제 풀이
1000번
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int A = in.nextInt();
int B = in.nextInt();
System.out.println(A+B);
in.close();
}
}1001번
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int A = in.nextInt();
int B = in.nextInt();
System.out.println(A-B);
in.close();
}
}10998번
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int A = in.nextInt();
int B = in.nextInt();
System.out.println(A*B);
in.close();
}
}1008번
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
double a=in.nextDouble();
double b=in.nextDouble();
in.close();
System.out.print(a/b);
}
}10869번
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
sc.close();
System.out.println(a + b);
System.out.println(a - b);
System.out.println(a * b);
System.out.println(a / b);
System.out.println(a % b);
}
}10926번
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc= new Scanner(System.in);
String str = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println(str+"??!");
}
}18108번
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print(n-543);
}
}10430번
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int A = in.nextInt();
int B = in.nextInt();
int C = in.nextInt();
in.close();
System.out.println( (A+B)%C );
System.out.println( (A%C + B%C)%C );
System.out.println( (A*B)%C );
System.out.println( (A%C * B%C)%C );
}
}2588번
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int A = in.nextInt();
String B = in.next();
in.close();
System.out.println(A * (B.charAt(2) - '0'));
System.out.println(A * (B.charAt(1) - '0'));
System.out.println(A * (B.charAt(0) - '0'));
System.out.println(A * Integer.parseInt(B));
}
}1330번
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int A = in.nextInt();
int B = in.nextInt();
in.close();
if(A>B) System.out.println(">");
else if(A<B) System.out.println("<");
else System.out.println("==");
}
}9498번
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int A = in.nextInt();
in.close();
if(A>=90) System.out.println("A");
else if(A>=80) System.out.println("B");
else if (A>=70) System.out.println("C");
else if(A>=60) System.out.println("D");
else System.out.println("F");
}
}2753번
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int y = in.nextInt();
in.close();
if(y%4==0) {
if(y%400==0) System.out.println("1");
else if(y%100==0) System.out.println("0");
else System.out.println("1");
}
else System.out.println("0");
}
}