- Destructuring Arrays
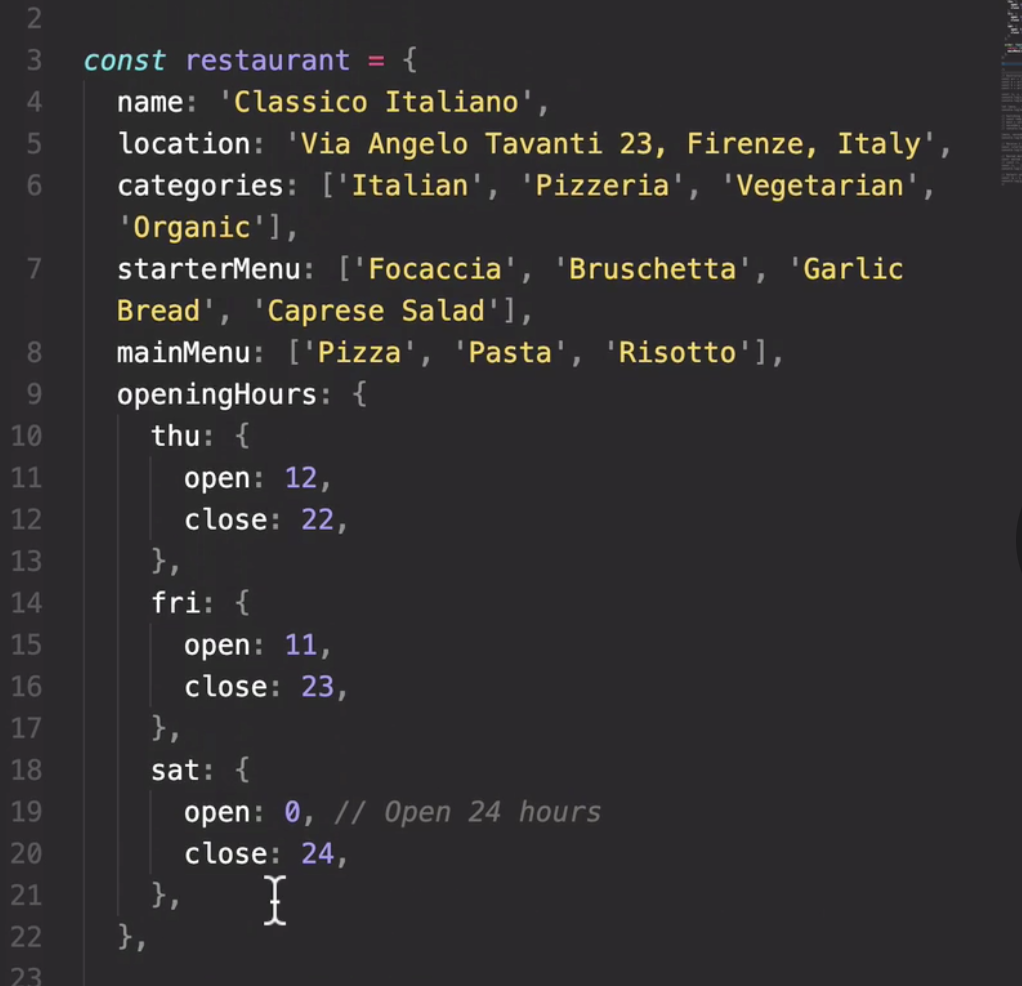
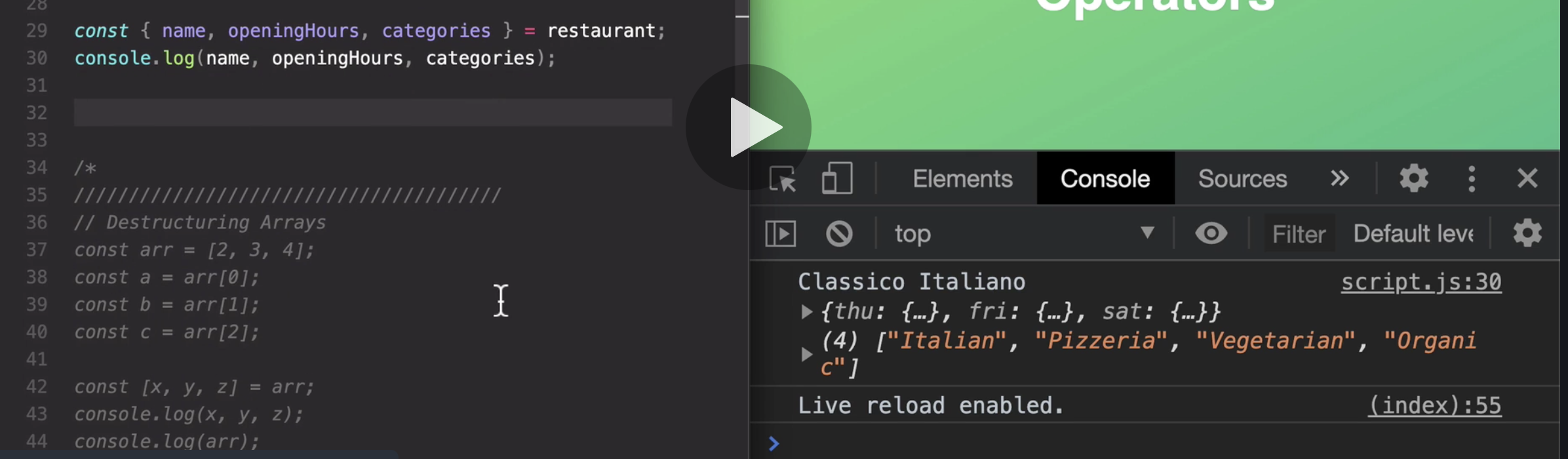
that these three are actually the exact same name, but we were able to give them new variable names. Which again that's gonna be immensely helpful
when dealing with third-party data.
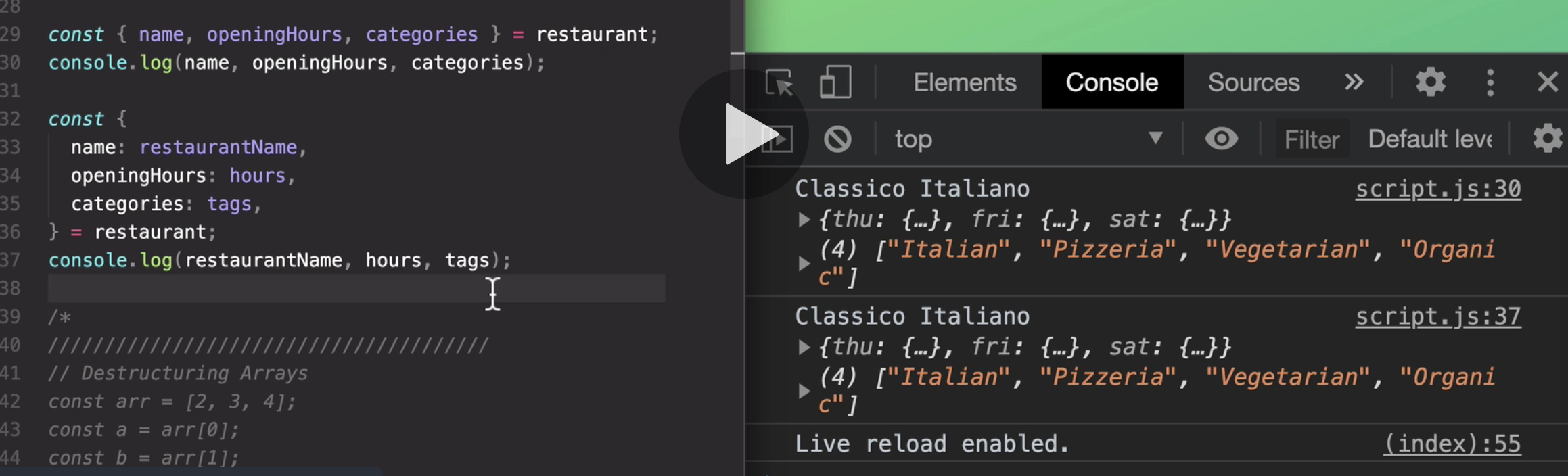
And another useful feature for when we are dealing with third-party data like that.
So like an object that we get from somewhere else,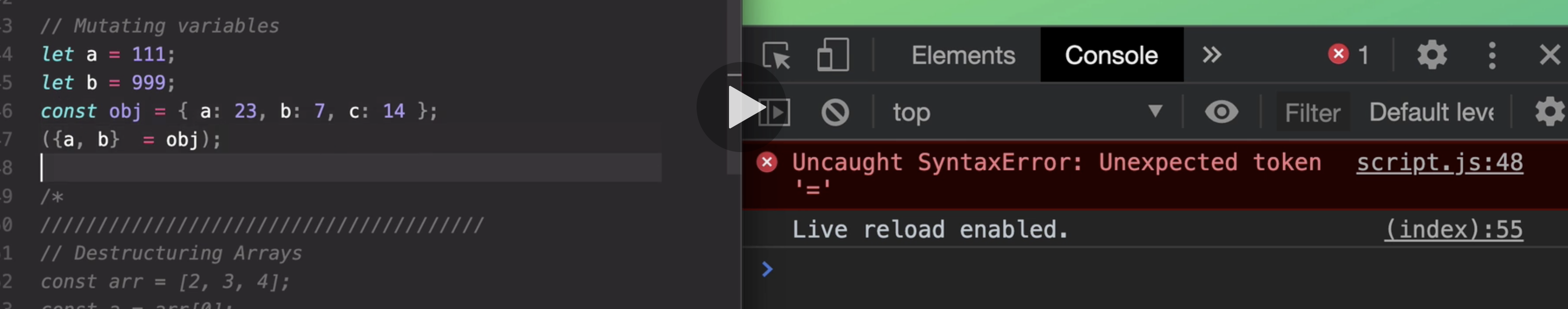
is that when we start a line with a curly brace like this,
then JavaScript expects a code block, all right?
And since we cannot assign anything to a code block like we did here with the equal sign,
then we get this error, unexpected token with the equal there.
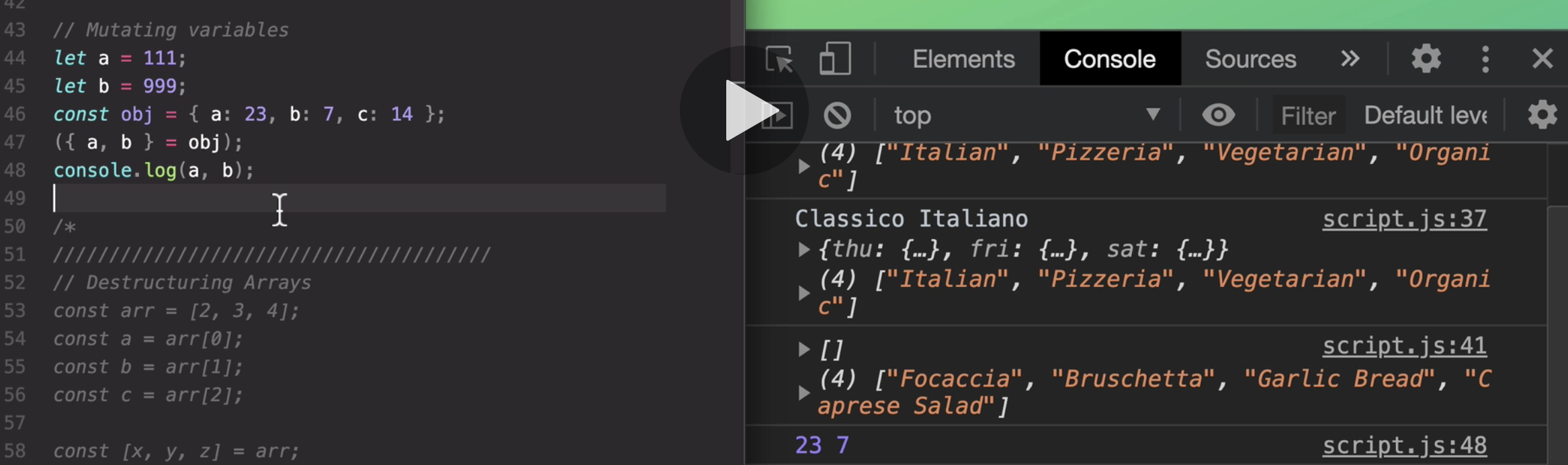
So to solve this here,
the trick is to wrap all of this into a parenthesis. And so that's the thing that I wanted to show you here.
object안에 object 가져오고 싶을때
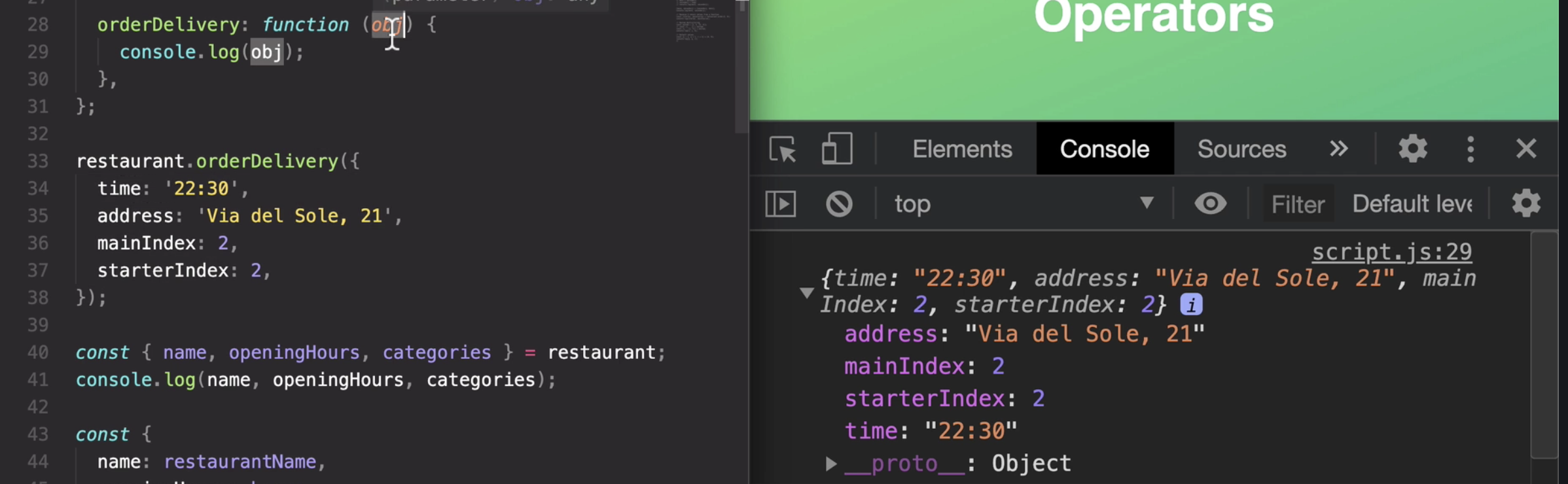
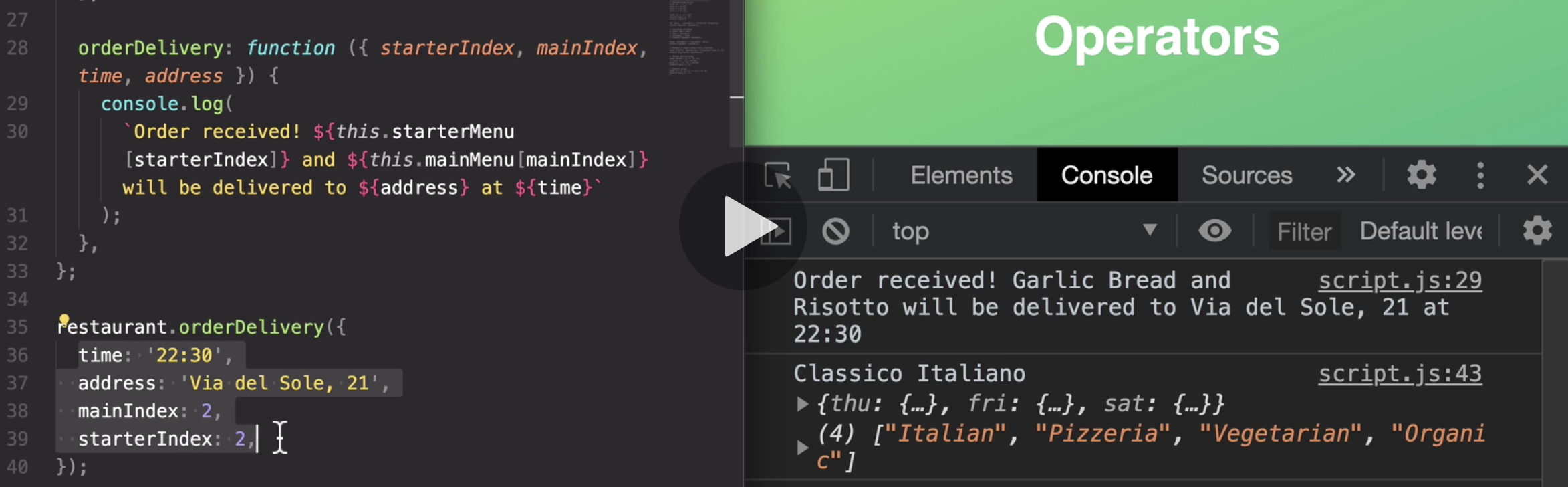
So what we just did was to call this function here and passing in an object of options.
- The Spread operator ( ...)
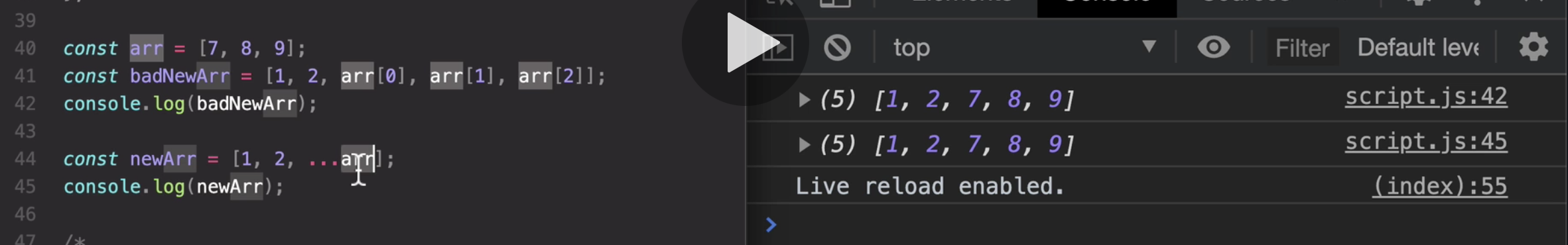
So what the spread operator does is to basically take all the values out of this arr. array, and then write them individually**
as if we wrote seven, eight, nine here manually.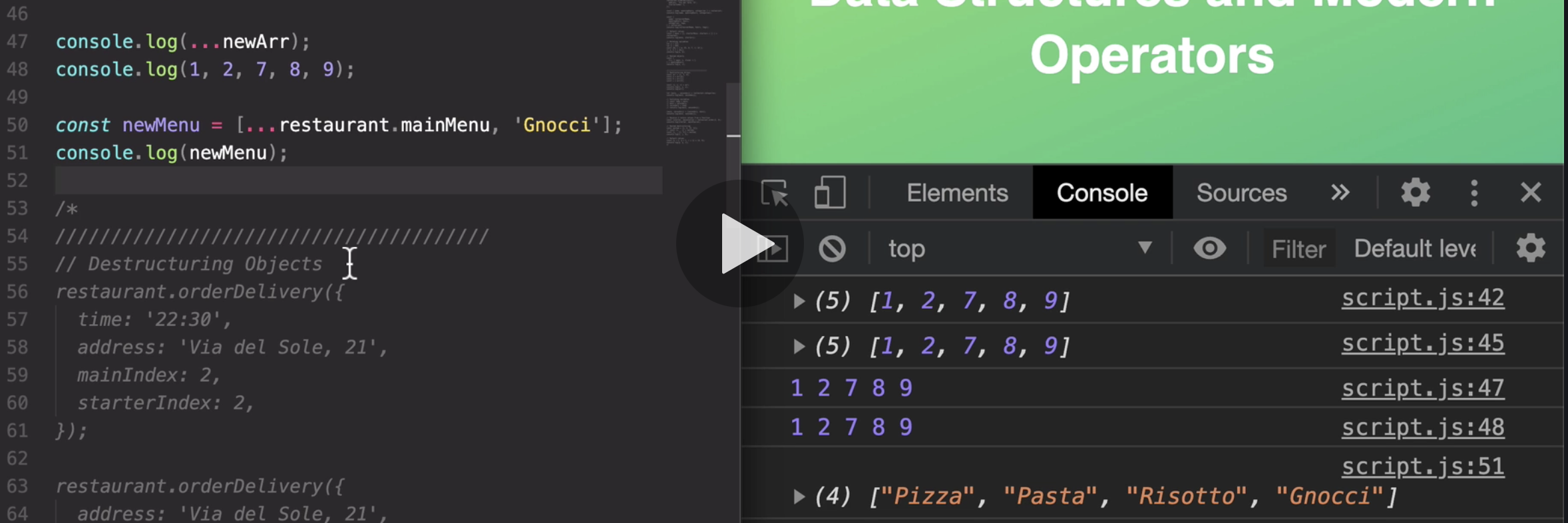
because actually, the spread operator works on all so-called iterables.
Now what is an iterable? Well, there are different iterables in JavaScript.
And we will talk about all of them by the end of the course,
but for now, just know that iterables are things like all arrays, strings, maps, or sets, but not objects.'
Now just keep in mind that we can still only use the spread operator
when building an array, or when we pass values into a function.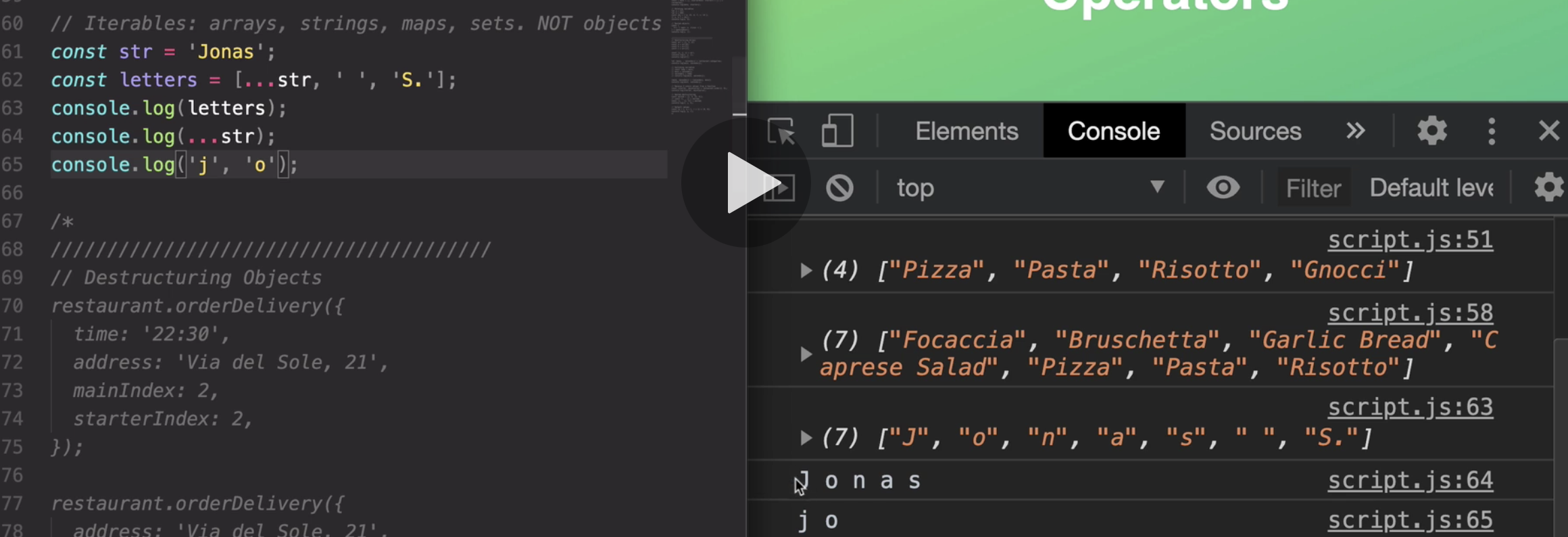
106. Rest Pattern and Parameters
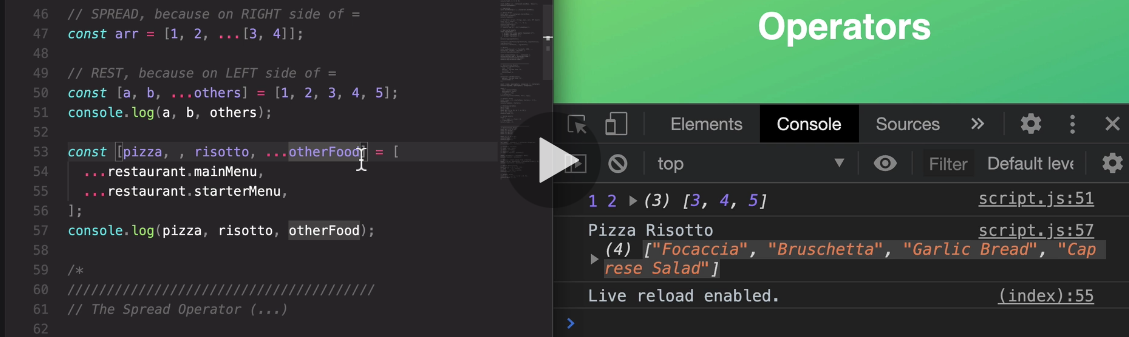
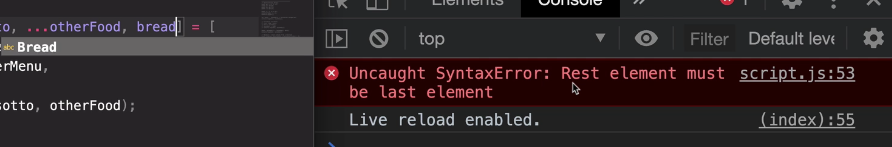
there can only ever be one rest in any destructuring assignment, okay
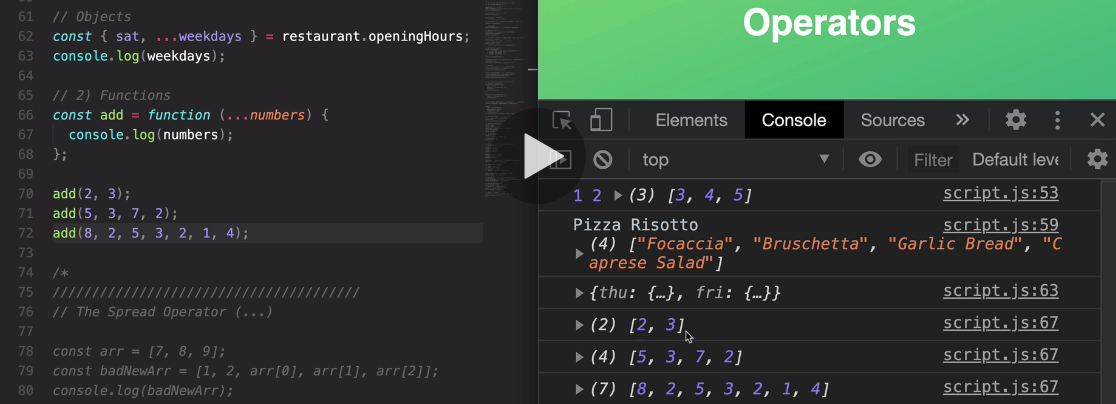
and so now once again, as I said in the beginning the rest syntax is taking multiple numbers or multiple values and then packs them all into one array.
107. Short Circuiting (&& and ||)
short circuiting means that if the first value is a truthy value,
it will immediately return that first value. So that's exactly what we see here with the three which is a truthy value.
So again, if the first operand is truthy here in the OR operator, then the other operand will not even be evaluated.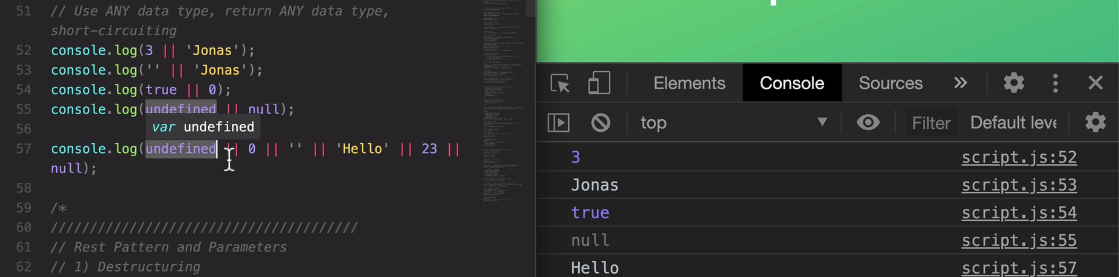
0, '' is falsy
But anyway, let's now summarize. So the OR operator will return the first truthy value of all the operands, or simply the last value if all of them are falsy.
||
왼쪽 값이 Truthy 하면 왼쪽 값을 리턴한다.
왼쪽 값이 Falsy 하면 오른쪽 값을 리턴한다.
So that's what happened here, right?
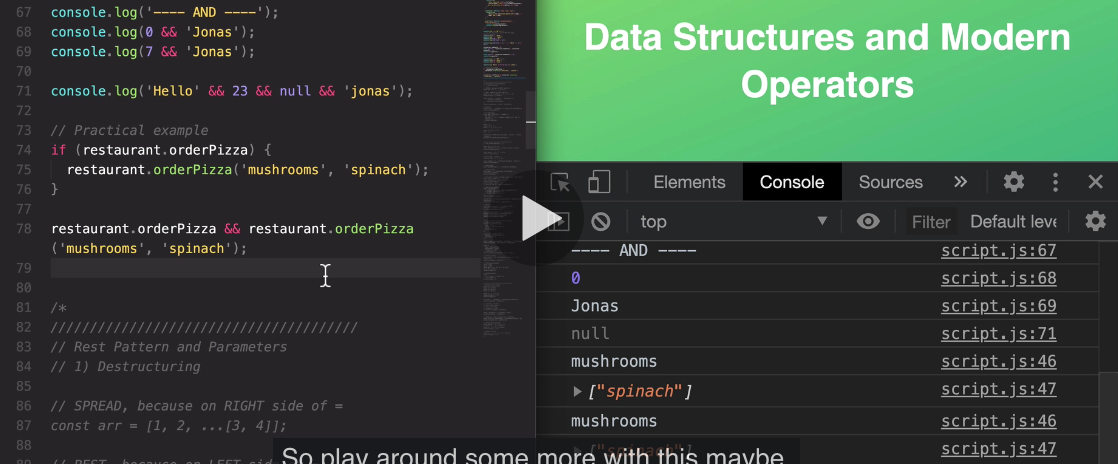
On the other hand, the AND operator will return the first falsy value or the last value if all of them are truthy.
And as for practical applications, we can use the OR operator to set default values, and we can use the AND operator to execute code in the second operand if the first one is true.
&&
첫번째 value가 true이면 두번째 value를 실행
왼쪽 값이 Truthy 하면 오른쪽 값이 리턴된다.
왼쪽 값이 Falsy 왼쪽 값이 리턴된다.
108. The Nullish Coalescing Operator (??)
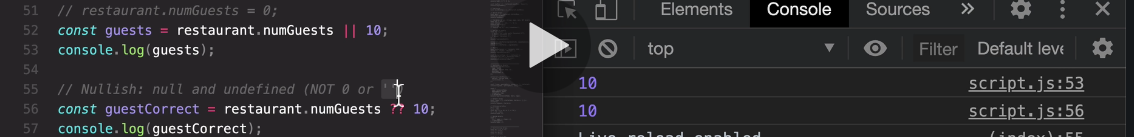
So basically, for the nullish coalescing operator,
it is as if the zero and the empty stringwere not falsy values and were instead truthy values as well.
Okay, so only if this was null or undefined,only then the second operand here would be executed and returned.
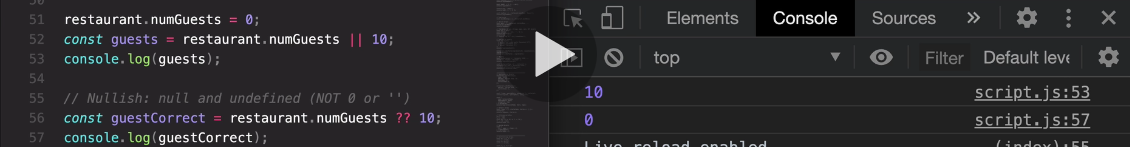
and zero is not a nullish value. And therefore, the evaluation here is short circuited, and immediately, this first non-nullish value is returned.
