
Chapter 14 : 다 배운 것 같지만, 예외라는 중요한 것이 있어요
5. 두 개 이상의 catch
Java 에도 당연히 Exception Handling 이 존재한다. 이는 Python 의 try-except 와 상당히 유사하다. (둘 사이간 차이가 거의 없어 보일 정도)
Java 에서는 try-catch 구문을 통해 예외처리를 할 수 있다.
int[] array = new int[5];
try {
System.out.println(array[50]);
}
// catch (Exception e) {System.out.println("Unexpected Exception");} // compile error
// Unresolved compilation problems:
// Unreachable catch block for NullPointerException. It is already handled by the catch block for Exception
// Unreachable catch block for ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException. It is already handled by the catch block for Exception
// Unreachable catch block for Exception. It is already handled by the catch block for Exception
catch (NullPointerException e) {System.out.println("NullPointerException");}
catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {System.out.println("ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException");}
catch (Exception e) {System.out.println("Unexpected Exception");}
finally {
System.out.println("End of test");
}ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
End of testJava 의 try-catch 구문은, (Python 에서와 동일하게) 다수의 예외처리를 진행할 때 앞서 부모 예외 클래스 를 catch 구문으로 선언하면 compile error 를 뱉어낸다.
6. 예외의 종류는 세 가지다
Java 에서 예외는 3 종류이다. Error, Runtime Exception, Checked Exception 이며, [1] 이에 대한 구현 관계를 나타내면 다음과 같다.
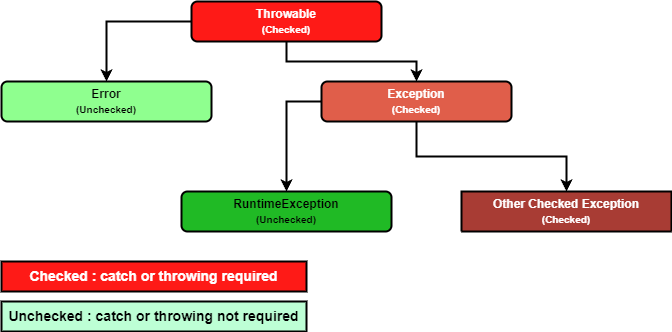
Java 의 클래스 파일을 뜯어보면 정말로 Error, RuntimeException 클래스가 존재하고, (java.lang.Error, java.lang.RuntimeException) 이를 상속하는 (자기 자신 포함) 모든 예외들은 Error 또는 RuntimeException 예외들이다.
하지만 Checked Exception 의 경우 CheckedException 과 같은 클래스는 존재하지 않고 그냥 알아서 잘 나눠 구현되어 있다.
또한 Throwable 클래스와 Exception 클래스 또한 Checked Exception 에 속하는데, 이는 Checked Exception 의 정의가 "Error, RuntimeException 을 제외한 모든 예외들" 이여서 그렇다. [2]
A. Checked Exception
Checked Exception 은 정말 간단히 말해 "compile error 를 일으킬 수 있는 예외들" 이다.
Oracle 의 공식 문서를 보면 Checked Exception 을 다음과 같이 정의하고 있다. [2]
"Checked Exception 은 Catch or Specify Requirement 의 대상이며, Error, RuntimeException 을 제외한 예외는 모두 Checked Exception 입니다."
여기서 말하는 "Catch or Specify Requirement" 란 다음과 같은 처리를 해야함을 의미한다. [5]
"Catch or Specify Requirement 는 예외가 발생할 수 있는 상황에서, 다음 두 처리 방법 중 적어도 하나를 수행하는 것을 의미합니다."try-catch구문을 이용한 예외 처리- 메서드 선언에
throws키워드를 이용해 호출된 메서드로 예외를 전달
"Catch or Specify Requirement 를 만족하지 못하는 코드는 compile 되지 않습니다."
이에 더불어 사실 Error 와 Runtime Exception 은 Catch or Specify Requirement 대상이 아니다. 때문에 Checked Exception 은 "어느 예외가 처리되지 않았을 때, compile error 를 일으키는 예외" 라 말할 수 있다.
B. Runtime Exception
교재에서는 이를 Unchecked Exception 이라고도 적었는데, 이는 좀 오해의 소지가 있을 것 같다.
말 그대로 "체크 되지 않는", Catch or Specify Requirement 를 만족하지 않아도 되는 예외는 Runtime Exception 과 Error 이며, 거기다 Unchecked 라는 이름 때문에 뭔가 Checked Exception 의 정 반대여야만 할 것 같기 때문이다.
Runtime Exception 은 Catch or Specify Requirement 의 대상이 아니므로 compile error 를 발생시키 않는다.
(교재에서 좀 더 설명이 붙어있지만 이렇게 마치는게 깔끔할 것 같다)
C. Error
Error 는 Java 프로그램 외적인 요인으로 인해 발생한 예외로, 대부분 critical 한 문제여서 개발자가 고칠 수단이 그렇게 없다.
교재에서 Error 와 Exception 의 차이는 프로세스에 영향을 주는지, 또는 스레드에 영향을 주는지 라고 한다. 이에 대한 설명은 나중에 스레드 부분에서 할 것이라 한다.
Reference
Exceptions - The Java™ Tutorials[1] : The Three Kinds of Exceptions[2]:Checked exceptionsare subject to theCatch or Specify Requirement. All exceptions arechecked exceptions, except for those indicated byError,RuntimeException, and their subclasses.[3]:Errorsare not subject to theCatch or Specify Requirement.Errorsare those exceptions indicated byErrorand its subclasses.[4]:Runtime exceptionsare not subject to theCatch or Specify Requirement.Runtime exceptionsare those indicated byRuntimeExceptionand its subclasses.
[5] : The Catch or Specify Requirement- This means that code that might throw certain exceptions must be enclosed by either of the following:
- A
trystatement that catches the exception. Thetrymust provide a handler for the exception, as described inCatching and Handling Exceptions. - A method that specifies that it can throw the exception. The method must provide a
throwsclause that lists the exception, as described inSpecifying the Exceptions Thrown by a Method.
- A
- This means that code that might throw certain exceptions must be enclosed by either of the following:
