
Chapter 16 : 클래스 안에 클래스가 들어갈 수도 있구나
1. 클래스 안의 클래스
Java 에도 클래스 안에 클래스가 들어갈 수 있다. 이러한 클래스를 "Nested Class" 라 부른다. Nested Class 선언 방식에 따라 Static Nested Class, Inner Class 로 나눌 수 있다. Inner Class 는 말 그대로 클래스 속에 정의된 클래스이고, Static Nested Class 는 이를 정적으로 정의한 클래스이다.
Nested Class 형태를 사용하는 가장 큰 이유는 코드를 간단히 표현하기 위함이다.
- 역할에 따라 클래스를 모아두어 코드가 보기 편함
(Static Nested Class) - 캡슐화를 이용해 좀 더 안전한 코드를 만들 수 있음
(Inner Class) - 이를 통해 코드의 가독성과 유지보수성을 높임
Java 에서 Nested Class 는 대개 Java 기반의 UI 를 처리할 때, 사용자의 입력이나 외부 이벤트에 대한 처리를 할 때 사용된다.
Inner Class 는 또 2 가지로 나눌 수 있는데, Local Inner Class, Anonymous Inner Class 이다.
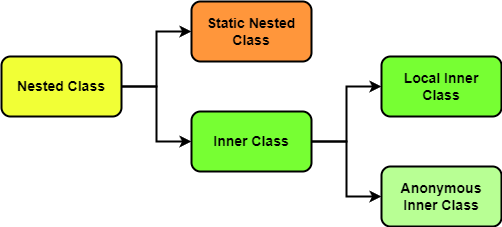
Nested Class 는 쉽게말해 "Outer Class 를 어느정도 사용할 수 있는 package" 라 할 수 있다.
다음 예시를 보자.
class OuterClass {
public int OuterValue = 10;
public InnerClass inner = new InnerClass();
class InnerClass {
public int InnerValue;
public void innerMethod() {
System.out.println("can access to OuterValue\t: " + OuterValue);
}
}
public void outerMethod() {
System.out.println("OuterClass can not access to InnerValue");
System.out.print("But InnerClass ");
inner.innerMethod();
}
}
OuterClass outerClass = new OuterClass();
OuterClass.InnerClass innerClass = outerClass.new InnerClass();
outerClass.OuterValue = 5;
outerClass.outerMethod(); System.out.println();
innerClass.innerMethod(); System.out.println();
System.out.println("hashCode\tidentityHashCode");
System.out.println(
String.format("0x%8x", outerClass.inner.hashCode()) + "\t" +
String.format("0x%8x", System.identityHashCode(outerClass.inner))
);
System.out.println(
String.format("0x%8x", innerClass.hashCode()) + "\t" +
String.format("0x%8x", System.identityHashCode(innerClass))
);OuterClass can not access to InnerValue
But InnerClass can access to OuterValue : 5
can access to OuterValue : 5
hashCode identityHashCode
0x2f2c9b19 0x2f2c9b19
0x7cca494b 0x7cca494bInnerClass 에서는 OuterClass 의 필드에 접근할 수 있다. 반면 OuterClass 에서는 InnerClass 의 필드에 접근할 수 없다.
innerClass 객체는 outerClass 로 인해 생성되었으므로, OuterValue 의 참조가 유지된다. 그래서 OuterValue 가 5 로 바뀌었음에도 그대로 유지됨을 볼 수 있다.
(OuterValue 의 참조만 유지될 뿐, outerClass.inner 인스턴스와 innerClass 객체가 동일하다는 것은 아니다)
2. static nested 클래스의 특징
Static Nested Class 는 static 키워드를 이용해 정의한 Inner Class 이다.
하지만 이로 인해 시스템 성능에 큰 차이를 이끌 수 있는데, Outer Class 가 GC 에 의해 수거될 수도 있고 아닐 수 있기 때문이다.
일반적으로 Java 의 GC 는 어느 객체가 "닿을 수 없는" (Unreachable), 즉 객체가 어디에서도 참조되지 않을 때 어느순간 해당 객체가 존재하는 메모리를 청소한다.
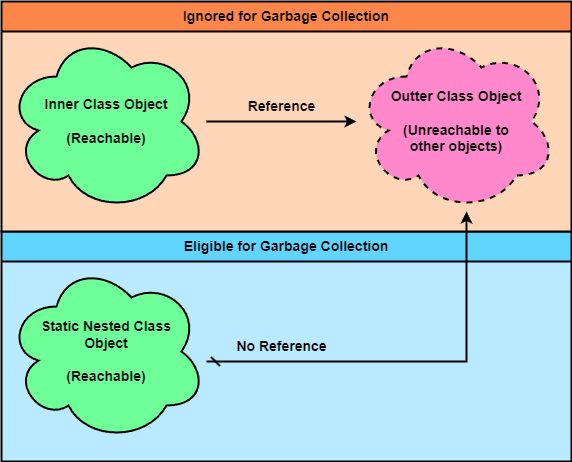
그런데 Inner Class 는 항상 어느 Outer Class 객체에 대한 참조를 가지고 있다. 때문에 Outer Class 객체가 다른 객체에 의한 참조가 없더라 해도, Inner Class 객체가 어딘가에서 Reachable 한 이상 GC 에 의해 수거되지 않는다. (Inner Class, Outer Class 모두 Unreachable 해야 수거된다)
반면 Static Nested Class 의 경우 Outer Class 객체의 참조를 가지고 있지 않다. 따라서 Inner Class 의 경우와 다르게 GC 의 수거대상에 올라간다.
또한 Static Nested Class 는 "Outer Class 에 대한 static 한 참조를 가질 뿐, static 하지 않은" 점에 유의해야 한다.
class OuterClassStatic {
public static int OuterValueStatic = 15;
public InnerClassStatc inner = new InnerClassStatc();
static class InnerClassStatc {
public int InnerValue;
public void innerMethod() {
System.out.println("can only access to OuterValueStatic\t: " + OuterValueStatic);
}
}
public void outerMethod() {
System.out.println("OuterClassStatic can not access to InnerValue");
System.out.print("But InnerClassStatc ");
inner.innerMethod();
}
}
OuterClassStatic outerClassStatic = new OuterClassStatic();
OuterClassStatic.InnerClassStatc innerClassStatc = new OuterClassStatic.InnerClassStatc();
OuterClassStatic.OuterValueStatic = 10;
outerClassStatic.outerMethod(); System.out.println();
innerClassStatc.innerMethod(); System.out.println();
System.out.println("hashCode\tidentityHashCode");
System.out.println(
String.format("0x%8x", outerClassStatic.inner.hashCode()) + "\t" +
String.format("0x%8x", System.identityHashCode(outerClassStatic.inner))
);
System.out.println(
String.format("0x%8x", innerClassStatc.hashCode()) + "\t" +
String.format("0x%8x", System.identityHashCode(innerClassStatc))
);OuterClassStatic can not access to InnerValue
But InnerClassStatc can only access to OuterValueStatic : 10
can only access to OuterValueStatic : 10
hashCode identityHashCode
0x2f2c9b19 0x2f2c9b19
0x7cca494b 0x7cca494b만약 OuterClassStatic.InnerClassStatc 클래스가 여타 static 필드와 같았다면, outerClassStatic.inner 객체와 innerClassStatc 객체의 identityHashCode 가 동일해야 한다.
하지만 이 둘은 다르다. OuterClassStatic.InnerClassStatc 클래스 는 OuterClassStatic 클래스 에 대한 참조를 가지고 있을 뿐, 그저 객체간 참조와 다르다는 것이다.
(OuterValueStatic 는 애초에 그냥 static 필드이므로 이를 공유하는 것은 당연하다)
3. 내부 클래스와 익명 클래스
내부 클래스 (Inner Class)
앞서 1. 클래스 안의 클래스 에서 Inner Class 에 대한 예시를 보았다. Inner Class 객체를 생성하기 위해선 다음과 같이 만들 수 있다.
class OuterClass {
class InnerClass {}
}
OuterClass outer = new OuterClass();
OuterClass.InnerClass inner1 = outer.new InnerClass();
OuterClass.InnerClass inner2 = new OuterClass().new InnerClass();위 문법에서 Inner Class 에 대한 특징을 잘 보여준다. OuterClass 타입 객체를 생성하지 않고는 OuterClass.InnerClass 타입 객체를 생성할 수 없기 때문이다.
때문에 이를 생성하기 위해선 OuterClass 타입 객체를 생성한 후 outer.new InnerClass(), new OuterClass().new InnerClass() 와 같이 생성할 수밖에 없다.
익명 클래스 의 경우, 교재에서 마음에 드는 정의가 없어 추가로 찾아봤다. 그 결과 익명 내부 클래스 (Anonymous Inner Class) 와 익명 클래스 (Anonymous Class) 가 비슷하면서도 다른 것을 확인하였다.
익명 클래스 (Anonymous Class)
익명 클래스 는 interface, 추상 클래스 등을 클래스 선언 없이 확장 (extends) 하거나 구현 (implements) 한 클래스이다.
interface SomeInterface {
default public void method1() {
System.out.println("SomeInterface method1 origin");
}
public void method2();
}
abstract class SomeClass {
public abstract void method1();
public void method2() {
System.out.println("SomeClass method2 origin");
}
}
SomeInterface anonymousClass1 = new SomeInterface() {
@Override
public void method2() {
System.out.println("SomeInterface method2 modified");
}
};
SomeClass anonymousClass2 = new SomeClass() {
@Override
public void method1() {
System.out.println("SomeClass method1 modified");
}
};
anonymousClass1.method1();
anonymousClass1.method2(); System.out.println();
anonymousClass2.method1();
anonymousClass2.method2();SomeInterface method1 origin
SomeInterface method2 modified
SomeClass method1 modified
SomeClass method2 origin이전 interface, 추상 클래스 에서는 이를 상속하여 새로운 클래스를 만들거나 하였다. 하지만 굳이 새로운 클래스를 만들지 않아고 특정 메서드만 Override 하면 되는 경우, 위처럼 익명 클래스 방법을 사용해 좀더 간결한 코드를 만들 수 있다.
익명 내부 클래스 (Anonymous Inner Class)
익명 내부 클래스 는 위 interface, 추상 클래스 등이 Inner Class 로 바뀐 것일 뿐이다.
class OuterClass {
class InnerClass {
public void someInnerMethod() {
System.out.println("Inner Method origin");
}
}
public void someMethod(InnerClass input) {
if (input.getClass() != InnerClass.class) return;
System.out.println("Outer Method origin");
}
}
OuterClass outer = new OuterClass() {
@Override
public void someMethod(InnerClass input) {
System.out.println("Outer Method modified");
}
};
OuterClass.InnerClass anonymousInnerClass = new OuterClass().new InnerClass() {
@Override
public void someInnerMethod() {
System.out.println("Inner Method modified");
}
};
outer.someMethod(new OuterClass().new InnerClass());
anonymousInnerClass.someInnerMethod();이전 익명 클래스 에서와 동일하게 어느 메서드를 Override 할 수 있다.
이처럼 "뭔가를 만들어야 됐었는데 만들지 않거나, 객체를 숨기는 방식" 이기 때문에 익명 이라는 단어가 붙은 것 같다.
4. Nested 클래스의 특징은 꼭 알아야 한다
지금까지 클래스의 선언 방식에 따른 Nested Class 을 알아 보았다. 그러면서 잠시 Nested Class 에서 Outer Class 의 필드를 참조하는 것을 보았고, 그 반대는 할 수 없는 것을 보았다.
이를 제대로 알아보자.
Static Nested Class 에서 참조 가능한 범위
Static Nested Class 는 접근제한자에 상관 않고 Outer Class 의 Static 필드에만 접근할 수 있다. 이는 Outer Class 또한 마찬가지이다.
class OuterClass {
public String publicScope = "publicScope";
public static String pubStaticScope = "pubStaticScope";
String packScope = "packScope";
static String packStaticScope = "packStaticScope";
protected String proScope = "proScope";
protected static String proStaticScope = "proStaticScope";
private String priScope = "priScope";
private static String priStaticScope = "priStaticScope";
static class StaticNestedClass {
public String publicInnerScope = "publicInnerScope";
public static String pubStaticInnerScope = "pubStaticInnerScope";
String packInnerScope = "packInnerScope";
static String packStaticInnerScope = "packStaticInnerScope";
protected String proInnerScope = "proInnerScope";
protected static String proStaticInnerScope = "proStaticInnerScope";
private String priInnerScope = "priInnerScope";
private static String priStaticInnerScope = "priStaticInnerScope";
public void method() {
System.out.println("StaticNestedClass can only access to static fields: ");
System.out.println(pubStaticScope);
System.out.println(packStaticScope);
System.out.println(priStaticScope);
System.out.println(proStaticScope);
// System.out.println(publicScope); compile error: non-static variable priScope cannot be referenced from a static context
// System.out.println(packScope);
// System.out.println(proScope);
// System.out.println(priScope);
}
}
public void method() {
System.out.println("OuterClass can only access to static inner fields:");
System.out.println(OuterClass.StaticNestedClass.pubStaticInnerScope);
System.out.println(OuterClass.StaticNestedClass.packStaticInnerScope);
System.out.println(OuterClass.StaticNestedClass.priStaticInnerScope);
System.out.println(OuterClass.StaticNestedClass.proStaticInnerScope);
// System.out.println(OuterClass.StaticNestedClass.publicInnerScope); compile error: non-static variable publicInnerScope cannot be referenced from a static context
// System.out.println(OuterClass.StaticNestedClass.packInnerScope);
// System.out.println(OuterClass.StaticNestedClass.proInnerScope);
// System.out.println(OuterClass.StaticNestedClass.priInnerScope);
}
}
OuterClass outerClass = new OuterClass();
OuterClass.StaticNestedClass staticNestedClass = new OuterClass.StaticNestedClass();
staticNestedClass.method(); System.out.println();
outerClass.method();StaticNestedClass can only access to static fields:
pubStaticScope
packStaticScope
priStaticScope
proStaticScope
OuterClass can only access to static inner fields:
pubStaticInnerScope
packStaticInnerScope
priStaticInnerScope
proStaticInnerScope만약 non-static 한 필드에 접근할 시, static context 에서 접근할 수 없다는 컴파일 에러를 뱉어낸다.
Inner Class 에서 참조 가능한 범위
반면 Inner Class 의 경우 많이 다른데, Inner Class 에서 Outer Class 의 필드를 접근하는데는 아무런 제한도 없지만, Outer Class 에서 Inner Class 의 경우 상당히 제한된다.
class OuterClass {
public String publicScope = "publicScope";
public static String pubStaticScope = "pubStaticScope";
String packScope = "packScope";
static String packStaticScope = "packStaticScope";
protected String proScope = "proScope";
protected static String proStaticScope = "proStaticScope";
private String priScope = "priScope";
private static String priStaticScope = "priStaticScope";
class InnerClass {
public String publicInnerScope = "publicInnerScope";
public static String pubStaticInnerScope = "pubStaticInnerScope";
String packInnerScope = "packInnerScope";
static String packStaticInnerScope = "packStaticInnerScope";
protected String proInnerScope = "proInnerScope";
protected static String proStaticInnerScope = "proStaticInnerScope";
private String priInnerScope = "priInnerScope";
private static String priStaticInnerScope = "priStaticInnerScope";
public void method() {
System.out.println("InnerClass can access to every field: ");
System.out.println(pubStaticScope);
System.out.println(packStaticScope);
System.out.println(priStaticScope);
System.out.println(proStaticScope);
System.out.println(publicScope);
System.out.println(proScope);
System.out.println(priScope);
}
}
public void method() {
System.out.println("OuterClass can only access to static inner field bypass:");
System.out.println(OuterClass.InnerClass.pubStaticInnerScope);
System.out.println(OuterClass.InnerClass.packStaticInnerScope);
System.out.println(OuterClass.InnerClass.proStaticInnerScope);
System.out.println(OuterClass.InnerClass.priStaticInnerScope);
}
}
OuterClass outerClass = new OuterClass();
OuterClass.InnerClass innerClass = new OuterClass(). new InnerClass();
innerClass.method(); System.out.println();
outerClass.method(); System.out.println();
System.out.println("Outside of class, can not access to private-static field");
// System.out.println(OuterClass.InnerClass.priStaticInnerScope); compile error: priStaticInnerScope has private access in OuterClass.InnerClassInnerClass can access to every field:
pubStaticScope
packStaticScope
priStaticScope
proStaticScope
publicScope
proScope
priScope
OuterClass can only access to static inner field bypass:
pubStaticInnerScope
packStaticInnerScope
proStaticInnerScope
priStaticInnerScope
Outside of class, can not access to private-static field예시를 보면 InnerClass 에서는 모든 필드에 접근 가능하다. 하지만 OuterClass 에서는 어떠한 인스턴스 필드에 접근이 불가능하고 오직 static 필드만 접근 가능하다.
+ 사실 위 OuterClass 에서 InnerClass 필드에 접근할 수 있는 방법이 하나 있다. 그리고 이는 Static Nested Class 의 경우에도 적용 가능하다.
class OuterClass {
public String var = "String origin";
static class StaticNested {
private String staticPrivate = "staticPrivate";
}
class Inner {
private String innerPrivate = "innerPrivate";
public void method() {
System.out.println(var);
}
}
public void method() {
System.out.println("Actually, we can access(?) to those fields like this :");
OuterClass.StaticNested staticNested = new OuterClass.StaticNested();
OuterClass.Inner inner1 = new OuterClass(). new Inner();
OuterClass.Inner inner2 = new Inner();
System.out.println(staticNested.staticPrivate);
System.out.println(inner1.innerPrivate); System.out.println();
inner1.method();
inner2.method();
}
}
OuterClass outerClass = new OuterClass();
outerClass.var = "String modified";
outerClass.method();Actually, we can access(?) to those fields like this :
staticPrivate
innerPrivate
String origin
String modified어찌 생각하면 좀 당연한 논리이다. 새롭게 생성한 객체기는 하지만 여전히 OuterClass 안에 있기 때문이다.
또한 여기서 한가지 새로운 사실을 알아내었는데, inner1 와 inner2 의 차이이다.
inner1 은 새로운 OuterClass 에서 파생된 Inner 객체이다. 반면 inner2 는 현재 메서드가 실행되고 있는 OuterClass 에서 파생된 객체이다.
때문에 inner1.method(), inner2.method() 를 비교해보면 서로 다름을 알 수 있다. outerClass.method() 를 호출하기 전, outerClass.var 의 값을 바꿔, inner2 가 참조하는 var 가 바뀌었기 때문이다.
