JDBC 이해
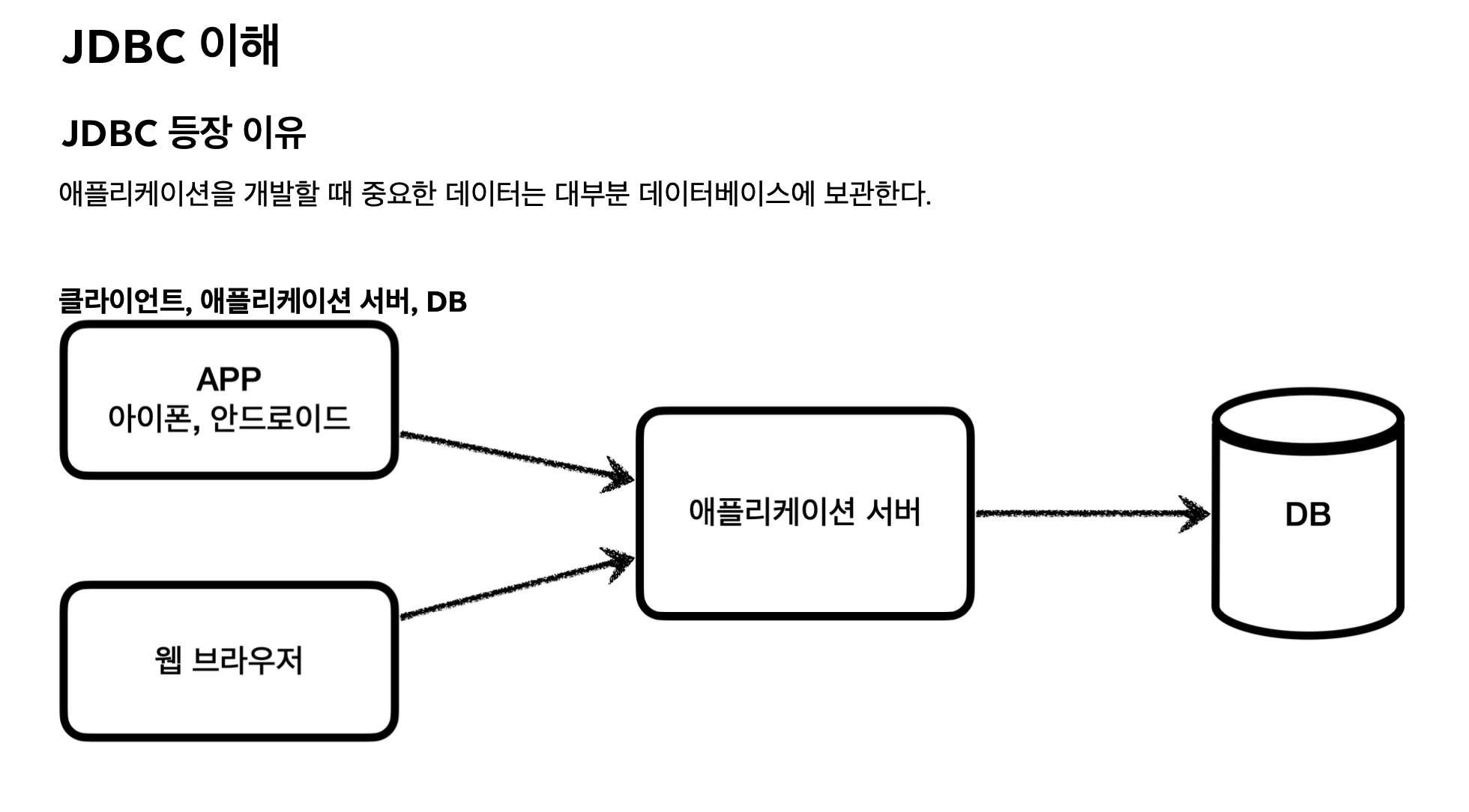
JDBC 등장 이유
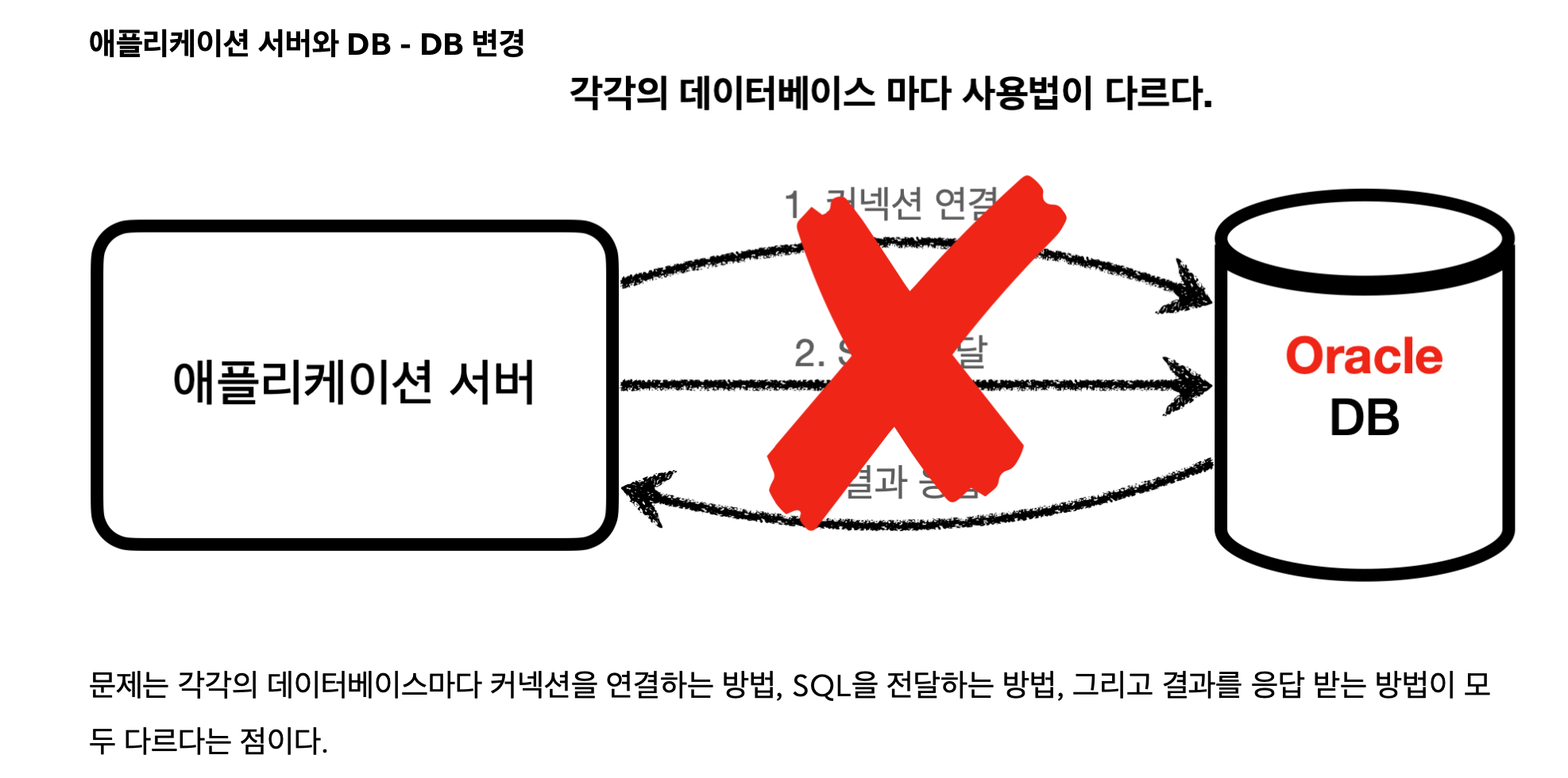
- 데이터베이스를 다른 종류의 데이터베이스로 변경하면 애플리케이션 서버에 개발된 데이터베이스 사용 코드도 함
께 변경해야 한다. - 개발자가 각각의 데이터베이스마다 커넥션 연결, SQL 전달, 그리고 그 결과를 응답 받는 방법을 새로 학습해야
한다.
이런 문제를 해결하기 위해 JDBC라는 자바 표준이 등장한다.
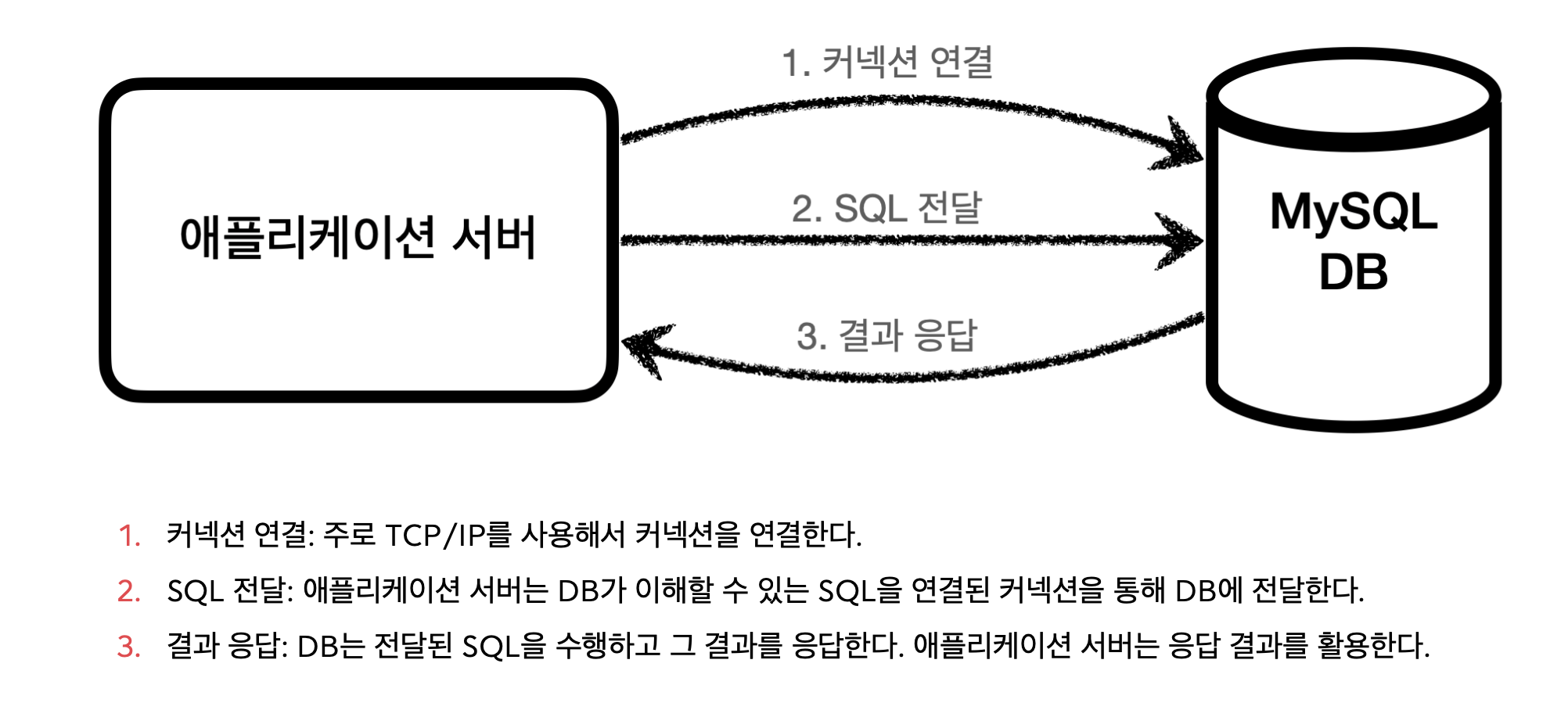
JDBC(Java Database Connectivity)는 자바에서 데이터베이스에 접속할 수 있도록 하는 자바 API다. JDBC
는 데이터베이스에서 자료를 쿼리하거나 업데이트하는 방법을 제공한다. - 위키백과
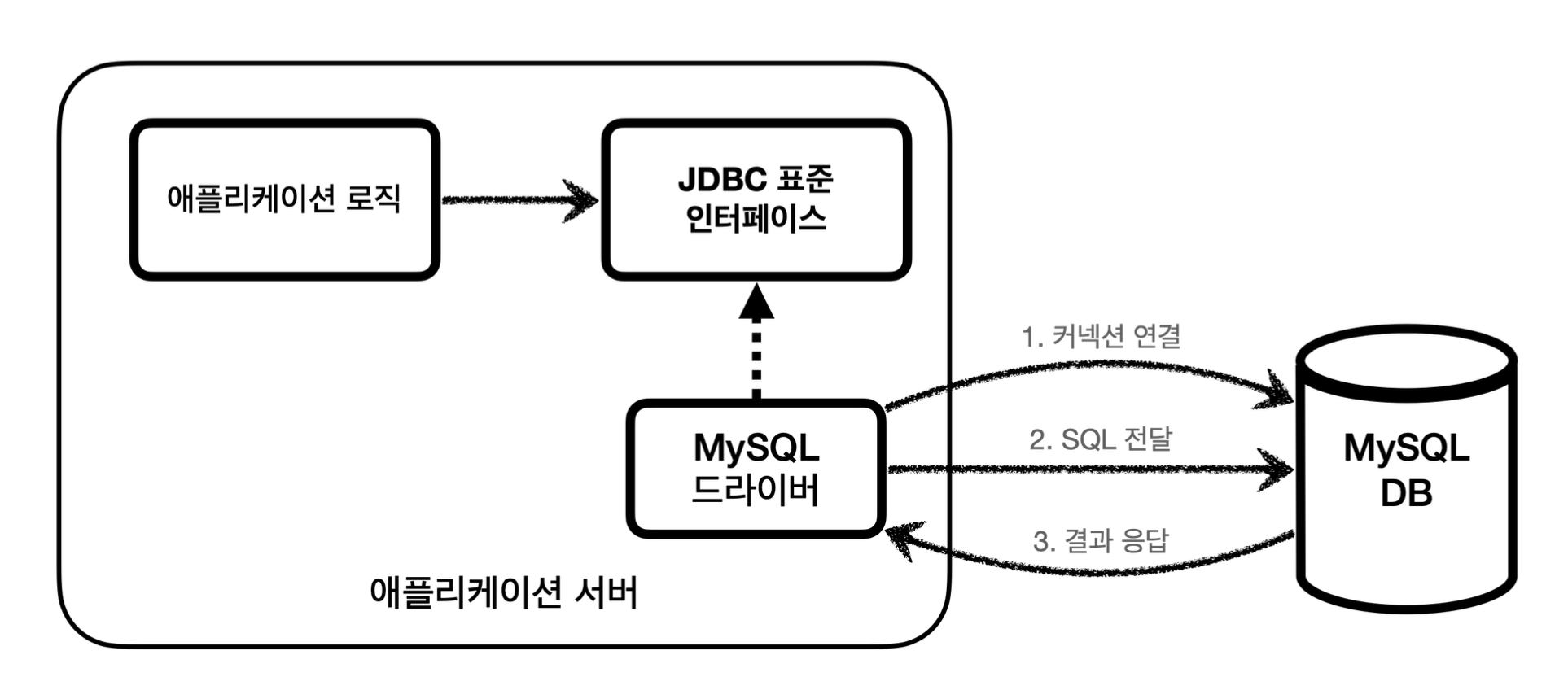
JDBC 표준 인터페이스
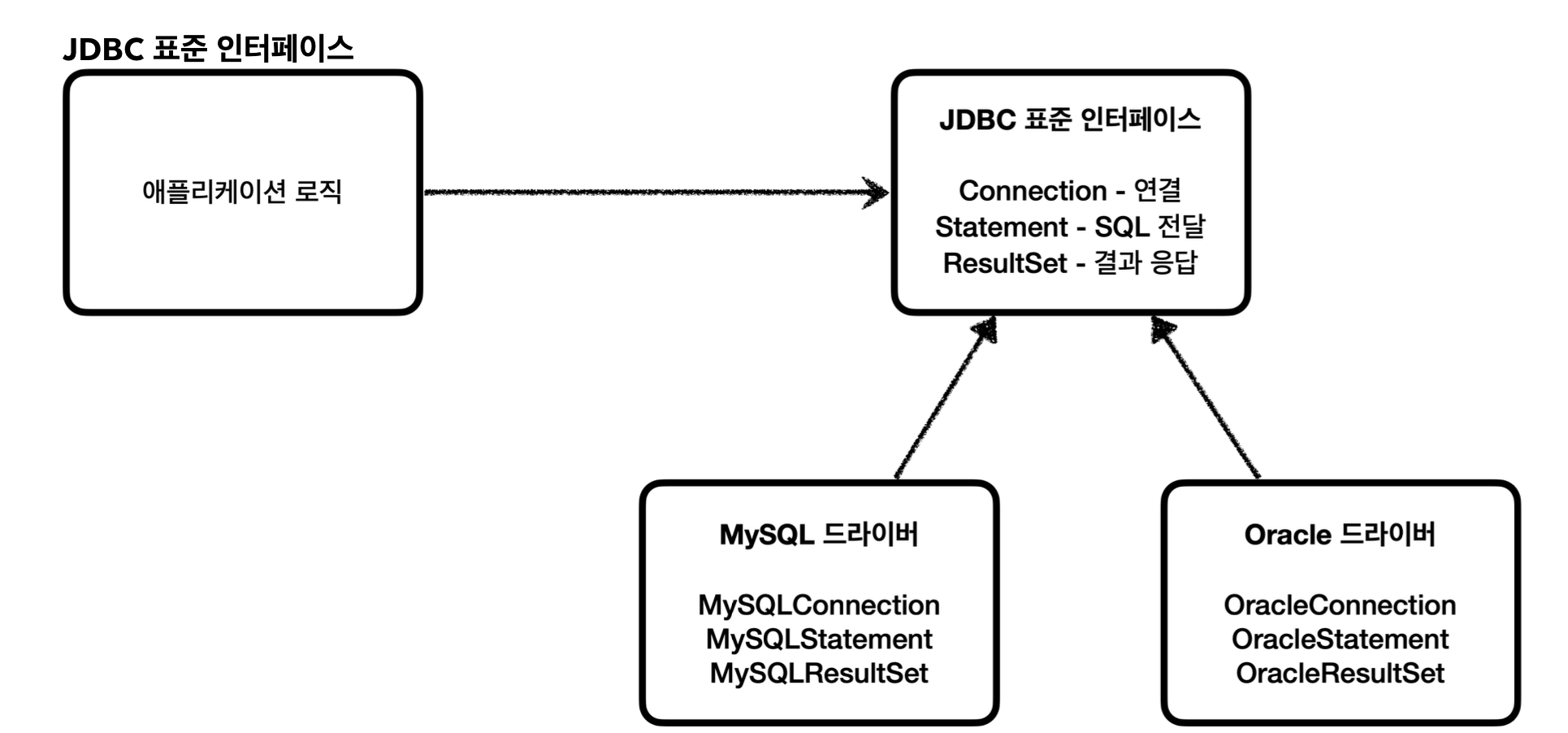
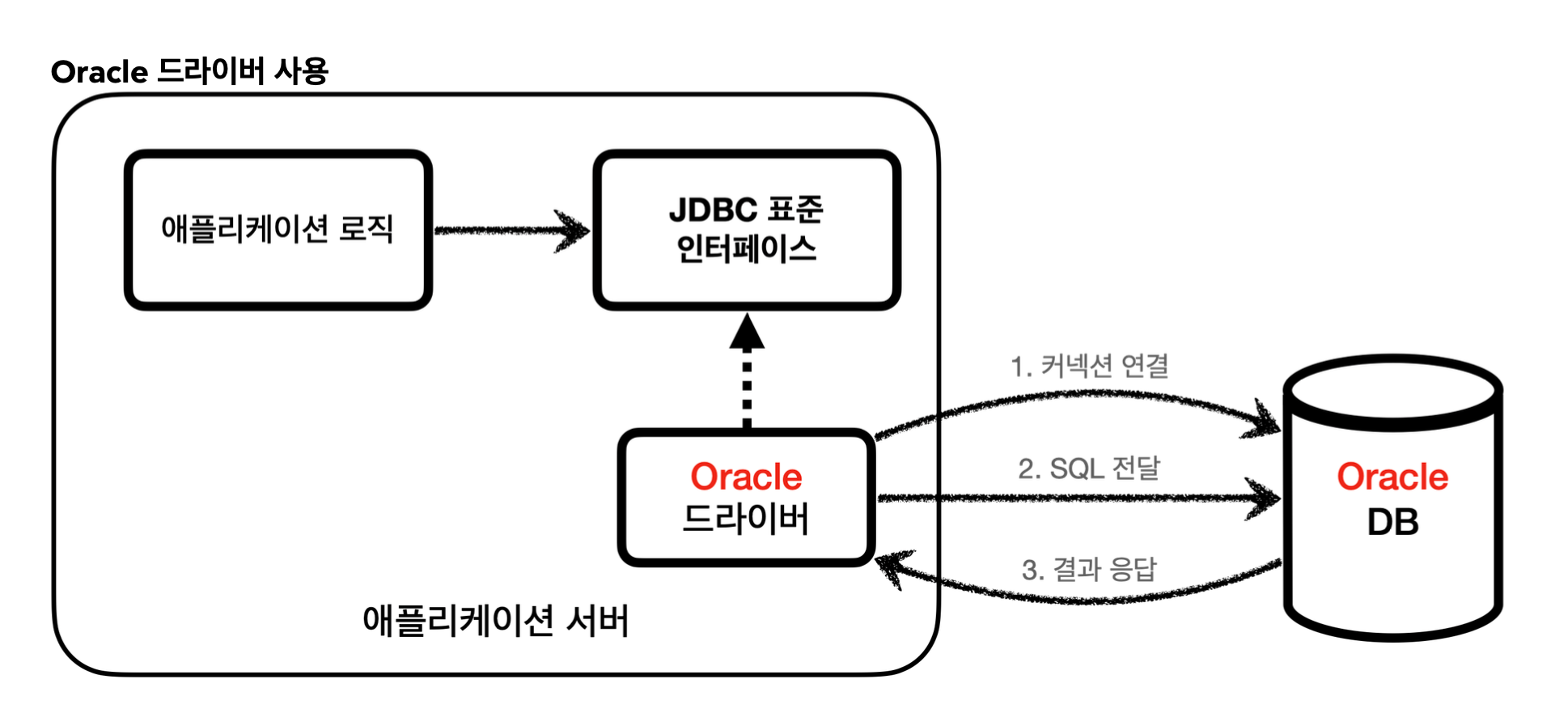
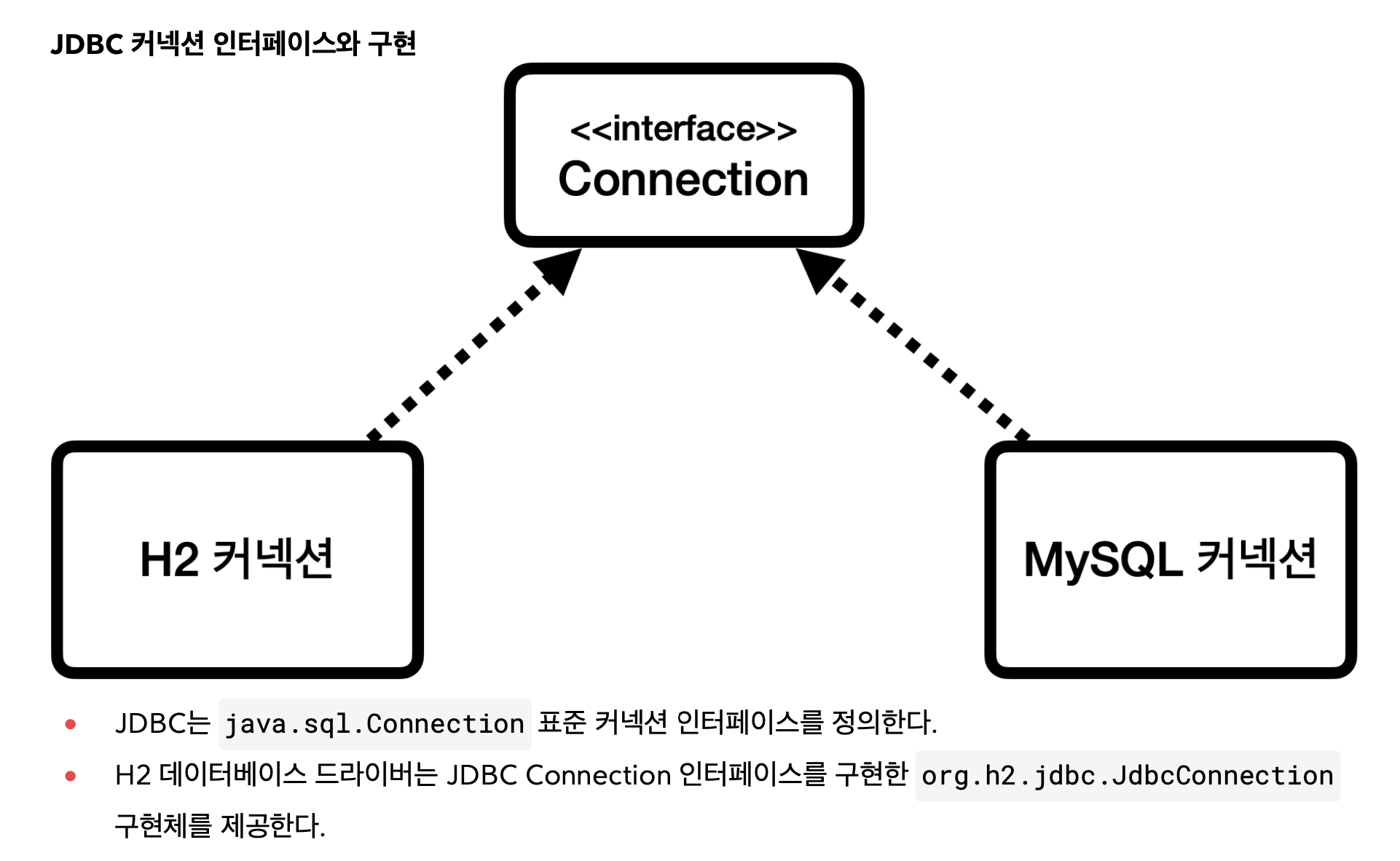
자바는 이렇게 표준 인터페이스를 정의해두었다. 이제부터 개발자는 이 표준 인터페이스만 사용해서 개발하면 된다. 그런데 인터페이스만 있다고해서 기능이 동작하지는 않는다. 이 JDBC 인터페이스를 각각의 DB 벤더(회사)에서 자신 의 DB에 맞도록 구현해서 라이브러리로 제공하는데, 이것을 JDBC 드라이버라 한다. 예를 들어서 MySQL DB에 접근 할 수 있는 것은 MySQL JDBC 드라이버라 하고, Oracle DB에 접근할 수 있는 것은 Oracle JDBC 드라이버라 한다.
정리
JDBC의 등장으로 다음 2가지 문제가 해결되었다.
- 데이터베이스를 다른 종류의 데이터베이스로 변경하면 애플리케이션 서버의 데이터베이스 사용 코드도 함께 변경 해야하는 문제
- 애플리케이션 로직은 이제 JDBC 표준 인터페이스에만 의존한다. 따라서 데이터베이스를 다른 종류의 데이 터베이스로 변경하고 싶으면 JDBC 구현 라이브러리만 변경하면 된다. 따라서 다른 종류의 데이터베이스로 변경해도 애플리케이션 서버의 사용 코드를 그대로 유지할 수 있다.
- 개발자가 각각의 데이터베이스마다 커넥션 연결, SQL 전달, 그리고 그 결과를 응답 받는 방법을 새로 학습해야하 는 문제
- 개발자는 JDBC 표준 인터페이스 사용법만 학습하면 된다. 한번 배워두면 수십개의 데이터베이스에 모두 동일하게 적용할 수 있다.
JDBC의 등장으로 많은 것이 편리해졌지만, 각각의 데이터베이스마다 SQL, 데이터타입 등의 일부 사용법 다르 다. ANSI SQL이라는 표준이 있기는 하지만 일반적인 부분만 공통화했기 때문에 한계가 있다. 대표적으로 실무 에서 기본으로 사용하는 페이징 SQL은 각각의 데이터베이스마다 사용법이 다르다.
결국 데이터베이스를 변경하면 JDBC 코드는 변경하지 않아도 되지만 SQL은 해당 데이터베이스에 맞도록 변경 해야한다.
참고로 JPA(Java Persistence API)를 사용하면 이렇게 각각의 데이터베이스마다 다른 SQL을 정의해야 하는 문제도 많은 부분 해결할 수 있다.
JDBC와 최신 데이터 접근 기술
JDBC는 1997년에 출시될 정도로 오래된 기술이고, 사용하는 방법도 복잡하다. 그래서 최근에는 JDBC를 직접 사용하 기 보다는 JDBC를 편리하게 사용하는 다양한 기술이 존재한다. 대표적으로 SQL Mapper와 ORM 기술로 나눌 수 있다.
SQL Mapper
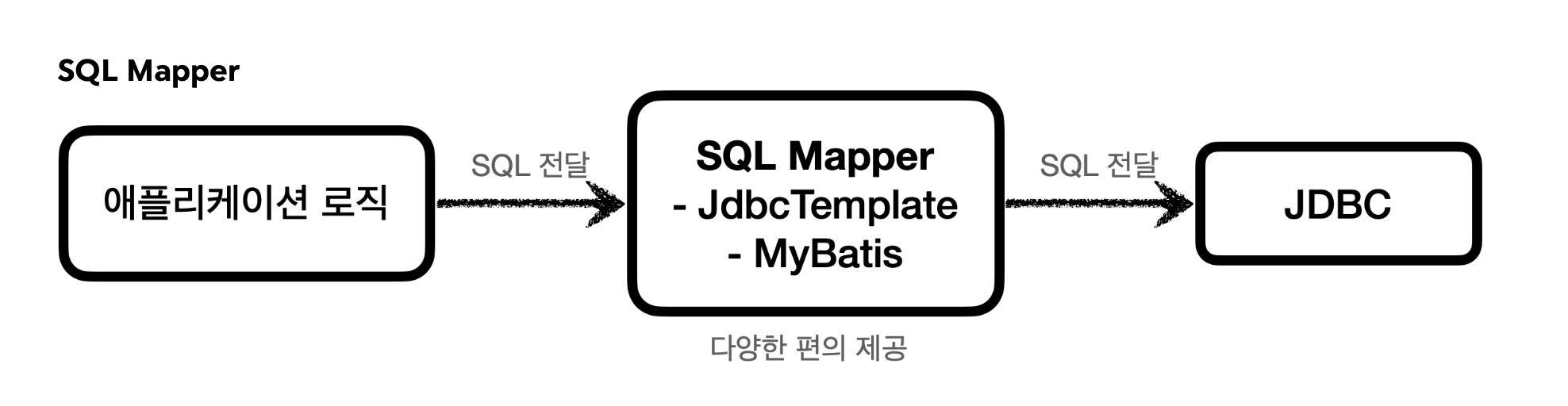
SQL Mapper
장점: JDBC를 편리하게 사용하도록 도와준다.
SQL 응답 결과를 객체로 편리하게 변환해준다. JDBC의 반복 코드를 제거해준다.
단점: 개발자가 SQL을 직접 작성해야한다.
대표 기술: 스프링 JdbcTemplate, MyBatis
ORM
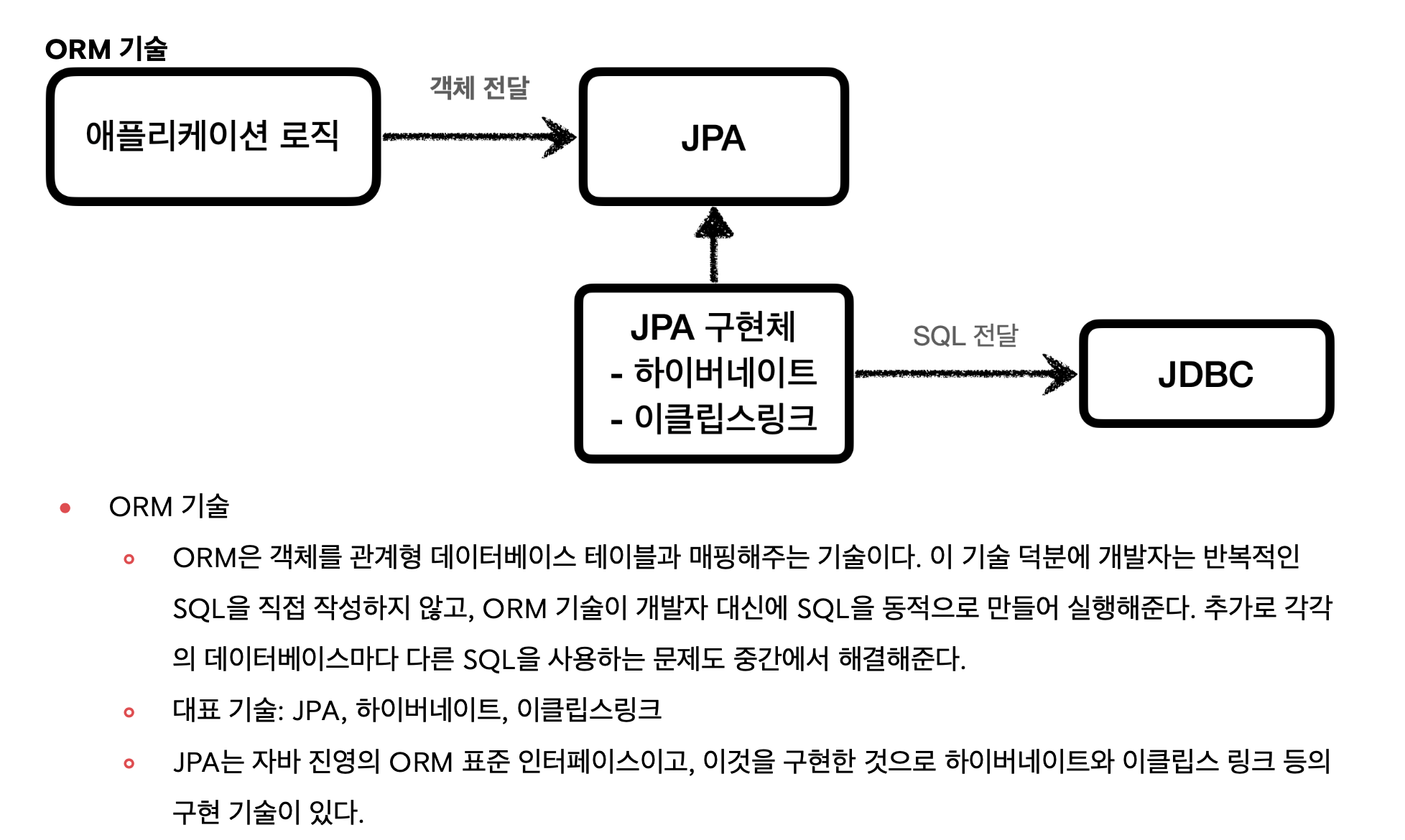
SQL Mapper vs ORM 기술
SQL Mapper와 ORM 기술 둘다 각각 장단점이 있다.
쉽게 설명하자면 SQL Mapper는 SQL만 직접 작성하면 나머지 번거로운 일은 SQL Mapper가 대신 해결해준다. SQL Mapper는 SQL만 작성할 줄 알면 금방 배워서 사용할 수 있다.
ORM기술은 SQL 자체를 작성하지 않아도 되어서 개발 생산성이 매우 높아진다. 편리한 반면에 쉬운 기술은 아니므로 실무에서 사용하려면 깊이있게 학습해야 한다.
강의 뒷 부분에서 다양한 데이터 접근 기술을 설명하는데, 그때 SQL Mapper인 JdbcTemplate과 MyBatis를 학습하 고 코드로
활용해본다. 그리고 ORM의 대표 기술인 JPA도 학습하고 코드로 활용해본다. 이 과정을 통해서 각각의 기술들의 장단 점을 파악하고, 어떤 기술을 언제 사용해야 하는지 자연스럽게 이해하게 될 것이다.
중요
이런 기술들도 내부에서는 모두 JDBC를 사용한다. 따라서 JDBC를 직접 사용하지는 않더라도, JDBC가 어떻게 동작하는지 기본 원리를 알아두어야 한다. 그래야 해당 기술들을 더 깊이있게 이해할 수 있고, 무엇보다 문제가 발 생했을 때 근본적인 문제를 찾아서 해결할 수 있다 JDBC는 자바 개발자라면 꼭 알아두어야 하는 필수 기본 기술 이다.
데이터베이스 연결
애플리케이션과 데이터베이스를 연결해보자.
ConnectionConst
package hello.jdbc.connection;
public abstract class ConnectionConst {
public static final String URL = "jdbc:h2:tcp://localhost/~/test";
public static final String USERNAME = "sa";
public static final String PASSWORD = "";
}DBConnectionUtil
@Slf4j
public class DBConnectionUtil {
public static Connection getConnection() {
try {
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, USERNAME, PASSWORD);
log.info("get connection={}, class={}", connection, connection.getClass());
return connection;
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(e);
}
}
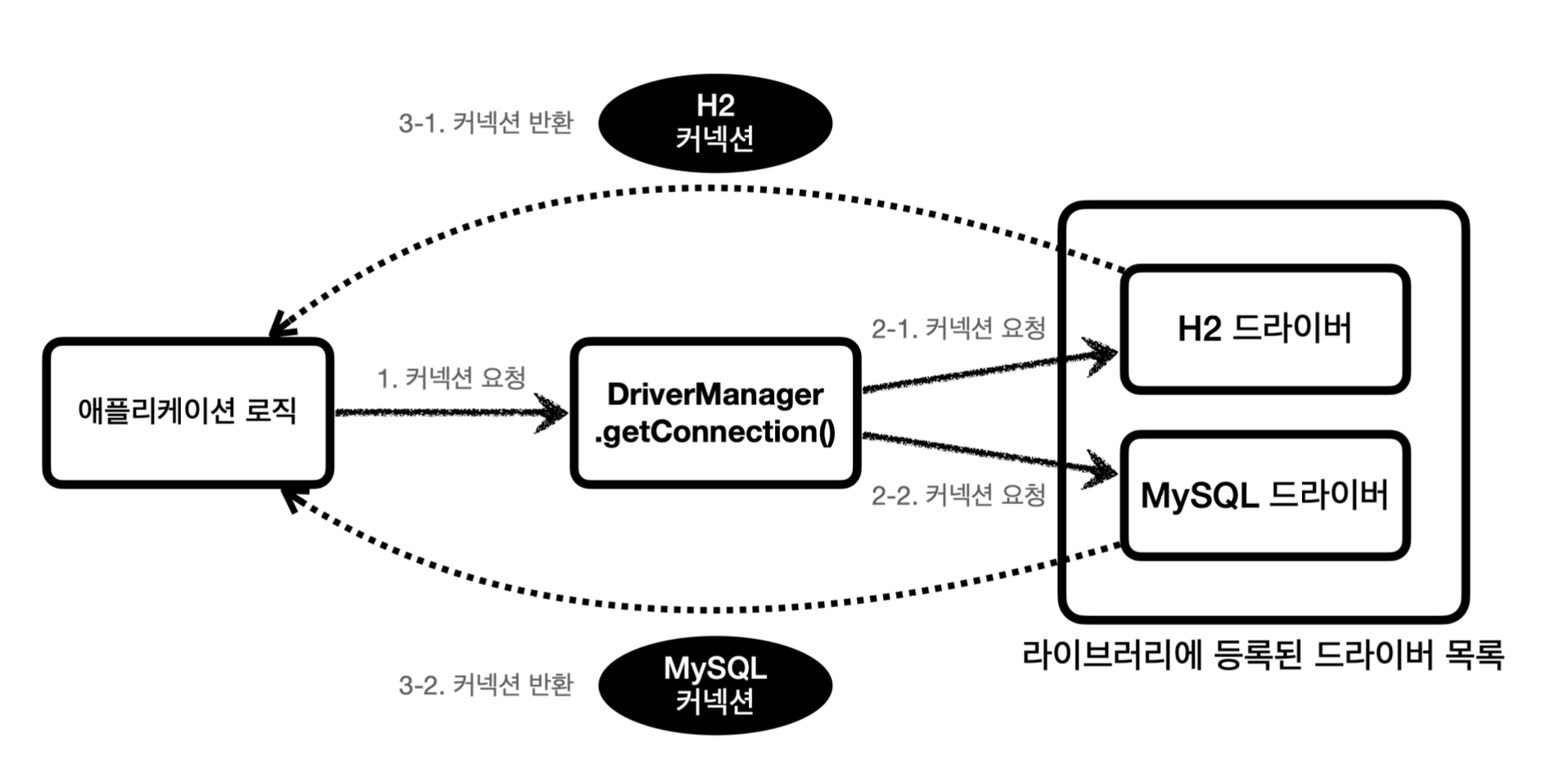
}JDBC가 드라이버를 찾아서 커넥션을 연결해준다.
그리고 Connection의 구현체 중 하나인 h2Driver를 반환한다.
테스트 해보자.
@Slf4j
class DBConnectionUtilTest {
@Test
void connection() {
Connection connection = DBConnectionUtil.getConnection();
assertThat(connection).isNotNull();
}
}JDBC로 CRUD 구현
@Slf4j
public class MemberRepositoryV0 {
public Member save(Member member) throws SQLException {
String sql = "insert into member(member_id, money) values (?, ?)";
Connection con = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
try {
con = getConnection();
pstmt = con.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString(1, member.getMemberId());
pstmt.setInt(2, member.getMoney());
pstmt.executeUpdate();
return member;
} catch (SQLException e) {
log.error("db error", e);
throw e;
} finally {
close(con, pstmt, null);
}
}
public Member findById(String memberId) throws SQLException {
String sql = "select * from member where member_id = ?";
Connection con = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
con = getConnection();
pstmt = con.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString(1, memberId);
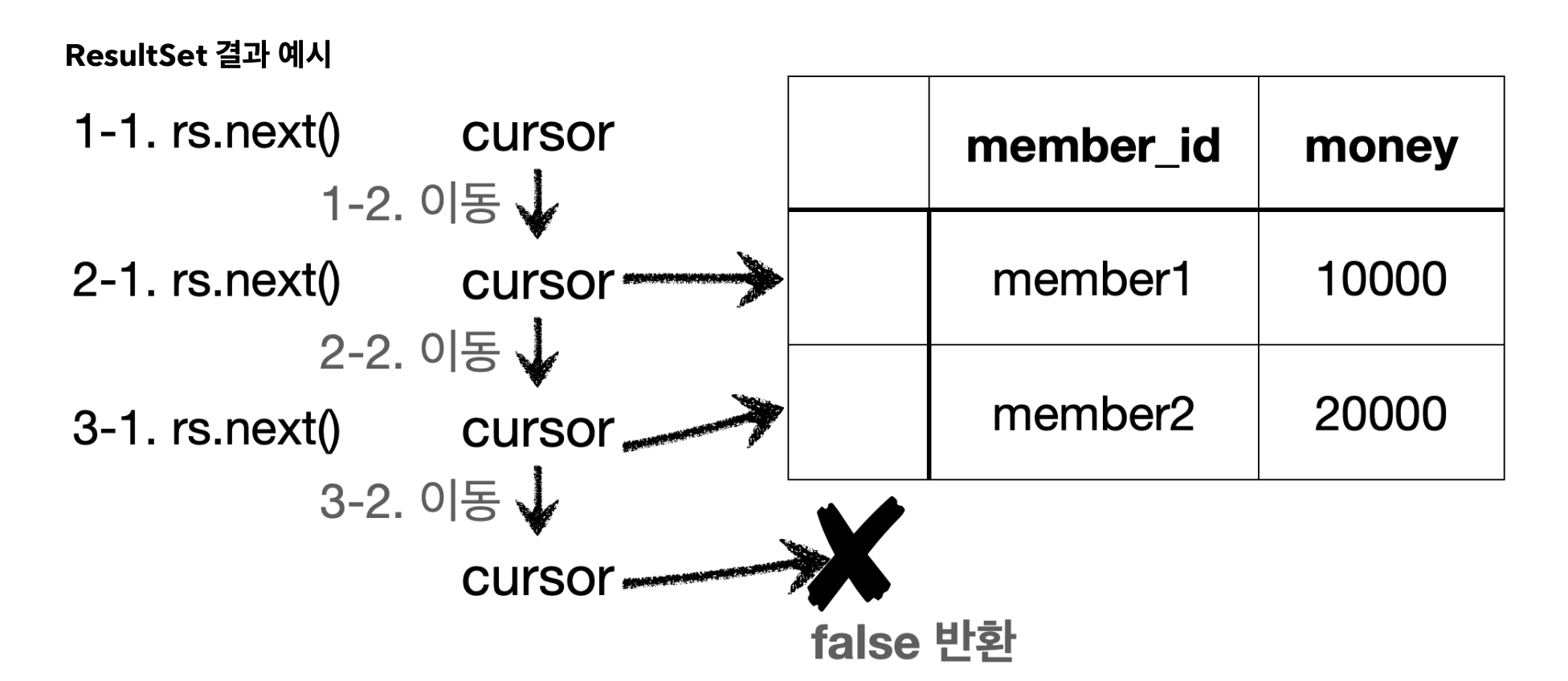
rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
if (rs.next()) {
Member member = new Member();
member.setMemberId(rs.getString("member_id"));
member.setMoney(rs.getInt("money"));
return member;
} else {
throw new NoSuchElementException("member not found memberId=" + memberId);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
log.error("db error", e);
throw e;
} finally {
close(con, pstmt, rs);
}
}
public void update(String memberId, int money) throws SQLException {
String sql = "update member set money=? where member_id=?";
Connection con = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
try {
con = getConnection();
pstmt = con.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setInt(1, money);
pstmt.setString(2, memberId);
int resultSize = pstmt.executeUpdate();
log.info("resultSize={}", resultSize);
} catch (SQLException e) {
log.error("db error", e);
throw e;
} finally {
close(con, pstmt, null);
}
}
public void delete(String memberId) throws SQLException {
String sql = "delete from member where member_id=?";
Connection con = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
try {
con = getConnection();
pstmt = con.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString(1, memberId);
pstmt.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
log.error("db error", e);
throw e;
} finally {
close(con, pstmt, null);
}
}
private void close(Connection con, Statement stmt, ResultSet rs) {
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
log.info("error", e);
}
}
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
log.info("error", e);
}
}
if (con != null) {
try {
con.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
log.info("error", e);
}
}
}
private Connection getConnection() {
return DBConnectionUtil.getConnection();
}
}
테스트 해보자
@Slf4j
class MemberRepositoryV0Test {
MemberRepositoryV0 repository = new MemberRepositoryV0();
@Test
void crud() throws SQLException {
//save
Member member = new Member("memberV100", 10000);
repository.save(member);
//findById
Member findMember = repository.findById(member.getMemberId());
log.info("findMember={}", findMember);
assertThat(findMember).isEqualTo(member);
//update: money: 10000 -> 20000
repository.update(member.getMemberId(), 20000);
Member updatedMember = repository.findById(member.getMemberId());
assertThat(updatedMember.getMoney()).isEqualTo(20000);
//delete
repository.delete(member.getMemberId());
assertThatThrownBy(() -> repository.findById(member.getMemberId()))
.isInstanceOf(NoSuchElementException.class);
}
}테스트 할 때 isEqualTo는 서로 다른 객체이기 때문에 falseㄱ가 나오지만 lombok이 지원하는 equals는 필드를 빌교하여 true를 준다.
회원을 삭제한 다음
findById()를 통해서 조회한다. 회원이 없기 때문에NoSuchElementException이 발생한 다.assertThatThrownBy는 해당 예외가 발생해야 검증에 성공한다.
마지막에 회원을 삭제하기 때문에 테스트가 정상 수행되면, 이제부터는 같은 테스트를 반복해서 실행할 수 있다. 물론 테스트 중간에 오류가 발생해서 삭제 로직을 수행할 수 없다면 테스트를 반복해서 실행할 수 없다. 트랜잭션을 활용하면 이 문제를 깔끔하게 해결할 수 있다.
