INTRODUCTION
어떻게 데이터를 관리하고 organize(어울리는 한국어 생각안남..) 구조화?할 것인가
- Schemas: 데이터를 어떻게 logically organized 할 것인가
- Normalization: 데이터가 반드시 최소 독립적, 최소 중복적(redundancy)이어야 하는 것인가?
(이및ㄴ 한국어가 더 어렵다 그냥 영어로하자) - Views: What joins will be done most often?
- Access control: Should all users of the data have the same level of access
- DBMS: how do I pick between all the SQL and noSQL opts?
- and more!
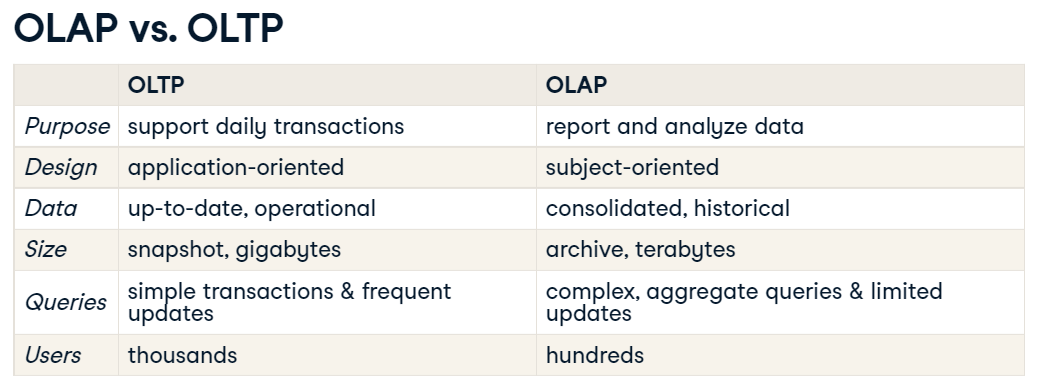
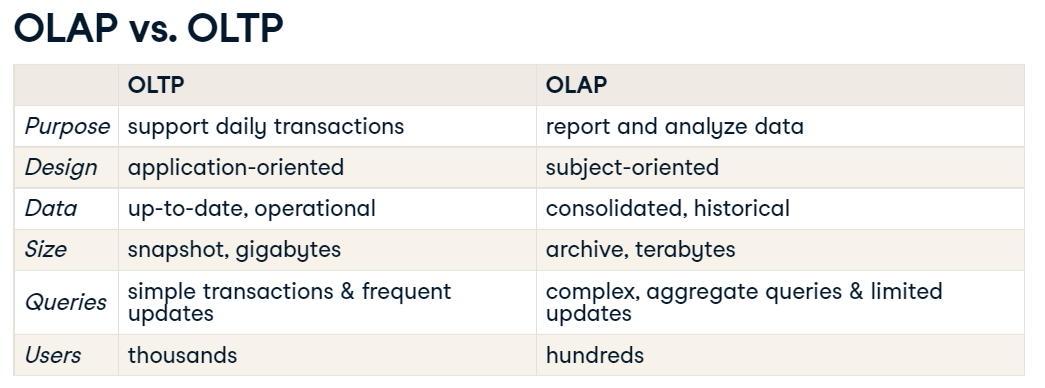
OLTP and OLAP
| OLTP | OLAP |
|---|---|
| Online Transaction Processing | Online Analytical Processing |
| find the price of a book | calculate books with best profit margin |
| update latest customer transaction | find most loyal customers |
- OLTP는 좀 더 day to day operations에 집중되어 있고, OLAP은 business적인 의사결정에 좀 더 집중되어있다.
Storing data
- Structured data
- Unstructed data
- Semi-structured data
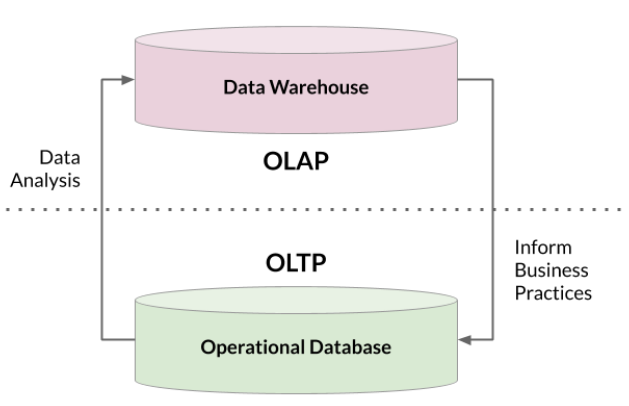
storing data beyond traditional DB
- Traditional DB
- for storing real-time relational sturucted data? OLTP
- Data warehouses
- for analyzing archived structured data? OLAP
- Data Lakes
- for stroing data of all structures = flexibility and scalability
- for analyzing big data
Data warehouses
-
optimized for analytics - OLAP
- organized for reading/aggregating data
- usually read-only
-
contains data from multiple sources
-
massively parallel processing (MPP)
-
typically uses a denormalized schema and dimensional modeling
-
Data marts
- subset of data warehouses
- dedicated to a specific topic
- easier access
Data lakes
- store all types of data at a lower cost
- retains all data and can take up petabytes
- schema-on-read as opposed to schema-on-write
- need to catalog data otherwise becomes a data swamp
- run big data analytics using services such as Apache Spark and Hadoop
- useful for deep learning and data discovery because activities require so much data
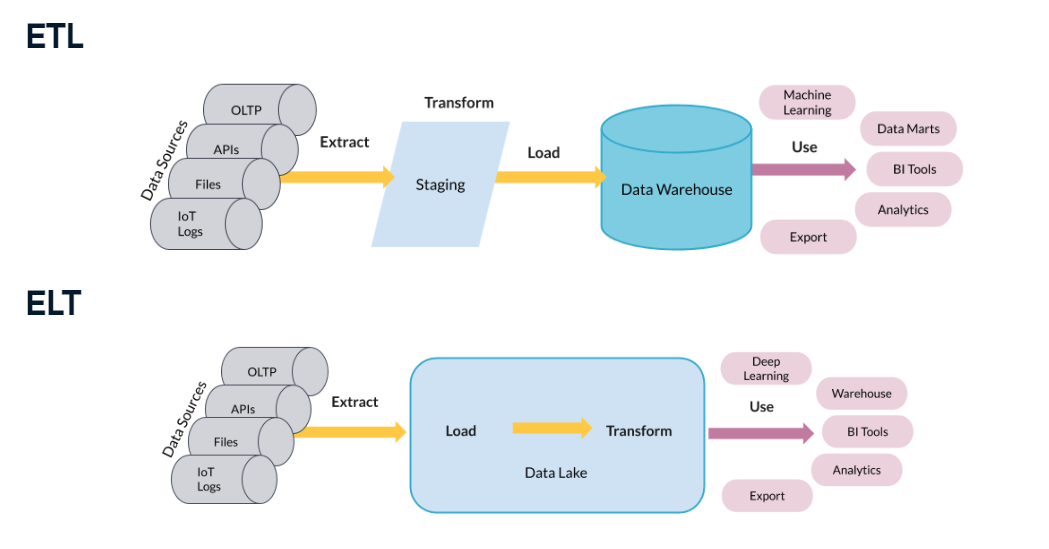
ETL and ELT
Database Design
- how data is logically stored
Data modeling
ref:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Data_model
Korean: https://ko.wikipedia.org/wiki/%EB%8D%B0%EC%9D%B4%ED%84%B0_%EB%AA%A8%EB%8D%B8
- Conceptual data model
- Logical data model
- Physical data model
