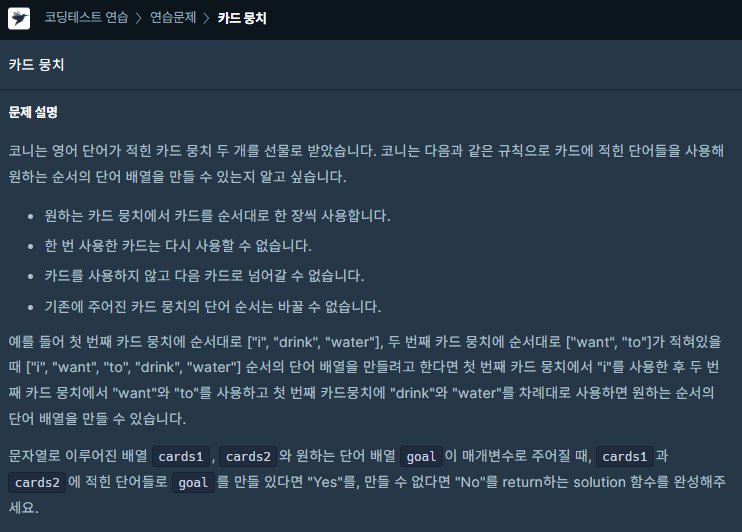
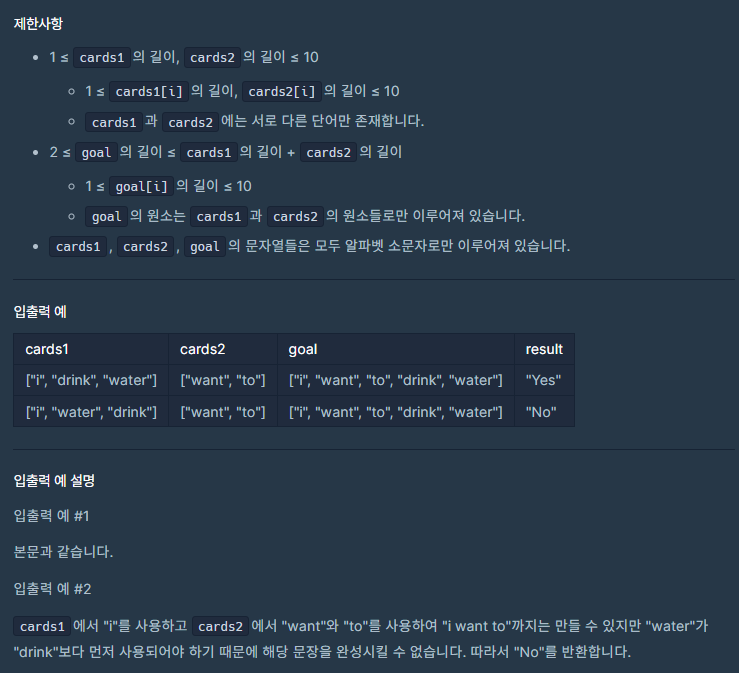
문제
정답 코드
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public String solution(String[] cards1, String[] cards2, String[] goal) {
String answer = "Yes";
List<String> arr1 = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(cards1));
List<String> arr2 = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(cards2));
List<String> goalArr = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(goal));
for (String s : goalArr) {
if(!arr1.isEmpty() && arr1.get(0).equals(s)) {
arr1.remove(0);
continue;
} else if (!arr2.isEmpty() && arr2.get(0).equals(s)) {
arr2.remove(0);
continue;
} else {
answer ="No";
break;
}
}
return answer;
}
}처음에 있는것과 비교해보고, 맞으면 삭제, 없으면 No로 끝나게 만들어야겠다고 설계. -> ArrayList 이용.
금방 풀었다.
배운 점은,
List<String> arr = Arrays.asList(card1);라고 한다면, ArrayList가 아닌 List로 선언되어 remove method를 사용 할 수 없다는 것이다.
다른 사람 풀이
import java.io.*;
class Solution {
public String solution(String[] cards1, String[] cards2, String[] goal) {
int cardIdx1 = 0;
int cardIdx2 = 0;
for(int i=0; i<goal.length; i++){
String target = goal[i];
if(cardIdx1 < cards1.length && target.equals(cards1[cardIdx1]))
cardIdx1 ++;
else if (cardIdx2 < cards2.length && target.equals(cards2[cardIdx2]))
cardIdx2++;
else
return "No";
}
return "Yes";
}
}나처럼 지우는게 아니라, 인덱스를 카운트 하면서 그것과 비교.

