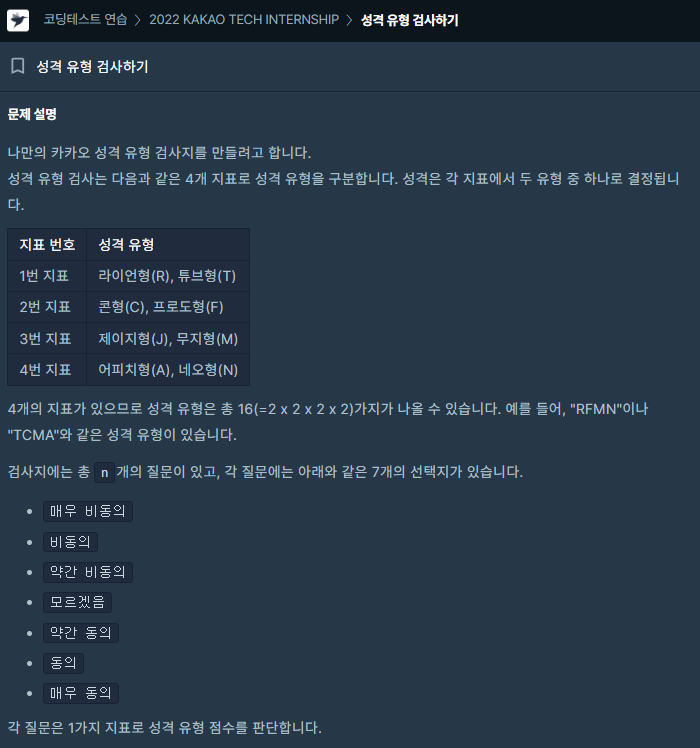
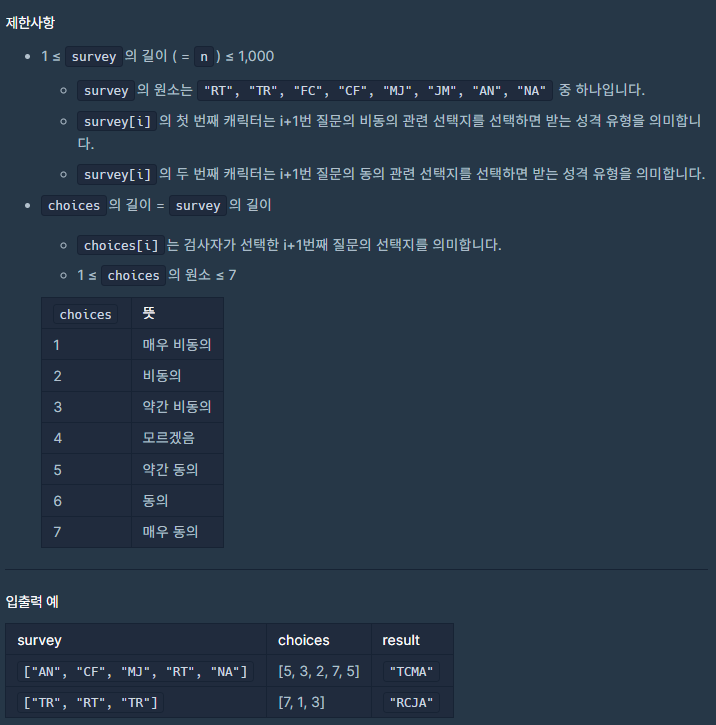
문제

정답 코드
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
class Solution {
public String solution(String[] survey, int[] choices) {
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("R",0);
map.put("T",0);
map.put("C",0);
map.put("F",0);
map.put("J",0);
map.put("M",0);
map.put("A",0);
map.put("N",0);
for (int i=0;i<survey.length;i++) {
int leftCurrentValue=map.get(Character.toString(survey[i].charAt(0)));
int rightCurrentValue=map.get(Character.toString(survey[i].charAt(1)));
switch (choices[i]) {
case 1:
map.put(Character.toString(survey[i].charAt(0)),leftCurrentValue+3);
break;
case 2:
map.put(Character.toString(survey[i].charAt(0)),leftCurrentValue+2);
break;
case 3:
map.put(Character.toString(survey[i].charAt(0)),leftCurrentValue+1);
break;
case 4:
break;
case 5:
map.put(Character.toString(survey[i].charAt(1)),rightCurrentValue+1);
break;
case 6:
map.put(Character.toString(survey[i].charAt(1)),rightCurrentValue+2);
break;
case 7:
map.put(Character.toString(survey[i].charAt(1)),rightCurrentValue+3);
break;
}
}
StringBuilder answer = new StringBuilder();
if (map.get("R")>=map.get("T")) {
answer.append("R");
} else {
answer.append("T");
}
if (map.get("C")>=map.get("F")) {
answer.append("C");
} else {
answer.append("F");
}
if (map.get("J")>=map.get("M")) {
answer.append(("J"));
} else {
answer.append(("M"));
}
if (map.get("A")>=map.get("N")) {
answer.append(("A"));
} else {
answer.append(("N"));
}
return answer.toString();
}
}map을 이용해서 풀었다. 코드가 명확해서 설명할 건덕지가 없다.
근데 너무 길어서 어거지로 풀은 느낌..? 풀면서도 이게 맞나 싶었다.
하지만 다른 분들의 정답들도 한 길이 하시는것을 보고 위안 삼았다.
다른 사람 풀이
import java.util.HashMap;
class Solution {
public String solution(String[] survey, int[] choices) {
String answer = "";
HashMap<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put('R', 0);map.put('T', 0);
map.put('C', 0);map.put('F', 0);
map.put('J', 0);map.put('M', 0);
map.put('A', 0);map.put('N', 0);
for (int i = 0; i < survey.length; i++) {
if (choices[i] > 4)
map.put(survey[i].charAt(1), map.get(survey[i].charAt(1)) + choices[i] - 4);
else if (choices[i] < 4) {
map.put(survey[i].charAt(0), map.get(survey[i].charAt(0)) + 4 - choices[i]);
}
}
if (map.get('R') >= map.get('T'))
answer = "R";
else
answer = "T";
if (map.get('C') >= map.get('F'))
answer += "C";
else
answer += "F";
if (map.get('J') >= map.get('M'))
answer += "J";
else
answer += "M";
if (map.get('A') >= map.get('N'))
answer += "A";
else
answer += "N";
return answer;
}
}이분은 나와 비슷하게 풀었다.
배울 점이라면 나의 장황한 switch-case문이 if문으로 간단하게 바뀌었다는 것이다.
