🍒 Promise
앞에서 본 콜백지옥에서 탈출하기 위해서는 어떻게 해야 할까?
바로 promise를 사용하면 된다.
Promise의 기능
promise는 실제 약속하다 라는 뜻을 가지고 있고, 이는 JS에서 콜백함수를 다시 부르겠다는 뜻으로 쓰인다.
- JS에서 제공하는 비동기를 간편하게 처리할 수 있도록 도와주는 오브젝트
- 정해진 장시간의 기능을 수행하고 나서 정상적으로 기능이 수행되어졌다면 성공 메세지 & 처리된 결과값 전달, 예상치 못한 문제 발생 시 에러 전달
Promise에서 꼭 확인해보아야 할 것
- 상태(state) -> 성공 실패 여부
pending(대기)-resolve(해결)-fulfilled(성공)pending(대기)-reject(거부)-rejected(실패)
- producer(정보 제공), consumer(정보 소비)의 차이점 이해
🍒 1. Producer
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
// doing some heavy work(network, read files)
console.log('doing something...');
setTimeout(()=>{
resolve('ellie'); //성공하면 ellie 값 전달
reject(new Error('no network')); //실패하면 no network라는 에러 발생
},2000);
});
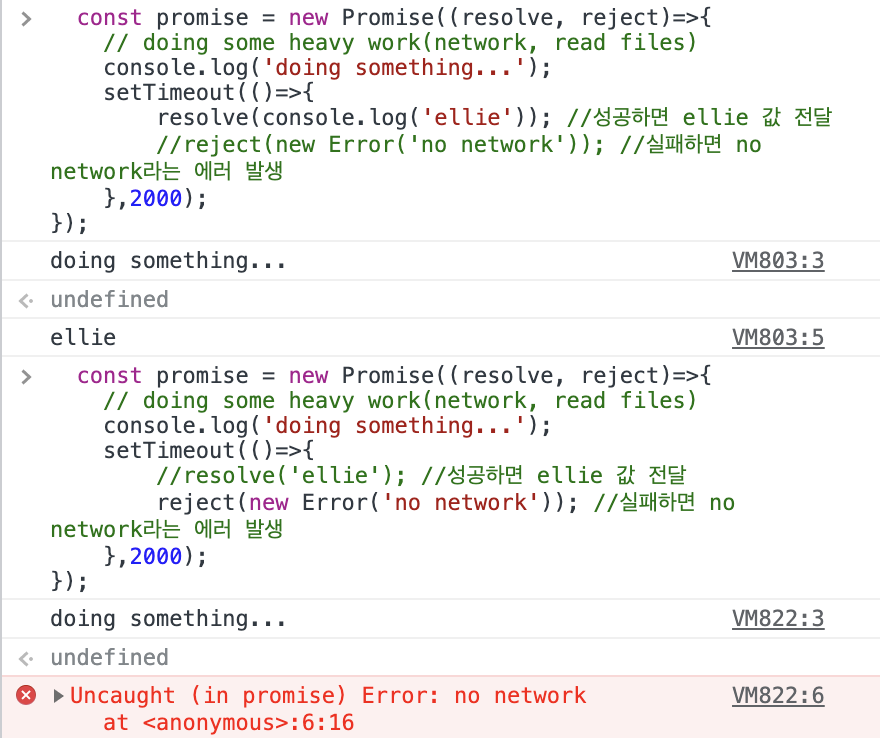
성공하면 ellie 값을 반환하고, 실패하면 error를 반환한다. (성공 시 콘솔창에서 확인할 수 있는 방법이 없어 임의로 코드를 변경해서 ellie 값을 출력하도록 했다.)
promise가 만들어지는 그 순간 네트워크 통신을 시작함에 유의할 것!
🍒 2. Consumer
promise.then((value)=>{
console.log(value); //성공하면 then
}).catch(error=>{
console.log(error); //실패하면 catch
}).finally(()=>{
console.log('finally');
}); //성공하든 실패하든 상관 없이 어떤 기능을 마지막으로 수행하고 싶을 때 finally이렇게 .then .catch .finally 로 이어진 것을 promise chain이라고 한다.
🍒 3. Promise Chaining
const fetchNumber = new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=>resolve(1),1000);
});
fetchNumber
.then(num=>num * 2) //2
.then(num=>num*3) //6
.then(num=>{
return new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=>resolve(num-1),1000); //5
});
})
.then(num=>console.log(num)); //5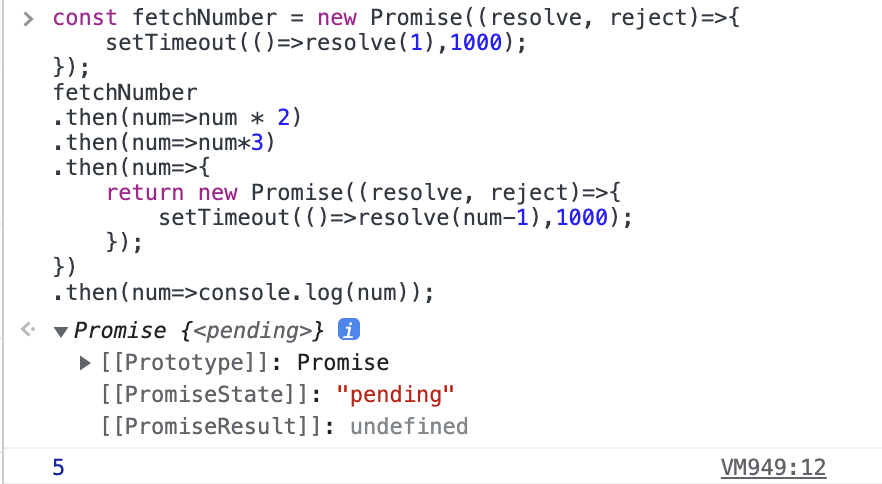
then의 값은 바로 전달해도 되고, 또 다른 비동기 프로미스를 전달해도 된다.
🍒 4. error handling
const getHen = () =>
new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=> resolve('닭'),1000);
});
const getEgg = hen =>
new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=>reject(`error! ${hen}=> 알`),1000);
});
const cook = egg =>
new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=> resolve(`${egg}=> 프라이`),1000);
});
getHen()// 닭
.then(hen=>getEgg(hen)) // 닭 => 알
.then(egg =>cook(egg)) // 닭 => 알 => 프라이
.then(meal => console.log(meal)); // 닭 => 알 => 프라이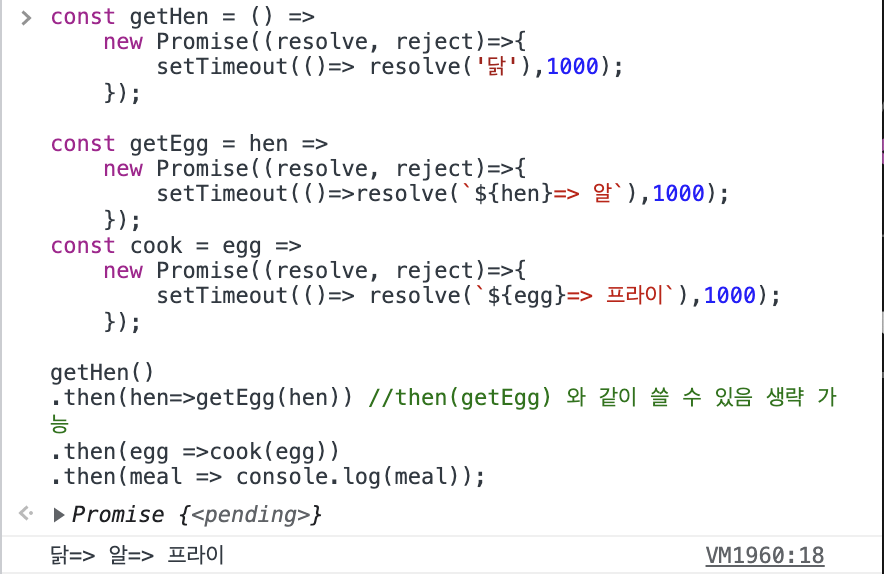
하지만 여기서 다음과 같이 만약 egg 함수에서 오류를 반환한다면 이후에 코드가 실행이 되지 않는다.
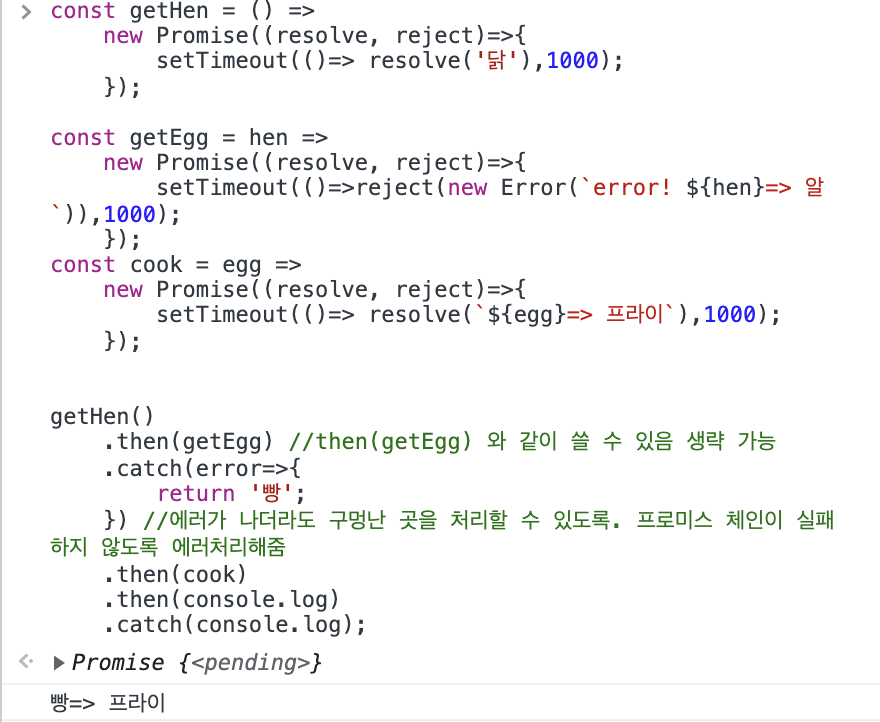
const getEgg = hen =>
new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=>reject(new Error(`error! ${hen}=> 알`)),1000);
});뒤에 코드도 매끄럽게 실행이 되도록 오류처리를 해보자!
getHen()
.then(getEgg) //then(getEgg) 와 같이 쓸 수 있음 생략 가능
.catch(error=>{
return '빵';
}) //에러가 나더라도 구멍난 곳을 처리할 수 있도록. 프로미스 체인이 실패하지 않도록 에러처리해줌
.then(cook)
.then(console.log)
.catch(console.log);catch 문을 통해서 에러를 받아서 특정 값을 반환해주면 이후에 값도 확인할 수 있다.
🍒 마지막 정리
- 비동기를 간편하게 처리하기 위해 promise를 사용한다.
- promise는 성공 실패 여부를 알 수 있는 상태값을 가진다.
- pending(대기상태) - resolve(해결) - fulfilled(성공)
- pending(대기상태) - reject(거부) - rejected(실패)
- 성공하면 then, 실패하면 catch, 성공 실패 관련없이 무조건 실행하는 finally
- then은 값을 바로 전달해도 되고, 또 다른 비동기 프로미스를 전달해도 된다. .then 등으로 계속 이어지는 것을 promise chaining 이라고 한다.
- catch를 통해 에러를 다룰 수 있다.
이번에 배운 promise를 통해서 callback 지옥을 벗어나는 법에 대해서 작성해보려고 한다.
🍒 Callback 지옥 탈출
- 사용자에게 아이디와 패스워드를 입력받음
- 서버에게 로그인 해줘!
- 로그인한 사용자의 아이디를 받아와서 roles를 다시 요쳥해서 받아올 것
- 역할이 성공적으로 받아와 진다면 사용자의 object가 있겠죠~
class UserStorage{
loginUser(id, password, onSuccess, onError){
setTimeout(()=>{
if(
(id==='ellie' && password ==='dream')||
(id==='coder'&& password === 'academy')
){
onSuccess(id);//id와 password가 다음과 같다면 성공!
}else{
onError(new Error('not found'));
}//아니라면 실패!
},2000);
}
getRoles(user, onSuccess, onError){
setTimeout(()=>{
if(user === 'ellie'){
onSuccess({name: 'ellie', role: 'admin'});//user가 ellie라면 ellie라는 이름과 역할을 줘!
}else{
onError(new Error('no access'));
}//아니면 오류 반환
},1000);
}
}
const userStorage = new UserStorage();
const id = prompt('enter your id');
const password = prompt('enter your password');
//콜백지옥 시작 주의깊게 볼 것!
userStorage.loginUser(//loginUser콜백함수 호출
id,
password,
user=>{
userStorage.getRoles(//getRoles콜백함수 호출
user,
userWithRole => {
alert(`hello ${userWithRole.name}, you have a ${userWithRole.role} role`);
},
error => {
console.log(error);
}
);
},
error=>{console.log(error)})위와 같은 코드는 로그인 기능을 간단하게 구현해본 코드이다.
loginUser 함수 내부에 getRoles 함수가 들어가 있어 콜백함수가 중첩되어있는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
콜백지옥의 단점
- 가독성이 안좋다, 비즈니스 로직을 한눈에 이해하는 것이 어려움
- 에러가 발생하거나 디버깅을 해야하는 경우에도 에러 파악하기 어려움
- 유지보수가 어려움
콜백지옥 Promise로 해결하자!
const userStorage = new UserStorage();
const id = prompt('enter your id');
const password = prompt('enter your password');
userStorage.loginUser(id, password)
.then(userStorage.getRoles)
.then(user=>alert(
`hello ${user.name}, you have a ${user.role} role`
))
.catch(console.log);다음과 같이 then과 catch로 간단하게 구현할 수 있다.
앞으로 callback 지옥 빠져나오고 promise 가득가득 쓰기!
