Raycaster

raycasting 클래스는 주로 3D Scene 에서 마우스로 오브젝트를 선택하는 데 사용된다.
레이캐스팅을 사용하면 Scene의 3D Point 에서 Vector 를 생성하고 Vector 가 교차(intersect)하는 오브젝트를 감지할 수 있다.
set() 또는 setFromCamera() 메서드를 사용하여 Raycaster의 위치와 방향을 설정한 다음, intersectObject() 또는 intersectObjects() 메서드를 호출하면 다음과 같이 레이와 교차한 씬 오브젝트에 대한 많은 정보를 알 수 있다.
- 레이캐스터 위치에서 교차점까지의 거리
- 3D Scene 에서 교차점의 위치
- 교차(intersected)된 오브젝트의 얼굴
- 면 법선(faces normal)의 방향
- 얼굴에 있는 교차점의 UV coord (좌표)
- 교차된 오브젝트 자체에 대한 참조
이제 이를 사용해서 더블 클릭을 하면 해당 Mesh 위에 3D Object 를 생성해보자.
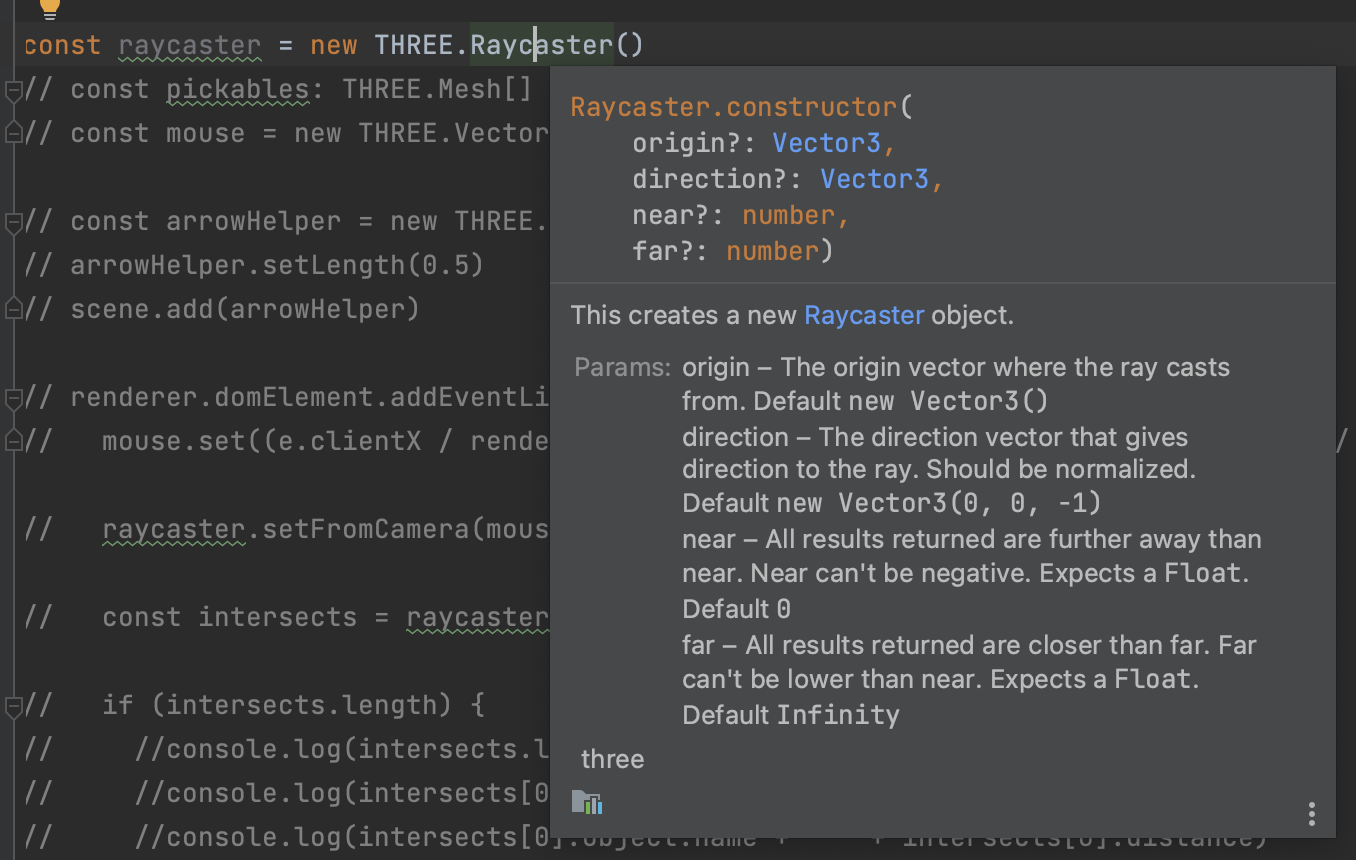
위 코드를 보면 Camera 와 같이 near, far 와 같은 속성 값을 넣을 수 있다. 그래서 해당 far, near plane 의 범위 안에서만 intersect 를 할 수 있도록 설정할 수 있다.
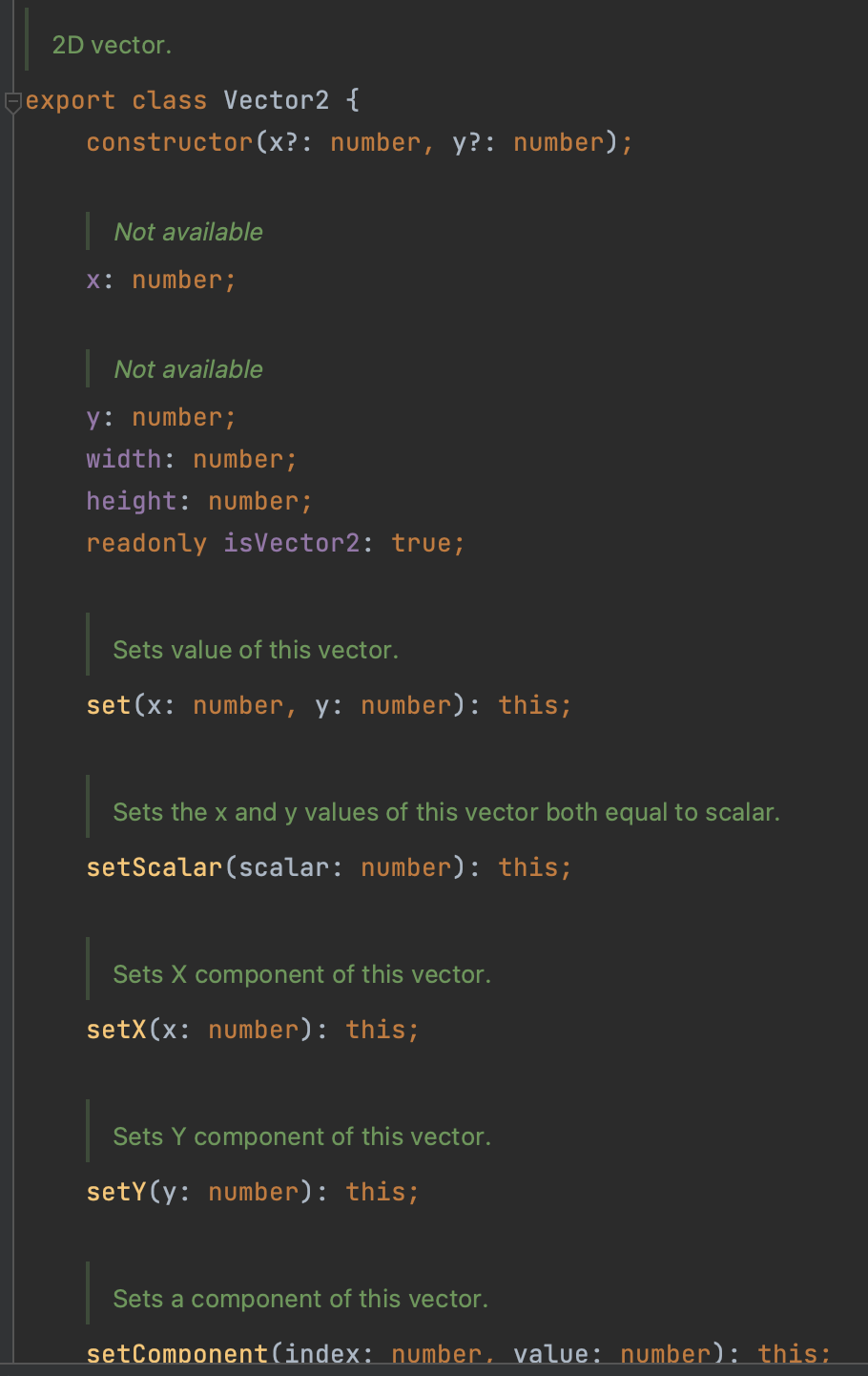
그리고 마우스이벤트를 위한 Vector2 객체를 생성한다.
왜냐하면 renderer 캔버스에 마우스를 올려서 뭔가를 욺직인다고 하여 마우스 위치를 three.js 가 자동으로 읽어오는 재주는 없기 때문이다.
따라서 마우스가 욺직일 때마다 raycaster 에 마우스 위치를 일러주는 것이다.
그러면 추후 raycaster 가 ray 를 그려주고, 해당 마우스 위치에 어떤 object 가 걸리는지 알려주는 것이다.
const raycaster = new THREE.Raycaster()
// 마우스를 추적하기 위한 Vector2 객체
const mouse = new THREE.Vector2()
// renderer 에 'mousemove' 이벤트를 생성
renderer.domElement.addEventListener('mousemove', (e) => {
// 'mousemove' 이벤트에 마우스 위치를 계산하여 캔버스에 위치 입력
mouse.set((e.clientX / renderer.domElement.clientWidth) * 2 - 1, -(e.clientY / renderer.domElement.clientHeight) * 2 + 1)
})
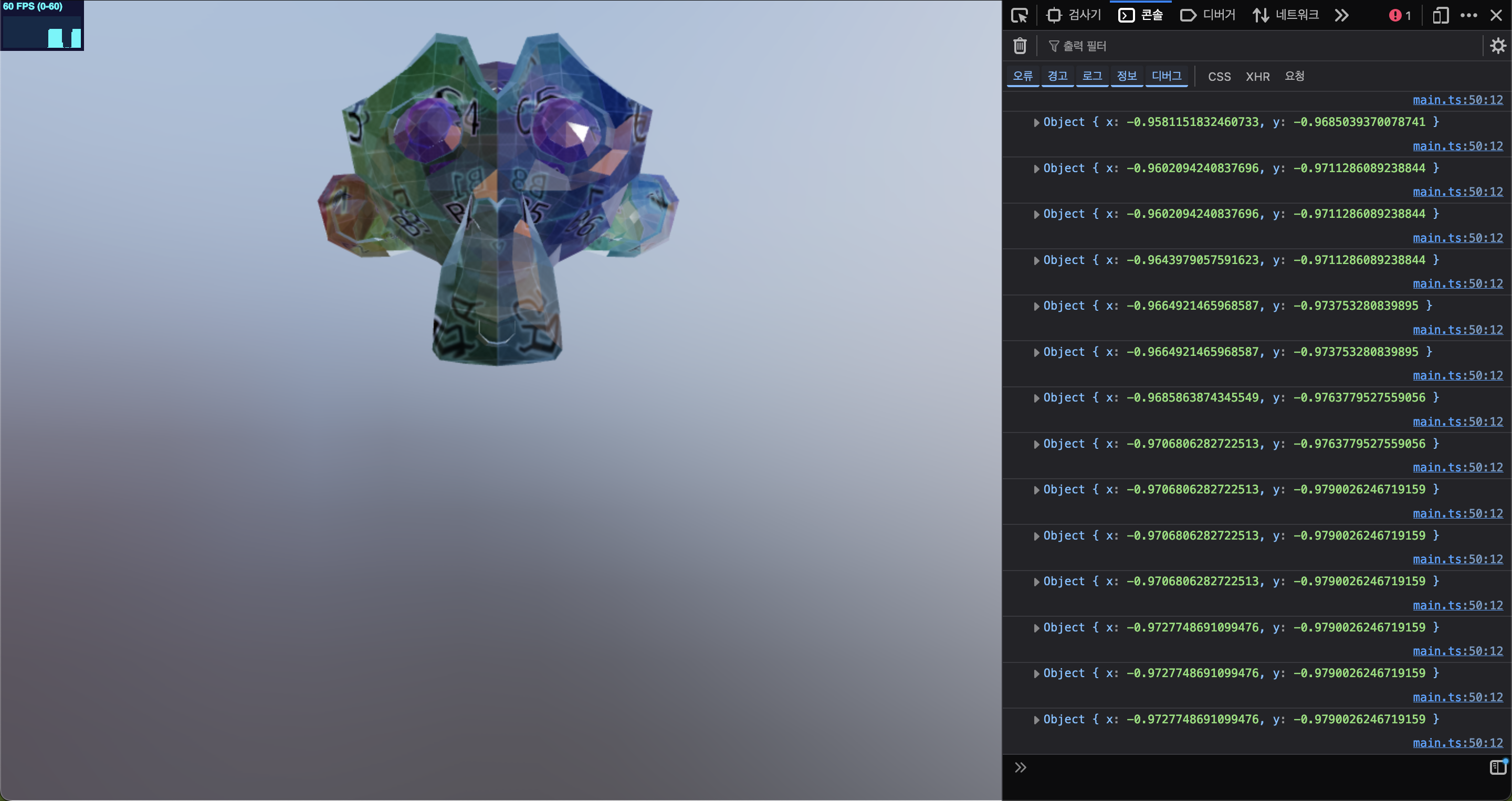
그리고 이 마우스를 로그를 찍어보면
오른쪽 끝, 최상단 Vector2 값 => (1, 1)
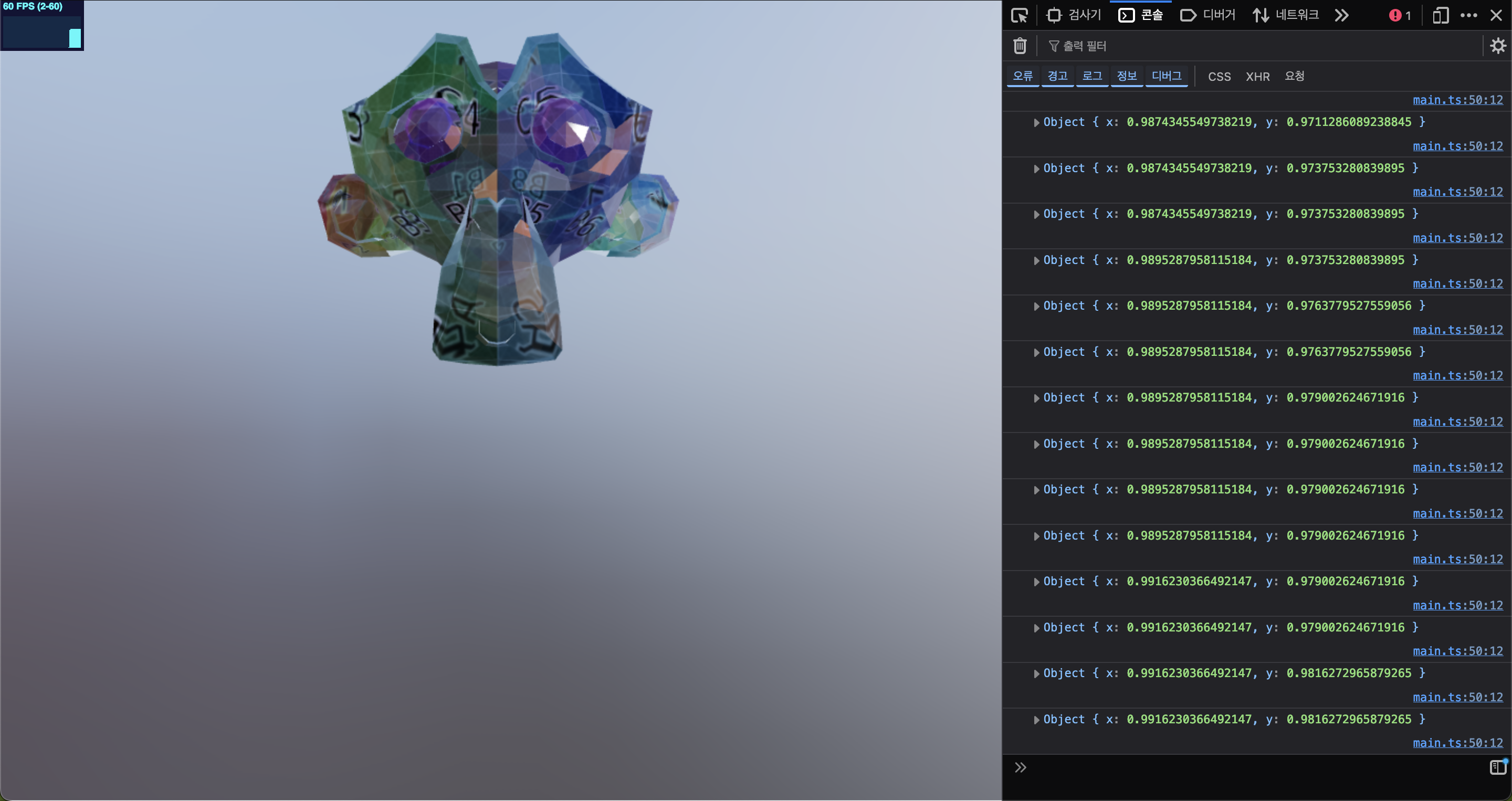
왼쪽 끝, 최하단 Vector2 값 => (-1, -1) 이 된다.
const raycaster = new THREE.Raycaster()
const pickables: THREE.Mesh[] = []
// 마우스를 추적하기 위한 Vector2 객체
const mouse = new THREE.Vector2()
// renderer 에 'mousemove' 이벤트를 생성
renderer.domElement.addEventListener('mousemove', (e) => {
// 'mousemove' 이벤트에 맞춰서 캔버스에 마우스 위치 입력
mouse.set((e.clientX / renderer.domElement.clientWidth) * 2 - 1, -(e.clientY / renderer.domElement.clientHeight) * 2 + 1)
// 새로운 마우스 위치와 방향으로 Ray를 업데이트
raycaster.setFromCamera(mouse, camera)
const intersects = raycaster.intersectObjects(pickables, false);
if (intersects.length) {
console.log(intersects)
}
})
new GLTFLoader().load('models/suzanne_the_monkey.gltf', (gltf) => {
const suzanne = gltf.scene.getObjectByName('수잔') as THREE.Mesh
console.log(suzanne.material);
suzanne.castShadow = true
// @ts-ignore
suzanne.material.map.colorSpace = THREE.LinearSRGBColorSpace
// raycater 에 intersect 할 수 있는 부분을 추가.
pickables.push(suzanne)
...
scene.add(gltf.scene)
})intersectObjects()
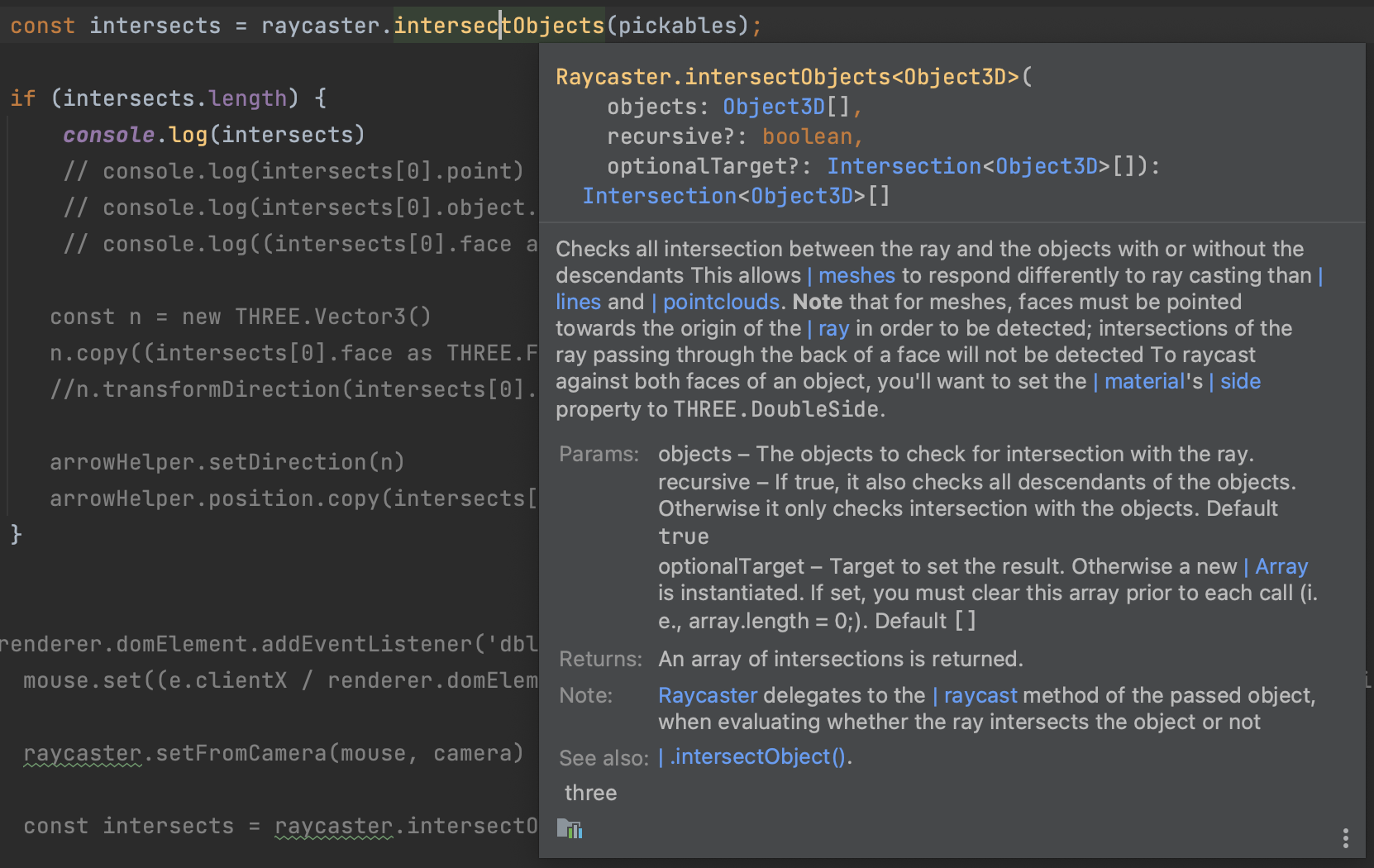
파라미터로 objects, resursive, optionalTarget 을 받는다.
object 는 raycaster 와 상호작용을 할 Mesh 의 배열을 파라미터로 받는다.
resursive 는 default 값은 true 이며, intersect 한 Mesh 객체와 의존관계를 recursive 하게 돌면서 모두 파악한다.
반환값은 Raycaster 와 가까운 순서대로 배열로 반환을 한다. 여기서 가까운 것은 .setFromCamera() 에 설정한 사용자가 바라보는 카메라를 기준으로 한다.
z-fighting
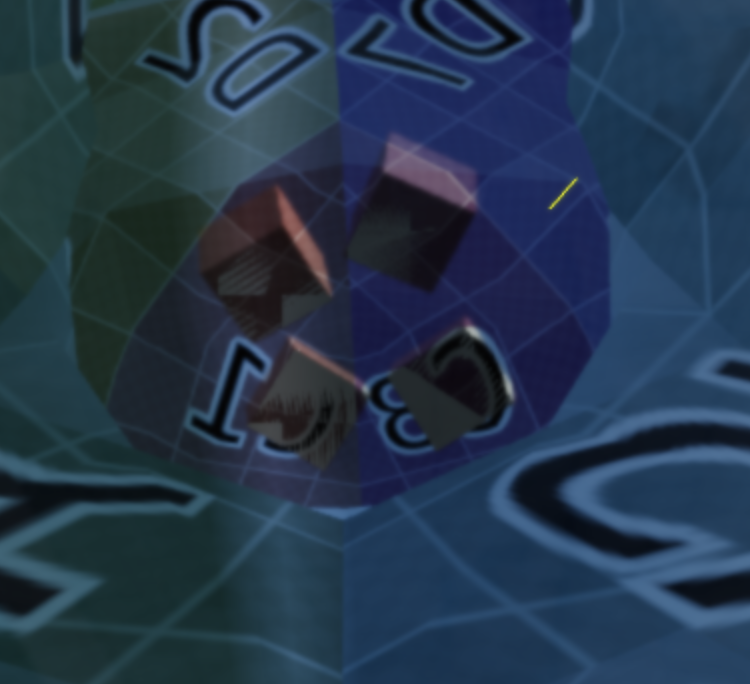

평면과 평면이 마주보며 flikering 현상을 일으키는 것.
보면 추가한 Mesh 와 기존의 수잔 Mesh 가 같은 z 축에 위치함으로써 rederer 가 어느 평면을 그려줘야할 지 몰라서 생기는 현상이다.
transformDirection( payload:Matrix4 )
new GLTFLoader().load('models/suzanne_the_monkey.gltf', (gltf) => {
const suzanne = gltf.scene.getObjectByName('수잔') as THREE.Mesh
suzanne.rotation.x = Math.PI / 4;
suzanne.castShadow = true
// @ts-ignore
suzanne.material.map.colorSpace = THREE.LinearSRGBColorSpace
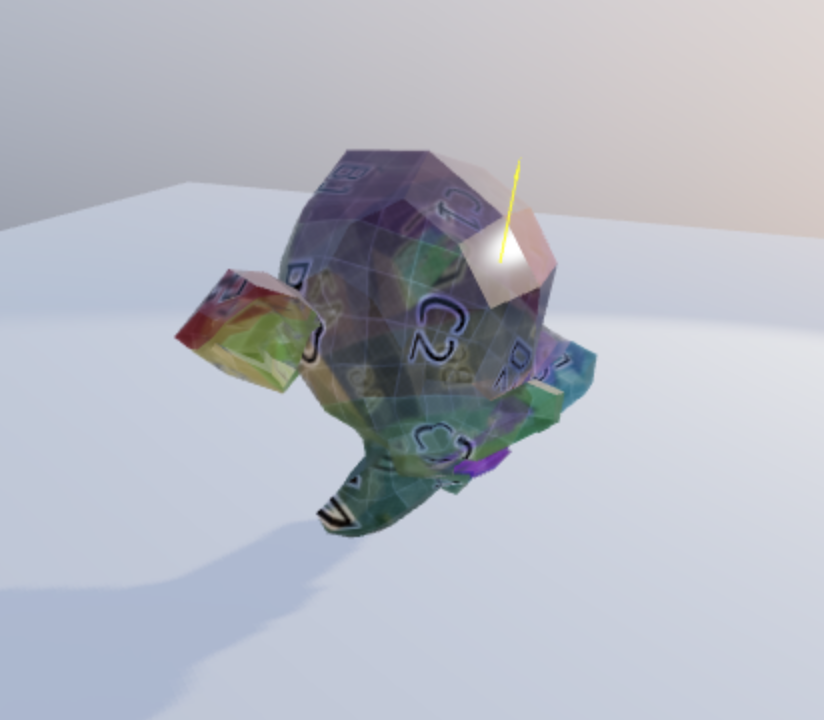
pickables.push(suzanne)우선 원숭이를 45도 기울여보면 face normal 이 기울인 원숭이와 맞지 않다. 즉, 위 사진처럼 45도 기울인 Mesh의 평면과 수직이 아닌 기존의 0도 기울인 값을 계산하여 원숭이 위에 표출하고 있다.
따라서 face normal 을 현재 matrix 값으로 맞춰줘야한다.
const n = new THREE.Vector3()
n.copy((intersects[0].face as THREE.Face).normal)
n.transformDirection(intersects[0].object.matrixWorld)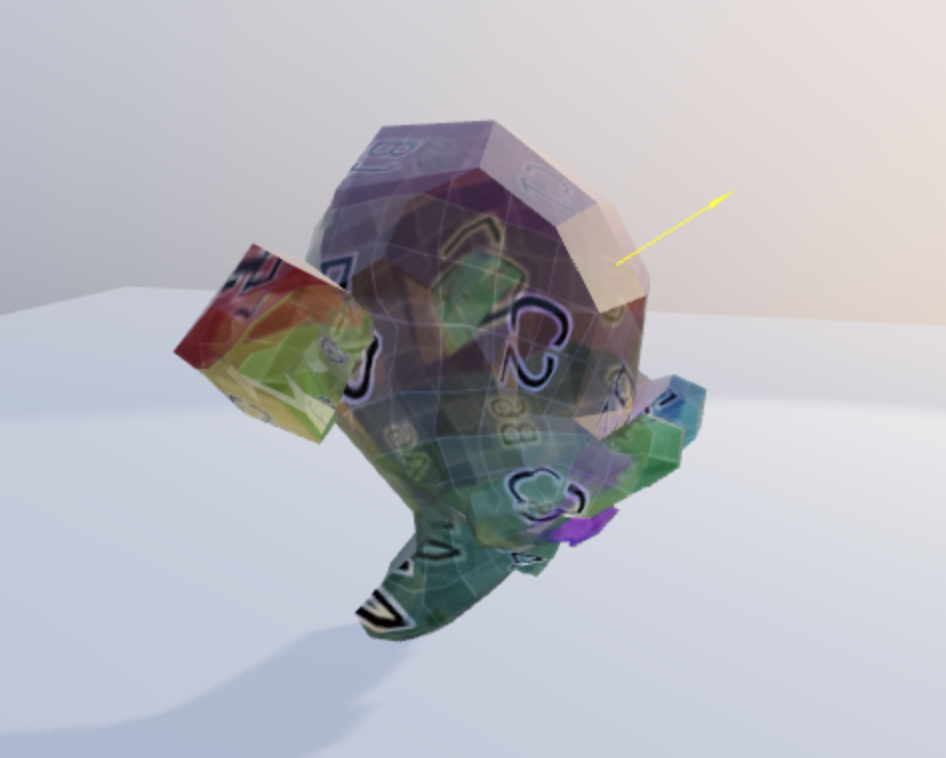
💻 전체 코드
import './style.css'
import * as THREE from 'three'
import {OrbitControls} from 'three/addons/controls/OrbitControls.js'
import {GLTFLoader} from 'three/addons/loaders/GLTFLoader.js'
import {RGBELoader} from 'three/addons/loaders/RGBELoader.js'
import Stats from 'three/addons/libs/stats.module.js'
const scene = new THREE.Scene()
new RGBELoader().load('img/venice_sunset_1k.hdr', (texture) => {
texture.mapping = THREE.EquirectangularReflectionMapping
scene.environment = texture
scene.background = texture
scene.backgroundBlurriness = 0.5
})
const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(75, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 0.1, 100)
camera.position.set(0, 0, 3)
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({antialias: true})
renderer.toneMapping = THREE.ACESFilmicToneMapping
renderer.toneMappingExposure = 0.8
renderer.shadowMap.enabled = true
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight)
document.body.appendChild(renderer.domElement)
window.addEventListener('resize', () => {
camera.aspect = window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight
camera.updateProjectionMatrix()
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight)
})
const controls = new OrbitControls(camera, renderer.domElement)
controls.enableDamping = true
const raycaster = new THREE.Raycaster()
const pickables: THREE.Mesh[] = []
// 마우스를 추적하기 위한 Vector2 객체
const mouse = new THREE.Vector2()
const arrowHelper = new THREE.ArrowHelper()
arrowHelper.setLength(0.5)
scene.add(arrowHelper)
// renderer 에 'mousemove' 이벤트를 생성
renderer.domElement.addEventListener('mousemove', (e) => {
// 'mousemove' 이벤트에 맞춰서 캔버스에 마우스 위치 입력
mouse.set((e.clientX / renderer.domElement.clientWidth) * 2 - 1, -(e.clientY / renderer.domElement.clientHeight) * 2 + 1)
// 새로운 마우스 위치와 방향으로 Ray를 업데이트
raycaster.setFromCamera(mouse, camera)
const intersects = raycaster.intersectObjects(pickables);
if (intersects.length) {
// console.log(intersects)
// console.log(intersects[0].point)
// console.log(intersects[0].object.name + ' ' + intersects[0].distance)
// console.log((intersects[0].face as THREE.Face).normal)
const n = new THREE.Vector3()
n.copy((intersects[0].face as THREE.Face).normal)
n.transformDirection(intersects[0].object.matrixWorld)
arrowHelper.setDirection(n)
arrowHelper.position.copy(intersects[0].point)
}
})
renderer.domElement.addEventListener('dblclick', (e) => {
mouse.set((e.clientX / renderer.domElement.clientWidth) * 2 - 1, -(e.clientY / renderer.domElement.clientHeight) * 2 + 1)
raycaster.setFromCamera(mouse, camera)
const intersects = raycaster.intersectObjects(pickables, false)
if (intersects.length) {
const n = new THREE.Vector3()
// n 에 face normal 을 넣어주기
n.copy((intersects[0].face as THREE.Face).normal)
n.transformDirection(intersects[0].object.matrixWorld)
const cube = new THREE.Mesh(new THREE.BoxGeometry(0.2, 0.2, 0.2), new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial())
cube.lookAt(n)
cube.position.copy(intersects[0].point)
// 0,0,0, 위치에 놓이기 때문에 수잔 Mesh 를 뚫고 들어가기 때문에 height 의 절반만 큼 up 하줌.
// 그리고 z-fighting 때문에 아주 조금 값을 더해줌.
cube.position.addScaledVector(n, 0.1001)
cube.castShadow = true
scene.add(cube)
pickables.push(cube)
}
})
new GLTFLoader().load('models/suzanne_the_monkey.gltf', (gltf) => {
const suzanne = gltf.scene.getObjectByName('수잔') as THREE.Mesh
suzanne.rotation.x = Math.PI / 4;
suzanne.castShadow = true
// @ts-ignore
suzanne.material.map.colorSpace = THREE.LinearSRGBColorSpace
pickables.push(suzanne)
const plane = gltf.scene.getObjectByName('평면') as THREE.Mesh
plane.receiveShadow = true
pickables.push(plane)
const spotLight = gltf.scene.getObjectByName('스폿') as THREE.SpotLight
spotLight.intensity /= 500
spotLight.castShadow = true
scene.add(gltf.scene)
})
const stats = new Stats()
document.body.appendChild(stats.dom)
function animate() {
requestAnimationFrame(animate)
controls.update()
renderer.render(scene, camera)
stats.update()
}
animate()