Pinia
-
vue3로 넘어오면서 vuex를 제치고 vue에서 채택한 표준 상태 관리 라이브러리로 vuex와 다르게 현저하게 편리한 직관적인 문법을 갖고있으며 학습곡선 또한 매우 낮다.
-
Pinia 공식문서에서 제공하는 cheat sheet도 pdf 2장 분량이다.
이제 Pinia의 사용법에 대해 알아보자.
참고로 이 포스팅에서는 vue3에서 주로 사용되는 Composition API를 기준으로 설명하겠다.
defineStore
- 우선 핵심 함수를 알아보기 전에 store를 선언하는 메서드에 대해 먼저 알아보자.
vuex의createStore포지션으로 통상 편리한 관리를 위해 store 하나도 다 쪼개서actions.js,getters.js,index.js,mutations.js로 분리하고 index.js는 또 상위 index.js에게 모듈로써 넘겨주는 아주 복잡한 구조를 가졌었다.
vuex createStore
import {createStore} from "vuex";
...
const store = createStore({
modules: {
admin: adminModules,
ask: askModules,
boards: boardsModules,
contact: contactModules,
messages: messagesModules,
mypage: mypageModules,
phrase: phraseModules,
},
state(){
return{
namespaced: true,
state() {
return{
id: null,
username: null,
rank: null,
email: null,
phoneNum: null,
foundUserId: null,
key: CryptoJS.lib.WordArray.random(32),
iv: CryptoJS.lib.WordArray.random(16)
}
},
actions,
getters,
mutations
}
},
mutations,
actions,
getters
})
export default store;Pinia defineStore
// 스토어를 정의하는 부분.
export const useMsrListStore = defineStore('msrListStore',()=>{
// 페이징 정보
const msrItemCount = ref<number>(0);
const msrTotalPageCount = ref<number>(0);
const msrList = ref<Array<MsrVO>>([]);
// 측기 데이터 가져오기
const setMsrList = async (arg:GetMsrList) => {
try {
const {data} = await getMsrList(arg);
msrItemCount.value = data.totalItemCount;
msrTotalPageCount.value = data.totalPageCount;
msrList.value = data.msrList
} catch (e) {
if(e instanceof AxiosError){
const errorObj = new Error(exceptionHandler(e.response!.status).text);
throw errorObj
}
}
}
// 측기 전체 데이터 가져오기
const msrTotalData = ref<Map<number, MsrVO>>(new Map<number, MsrVO>());
const setTotalMsrData = async()=>{
const payload:GetMsrList = {currentPageIndex:1, pageSize:msrItemCount.value}
try{
const{data} = await getMsrList(payload)
for (const child of data.msrList) {
msrTotalData.value.set(child.msrSeq, child);
}
} catch (e) {
if (e instanceof AxiosError) {
const errorObj = new Error(exceptionHandler(e.response!.status).text);
throw errorObj
}
}
...
}
// selected msr 데이터
const selectedMsr = ref<MsrVO>();
const changeSelectedMSr = (arg:MsrVO) => {
selectedMsr.value = arg;
}
// selected된 msr 데이터 update하는 함수
const updateSelectedMsr = async (arg:UpdateMsr) => {
try {
await updateMsr(arg);
}catch (e) {
if(e instanceof AxiosError){
const errorObj = new Error(exceptionHandler(e.response!.status).text);
throw errorObj
}
}
}
// selected된 msr 데이터 삭제하는 함수
const delSelectedMsr = async(arg:DelMsr)=>{
try {
await delMsr(arg);
} catch (e) {
if(e instanceof AxiosError){
const errorObj = new Error(exceptionHandler(e.response!.status).text);
throw errorObj
}
}
}
return{msrItemCount, msrTotalPageCount, msrList, selectedMsr, msrTotalData,
setMsrList, changeSelectedMSr, updateSelectedMsr, delSelectedMsr, setTotalMsrData}
})-
pinia의 definestore 함수는 매우 직관적이다. vue3와 같은 composition API 문법을 채용함으로써
.vue파일과 동일한 코드 구조를 띈다. -
또한 composition API를 채택함으로써 vuex로 치자면 state와 actions(mutations) 를 로직별로 구분하여 사용할 수 있어서 직관성도 좋고 관리가 매우 편리하다.
즉, 위 코드처럼 msr 데이터의 CRUD를 각각 분리하고 각각에 필요한 state 값들을 그 위에 선언하여 구분, 관리할 수 있다는 것이다.
storeToRefs
- 앞서 언급한 vuex의 마지막 getters 포지션으로 사실상 이게 끝이다.
<template>
<div class="about">
{{ name }} : {{ doubleCount }}
<button @click="store.increment">increment</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import { useCounterStore } from "@/store/counter";
import { storeToRefs } from "pinia";
const store = useCounterStore();
const { name, doubleCount } = storeToRefs(store);
</script>storeToRefs를 사용해야만 반응형이 유지가 된다.
- 사실 Vue3, Composition API를 사용하다 보면 그렇게 이상할 거 없는 문법이다.
구조 분해 할당을 통해 값을 가져올 때 반응형을 잃지 않도록 도와주는 toRefs가 이미 사용되고 있기 때문이다.
storeToRefs VS toRefs
- 그렇다면 storeToRefs 말고 그냥 toRefs로 쓰면 되지 않을까? 라는 의문을 가질수 있으나, storeToRefs에 대한 설명이 다음과 같이 쓰여있다.
Creates an object of references with all the state, getters, and plugin-added state properties of the store. Similar to toRefs() but specifically designed for Pinia stores so methods and non reactive properties are completely ignored.
(저장소의 모든 상태, getter 및 플러그인 추가 상태 속성을 사용하여 참조 개체를 만듭니다. toRefs()와 유사하지만 Pinia 저장소를 위해 특별히 설계되어 메서드와 비 반응 속성이 완전히 무시됩니다. - 구글 번역)
뭐 그냥 Pinia를 위해 특별히 설계되었다고 생각하면 될 것 같다.
이해를 돕기위한 예제 코드 2
<template>
<div>
<input type="text" v-model="text" />
<button @click="addList(text)">추가</button>
<h4>추가된 목록</h4>
<p v-for="(item, index) in getDataAll" :key="index">
{{ item }}
</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { computed, ref } from "vue";
import { useListStore } from "./stores/list";
//구조분해할당 활용
//import { storeToRefs } from "pinia";
export default {
setup() {
const text = ref("");
const list = useListStore();
//구조분해할당 활용
//const { getDataAll } = storeToRefs(list);
function addList() {
if (!text.value) return;
list.addList(text.value);
//액션 후촐 외에도 직접 내부 API로 데이터 변경 가능.
//list.$patch({ list: [...list.getDataAll, text.value] });
text.value = "";
}
return {
text,
addList,
getDataAll: computed(() => list.getDataAll),
//구조분해할당 활용
//getDataAll
};
},
};
</script>- Vue 컴포넌트 내에서는 위와 같은 형식으로 사용할 수 있다.
커스텀Store를 import해주고 내부의 코드를 호출해서 동작시키면 된다.
내부의 state를 변경 시키기위해 action을 사용할 수도 있지만, 이 외에도 내부 API인 $patch를 통해서 변경시킬 수 있다.
또한, computed 대신 구조분해 할당을 활용하게 되면 Vue3에서 반응형이 깨지기 떄문에 storeToRef로 묶어서 반응형으로 유지시켜 줘야만 한다.
storeA 의 값을 storeB 에서 사용하기
굉장히 자주 있을 수 있는 일이다.
언듯 보기엔 그냥 storeA를 storeB에 선언하여 속성값에 접근하여 바꾸면 될 것 같지만 에러가 뜬다
// storeA.js
export const useStoreA = defineStore("storeA",{
const valueA = ref<string>('This is value A');
const setValueA = (newValue:string) => {
this.valueA = newValue;
}
return {valueA, setValueA}
});
// storeB.js
import { defineStore } from 'pinia';
import { useStoreA } from './storeA';
export const useStoreB = defineStore("storeB",{
const storeA = useStoreA();
const somethingFn = async () => {
const res = await somethingHttpFn();
// 대충 res => "This is value B" 가 되는 로직
storeA.valueA.value = "This is value B"
}
return {};
});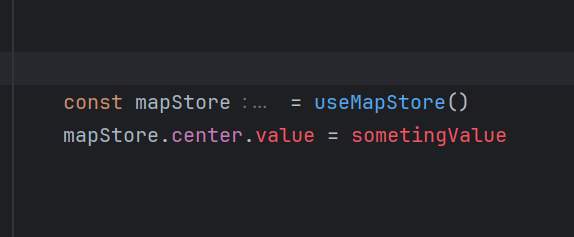
하지만 위 사진 처럼 바로 에러가 뜨는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
방법은 setter 함수를 만들어버리면 된다.
참고로 위는 composition API로 작성했으니 아래는 Options API로 작성하였다.
// storeA.js
import { defineStore } from 'pinia';
export const useStoreA = defineStore({
id: 'storeA',
state: () => ({
valueA: 'This is value A',
}),
actions: {
setValueA(newValue) {
this.valueA = newValue;
},
},
});
// storeB.js
import { defineStore } from 'pinia';
import { useStoreA } from './storeA';
export const useStoreB = defineStore({
id: 'storeB',
setup() {
const storeA = useStoreA();
return {
valueFromStoreA: computed(() => storeA.valueA),
changeValueA: () => {
storeA.setValueA('This is value B');
},
};
},
});
