엔지니어란? 문제를 해결하는 사람
- 앞으로 나올 문제들은 어려워질 것이다.
- 우리 앞에 나온 선배들이 이미 쉬운 문제는 다 풀었다.
- 어려운 문제일수록 분석이 중요하다.
왜 프로그램 랭귀지라고 할까?
language는 소통의 도구
프로그래머는 CPU와의 소통을 하는 사람이다.
리액트 시작해보기
eslint 설치
-> zen 코드라고 한다. js에서는 자동으로 제공해줌.
-> zen 코드 설정 후 모습
js01.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="ko">
<head>
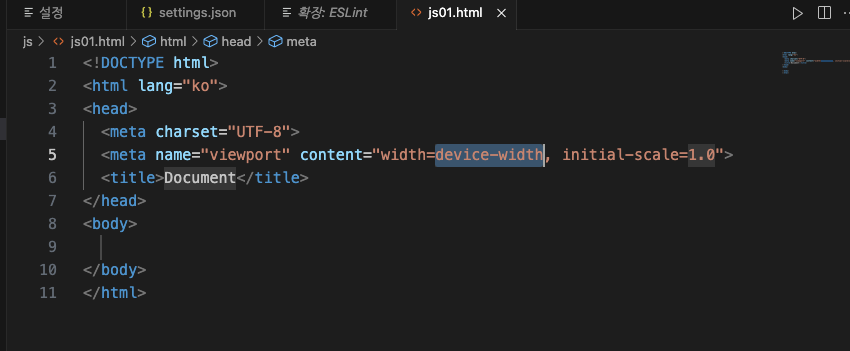
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
h1{
font-size: 50px;
font-family: "궁서체";
color: blueviolet;
}
/* class */
.title{
font-size: 60px;
color: blue;
}
/* id */
#title{
font-size: 30px;
color: cornflowerblue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!--
h1 tag 글자 크기 50px, 글자체: 궁서체, 색: blueviolet;
2개 - 글자 크기 60px, 색: blue;
2개 - 글자 크기 60px, 색: pink;
-->
<h1 class = "title" style="font-size:60px; color: blue;">html baisc</h1>
<h1 style="font-size:60px; color: blue;">html baisc</h1>
<h1 class = "title" style="font-size:60px; color: pink;">html baisc</h1>
<h1 id="title" style="font-size:60px; color: pink;">html baisc</h1>
<h1>html baisc</h1>
<h1>html baisc</h1>
<button type="button" onclick="changeContent()">내용 바꾸기</button>
<script>
function changeContent() {
document.getElementById('title').innerText = 'HTML 기본';
}
</script>
</body>
</html>css01.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="ko">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
/* 기본 선택자 */
.class01 { background-color: silver;}
#fruit { background-color: transparent;}
/* 복합 선택자 */
ul li { color: blue;} /* 자손 */
ul > li { background-color: pink;} /* 자식 */
li#기준 ~ li { color: plum; } /* 바로 뒤의 형제들 */
li#기준 + li { color: plum; } /* 바로 뒤의 형제들 */
/* 속성 선택자 */
li[title] {color: orange;} /* 속성 존재 여부 */
li[title="할인"] {color: red;} /* 속성 값이 같다면 */
li[title~="무료배송"]::after{content:"[무료배송]";} /* 공백 기준으로 포함된다면 */
li[title$="품절"] {color: grey;} /* 속성 값이 끝난다면 */
li[title^="hot"] {color: red; font-weight: bold;} /* 시작된다면 */
li[title*="무료"] {text-decoration: underline;} /* 포함된다면 */
li[title~="할인"][title~="무료배송"] {color:black;} /* and */
li[title~="할인"], li[title~="무료배송"] {color:black;} /* or */
/* 가상 선택자 */
#fruit > ol > li:nth-child(2n) { background-color: lime;}
#fruit > ol > li:hover { text-decoration: underline;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li>요소1</li>
<li>요소2</li>
<li>요소3</li>
<li>요소4</li>
<li id="fruit">요소5
<ol>
<li title="">사과</li>
<li title="할인">배</li>
<li title="할인 무료배송">바나나</li>
<li title="무료배송 품절">수박</li>
<li title="hot 무료배송">복숭아</li>
<li><a href="#" target="_blank" data-url="">외부 쇼핑</a></li>
</ol>
</li>
<li>요소6</li>
</ul>
<script>
$('li[title$="품절"]'.on('click', function() {
alert('품절입니다.');
}));
document.querySelector('li[title$="품절"]').addEventListener('click', function(){
alert('품절입니다.');
})
$('h1').on('click', function() {
$('body').append('<h1>Header</h1>');
});
</script>
</body>
</html>js02.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="ko">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
console.log(add(1, 2));
function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
console.log(add(1, 2));
var a = 10;
function add3() {
var c = 0;
for (i=0, cnt=arguments.length; i < cnt; i++) {
c += Number(arguments[i]);
}
return c;
}
console.log(add3(10));
console.log(add3(10, 20));
console.log(add3(10, 20, 30, 40, 50));
function add4(...a) {
var c = 0;
for (i=0, cnt=arguments.length; i < cnt; i++) {
c += Number(arguments[i]);
}
c = 0;
a.forEach((x) => c += x);
return c;
}
console.log(add4(10));
console.log(add4(10, 20));
console.log(add4(10, 20, 30, 40, 50));
function add5(a, b, ...f) {
var c = 0;
f.forEach((g) => c += g(a,b))
}
console.log(add5(1, 2, (a,b)=> a+b, (a,b) => a-b));
</script>
</body>
</html>호이스팅?
인터프리터가 코드를 실행하기 전에 함수, 변수, 클래스 또는 임포트(import)의 선언문을 해당 범위의 맨 위로 이동시키는 과정
JS에서는 global context가 무조건 만들어진다.
js03.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="ko">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var name = '가';
let name1 = 'A';
console.log(name, name1);
console.log(this.name, this.name1);
console.log(window.name, window.name1);
function test() {
var name = '나';
console.log(name);
console.log(this.name);
}
test();
window.test();
</script>
</body>
</html>