posted based on udemy video -
Android OS Internals😁
Android Architecutre
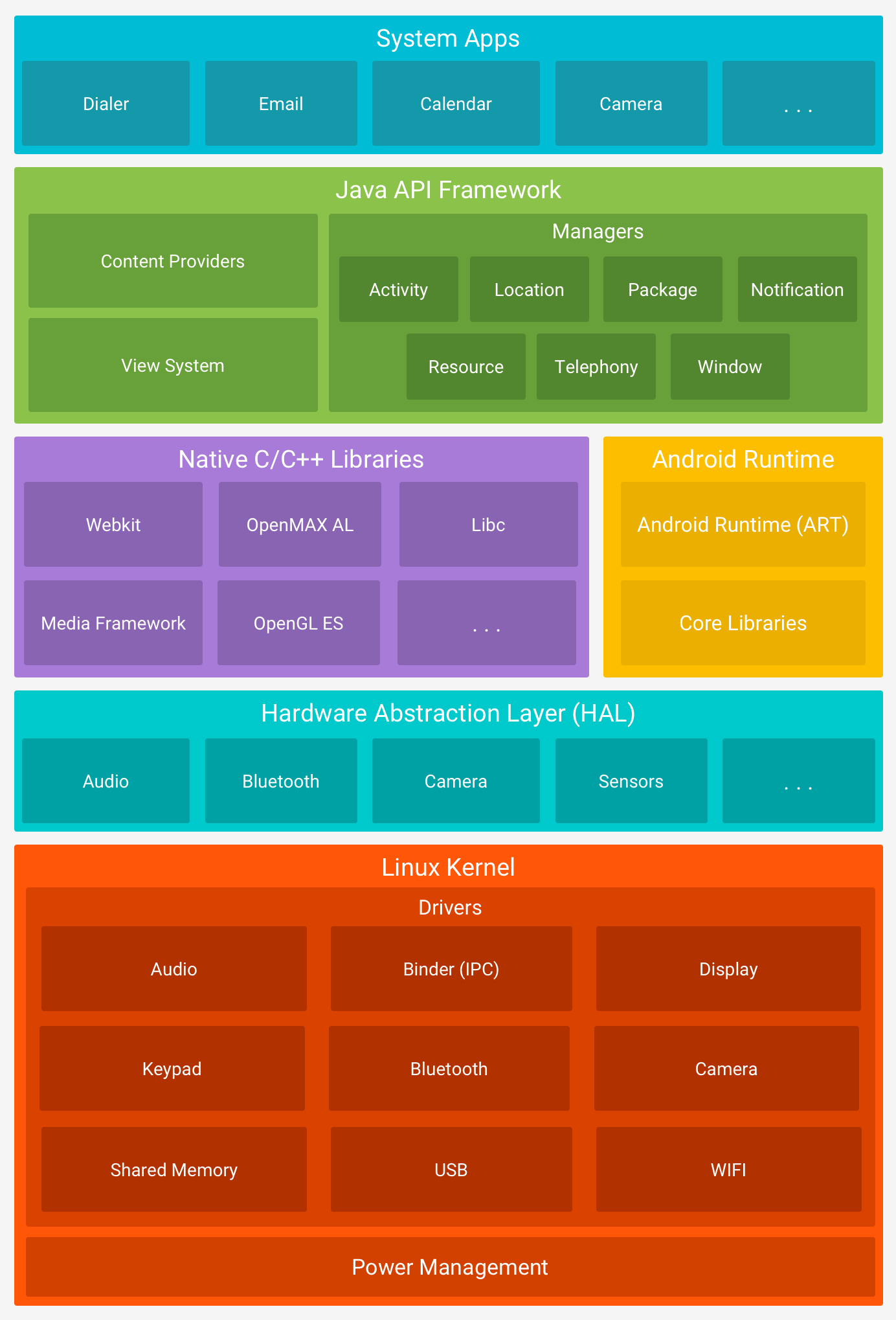
Application layer
Both built-in applications and non-system-level applications belong to the application layer.
Responsible for direct interatio with users, usually developed in Java or Kotlin.
Application framework layer (Java Framework)
The application framework layer provides developers with the APIs needed to develop applications.
This layer is written by Java code and can be called Java Framework.
Framework
| API | Description |
|---|---|
| ⭐ Activity Manager | Manage the life cycle of each application and the usual navigation fallback function |
| Location Manager | Provide the geographic location and positioning function services |
| Package Manager | Manage all applications installed in the Android system |
| Notification Manager | Allows the application to display custom prompt information in the status bar |
| Resource Manager | Provide various non-code resources the application uses, such as localized strings, pictures, layout files, color files, etc. |
| Telephony Manager | Manage all mobile device functions |
| Package Manager | Manage all application installed in the Android system |
| Window Manager | Manage all open windows |
| Content Providers | Allows data to be shared betwwen different applications |
| View System | Building the essential view components of an application |
System Runtime Layer (Native)
1. C/C++ Library
The C/C++ library can be used by different Android system components and provide developers service through the application framework.
So, all the services which we use through the application are dependent on the C/C++ library.
For example...
| Library | Description |
|---|---|
| OpenGL Embedded systems | 3D drawing function libray for embedded systems |
| Libc | Standard C system function library inherited from BSD(BSD stands for Berkeley Software Distribution, and this is basically customized for embedded Linux), specially customized for embedded Linux-based devices |
| Media Framework | Multimedia library supports recording and playback of various commonly used audio and video formats. |
| SQLite | The lightweight relational database engine |
| SGL | The underlying 2D graphics rendering engine |
| SSL | The secure socket layer is a security protocol that provides security and data integrity for network communications |
| FreeType | Portable font engine, it provides a unified interface to access a variety of font format files |
2. Android runtime library
The runtime library is divided into the core library and ART (after Android 5.0, Davlik virtual machine was replaced by ART)
The core library provides most of the Java language core library functions so that developers can use the Java language to write Android applications.
The ART/Dalvik virtual machine is specifically customized for mobile devices, allowing multiple instances of the virtual machine to run in limited memory simulataneuously, and each Dalvik application is executed as an independent Linux process.
So, since we have separate process, it prevents all programs from closing when the virtual machine crashes.
So that is the main advantage since we have different process.
Even if the virtual machine is virtual machine crashes, then it will prevent from all the apps or the programs from being closed.
So the reason why Dalvik virtual machine was migrated to SRT is that is provides some advantages compared to Dalvik virtual machine.
So under Dalvik the bytecode needs to be converted into machine code by a just in time compiler every time the application is run.
So Davlik basically used a just in time(JIT) compiler.
Whenever the application runs, it has to convert the code into machine code.
This will slow down the execution speed of the app with the introduction of error after Android five, the code of all the application will be pre compiled in the machine code when it is first installed in the device.
Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL)
The hardware abstraction layer is the interface between the operation system kernel and the ahrdware circuit.
Its purposeis to abstract the hardware. To protect the intellectual property rights of hardware manufacturers, it hides the hardware interface details of a specific platform and provides a virtual hardware platform for the operating system.
So that it has hardware independence, it can be transplated on various platforms.
It can be transplated on various platforms from the perspective of software and hardware testing, both software and hardware testing can be completed based on the hardware abstraction layer, making it possible to perform software and hardware testing in parallel.
Linux kenrnel layer
Android's core system services are based on the Linux kernel, and some Android-specific drivers have been added on this basis.
The system's security, memory management, process management, network protocol stack, and driver model depend on this kernel.
[References]
udemy - Android OS Internals
