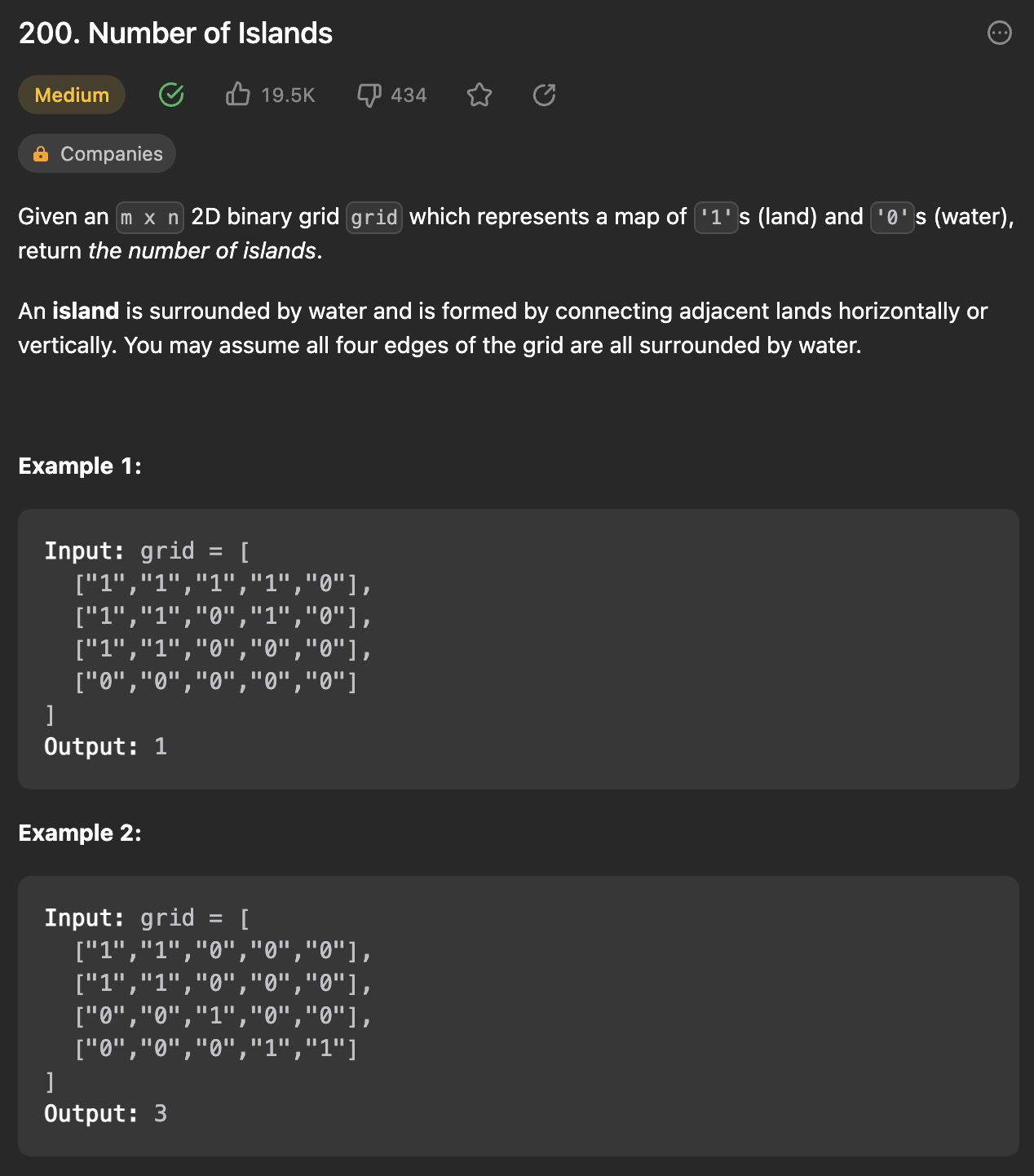
Problem
Solve
public static int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
int island = 0;
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length;
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[m][n];
for(int i = 0 ; i < m ; i++){
for(int j = 0 ; j < n ;j++){
if(grid[i][j] == '1' && !visited[i][j]){
//1. BFS
bfs(grid, visited, i,j);
//2. DFS
dfs(grid, visited, i,j);
island++;
}
}
}
return island;
}2차원 배열을 순회하면서 1, 즉 섬을 발견하면 너비든, 깊이든 연결되어 있는 섬을 세고, 또 for문을 통해 순회를 하면서 동 떨어져 있는 넓게 분포되어 있는 섬을 찾는다.
graph 문제로 BFS(Breadth-First-Search) 너비 우선 탐색과 DFS(Depth-First-Search) 깊이 우선 탐색으로 해결할 수 있다.
BFS
시작점으로 부터 가장 가까이에 있는 정점을 순서대로 순회하면서 점점 먼 정점을 향해 순회하는 그래프 탐색 방식
-> queue 이용
//BFS
public static void bfs(char[][] grid, boolean[][] visited, int x, int y){
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(new int[]{x,y});
visited[x][y] = true;
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int[] cur = queue.poll();
//System.out.println("("+cur[0]+","+cur[1]+")");
for(int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++){
int nx = cur[0] + dx[i];
int ny = cur[1] + dy[i];
if(nx < 0 || nx >= grid.length || ny < 0 || ny >= grid[0].length) continue;
if(grid[nx][ny] == '1' && !visited[nx][ny]){
visited[nx][ny] = true;
queue.add(new int[] {nx, ny});
}
}
}
}DFS
시작점에서 부터 가장 깊게 떨어진 정점을 향해 탐색하다가 더이상 전진할 정점이 없을 경우 다시 시작점에서 다른 방향으로 깊게 나아가는 그래프 탐색 방법
-> 재귀적 recrusive
//DFS
public static void dfs(char[][] grid, boolean[][] visited , int x, int y){
System.out.println("("+x+","+y+")");
visited[x][y] = true;
for(int i = 0 ; i < 4; i++){
int nx = x + dx[i];
int ny = y + dy[i];
if(nx < 0 || nx >= grid.length || ny < 0 || ny >= grid[0].length) continue;
if(grid[nx][ny] == '1' && !visited[nx][ny]){
dfs(grid, visited, nx, ny);
}
}
}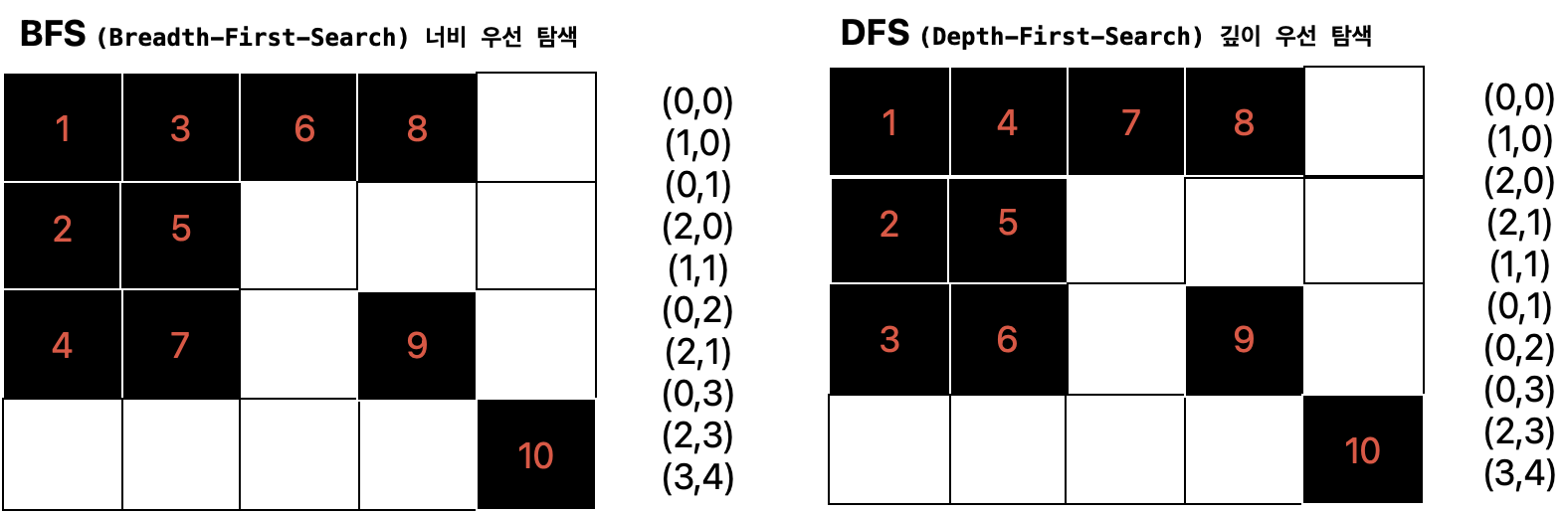
상하좌우를 순서대로 새로운 방향을 탐색했을 경우 방문하는 좌표 순서
