역할
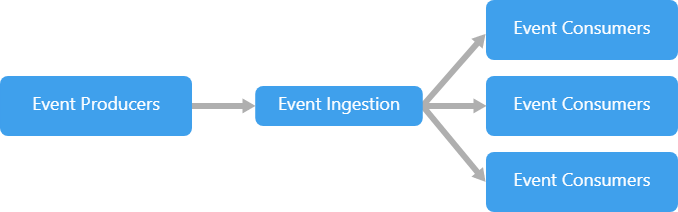
출처 : https://docs.microsoft.com/ko-kr/azure/architecture/guide/architecture-styles/event-driven
Event는 위처럼 Consumer(Subscriber, Listener)가 Producer(Publihser)를 구독하면 Producer에서 Event를 publish할 때마다 Consumer가 이 정보를 받아와 처리하는 구조이다
EventListener 등록
ApplicationListener구현
protected void registerListeners() {
// 정적 리스너 등록
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners()) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener);
}
// 우리가 추가한 리스너 등록
String[] listenerBeanNames = getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false);
for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeanNames) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(listenerBeanName);
}
}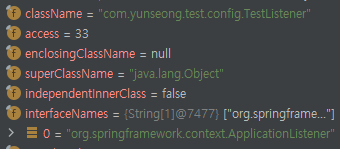
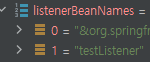
BeanDefinition목록 중 ApplicationListener.class타입인걸 찾아온 뒤 EventListener로 등록한다
( TestListener의 Type이 ApplicationListener인것도 확인가능 )
@EventListener
EventListener는 EventListnerMethodProcessor에의해 Listener로 등록된다
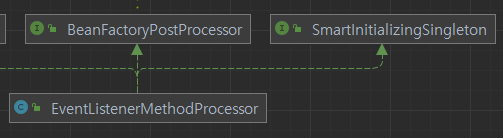
EventListenerMethodProcessor의 ClassDiagram을보면 SmartInitializingSingleton을 구현하는걸 볼 수 있다
이 SmartInitializingSingleton을 이용하면 Bean의 초기화 과정이 전부다 끝나고나서 제일 마지막에 호출되게 할 수 있다
즉 Bean의 생성이 완료됐다는걸 보장할 수 있으며 이에 대한 정확한 후처리가 가능해진다
실제 코드로봐도 Bean생성 다음에 afterSingletonsInstantiated()를 호출한다
@Override
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
...
Bean생성 및 초기화 ( IoC컨테이너 부분에서 자세히 설명합니다 )
...
for(..) {
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {
...
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
...
}
}EventListnerMethodProceossor는 위 기능을 이용해 @EventListener를 등록시킨다
EventListenerMethodProcessor.class
@Override
public void afterSingletonsInstantiated() {
...
processBean(beanName, type);
...
}
private void processBean(final String beanName, final Class<?> targetType) {
if (!this.nonAnnotatedClasses.contains(targetType) && AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(targetType, EventListener.class) &&
!isSpringContainerClass(targetType)) {
Map<Method, EventListener> annotatedMethods = null;
...
annotatedMethods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(targetType,
(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<EventListener>) method ->
AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(method, EventListener.class));
...
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(annotatedMethods)) {
...
}else {
...
ApplicationListener<?> applicationListener =
factory.createApplicationListener(beanName, targetType, methodToUse);
...
context.addApplicationListener(applicationListener);
...
}
}
}SmartInitializingSingleton에 의해 Bean이 완전히 초기화가 된 후 실행되며 @EventListener가 있는 Method들만 찾아내 이를 리스너로 등록한다
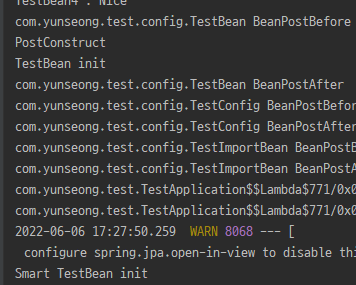
디버깅 과정을 보자
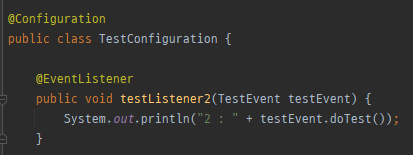
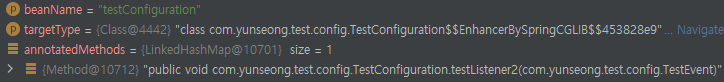
TestConfiguration안에 TestEvent가 정상적으로 등록된걸 볼 수 있다
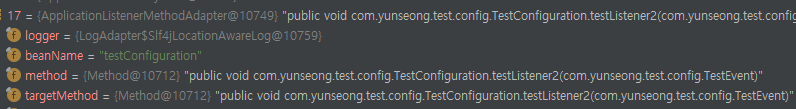
Context에는 ApplicationLsitenerMethodAdapter라는 Listener가 등록되고 이안에 해당 Method와 Bean정보가 기록된다
EventPublisher
ApplicationEventPublisher
ApplicationEventPublisher.publishEvent를 호출하면 아래의 동작으로 진행된다
AbstractApplicationContext.class
protected void publishEvent(Object event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
...
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(applicationEvent, eventType);
...
if (this.parent instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) {
((AbstractApplicationContext) this.parent).publishEvent(event, eventType);
}
else {
this.parent.publishEvent(event);
}
}getApplicationEventMulticaster를 통해 ApplicationEventMulticaster에게 처리를 위임시키고 현재 Context의 부모 Context에게도 Event를 publish한다
SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster.class
@Override
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
...
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {
if (executor != null) {
executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event)); // 비동기 실행
}
else {
invokeListener(listener, event); // 동기 실행
}
}
}
protected void invokeListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener, ApplicationEvent event) {
...
try {
doInvokeListener(listener, event);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
errorHandler.handleError(err); // 에러처리
}
...
}
private void doInvokeListener(ApplicationListener listener, ApplicationEvent event) {
...
listener.onApplicationEvent(event);
...
}Executor에 유무에 따라 Async처리와 Sync처리가 나뉘며 만약 Listener에 invoke도중 Error가 뜰경우 에러 핸들링까지 해주는 모습이다
최종적으로 listener의 onApplicationEvent(event)를 통해 Event를 기재하는걸 볼 수 있다
정리
- Event의 구조에 대해서 알 수 있었다 ( Publishser, Listener )
- Listener는 Annotation방식과 interface구현방식 2가지로 등록할 수 있다
- SmartInitializingSingleton라는 Bean의 후처리를 보다 확실하게 할 수 있는 interface에 대해서 알 수 있었다
- Publihser는 처리를 EventMulticaster에게 위임하는걸 알 수 있다
마무리
Event는 생각보다 간단한구조이고 Listener를 Bean으로 등록하는 과정들은 전부 이전포스팅에서 한 내용이기에 생각보다 짧게 끝난거 같습니다
다음에는 SpringApplication이 어떤 순서를 가지고 run을 하는지에 대해 알아볼 예정입니다
