역할
ApplicationContext는 Application에서 사용하는 Context(문맥) 즉 Application전역에서 사용할 수 있는 맥락이라는 의미이다
이를 좀더 풀어서 설명하면 서버가 켜지는 순간부터 꺼지는 순간까지 일관성있게 데이터를 사용할 수 있도록 도와주는 공간이라고 보면된다
Class Diagram
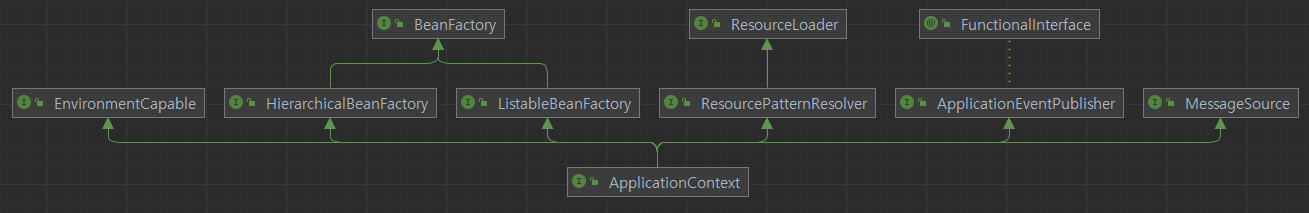
BeanFactory : 실제 Bean을 저장하고 생산해내는 인터페이스 명세이다
- HierarchicalBeanFactory : BeanFactory의 부모자식 구조를 표현해 BeanFacotry를 좀더 계층적이게 활용하도록 명세된 인터페이스
- ListableBeanFactory : 순차적인 접근이 가능한 BeanFactory로 실질적으로 Bean의 대한 정보를 관리한다
ResourceLoader : 파일Resource를 Load할 수 있게 명세된 인터페이스
ApplicationEventPublisher : 등록된 Listener에게 Event를 publish해주는 인터페이스
MessageSource : 국제화 지원을 도와주는 인터페이스
ApplicationContext는 실제 위와같은 기능들을 포함하고있으며 해당 Context또한 계층구조로 표현이 되어 각 서블릿마다 공통적으로 적용시킬 최상위 RootApplicationContext와 자식이면서 동시에 각 서블릿마다 다르게 적용시킬 ChildApplicationContext들이 있다
AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext
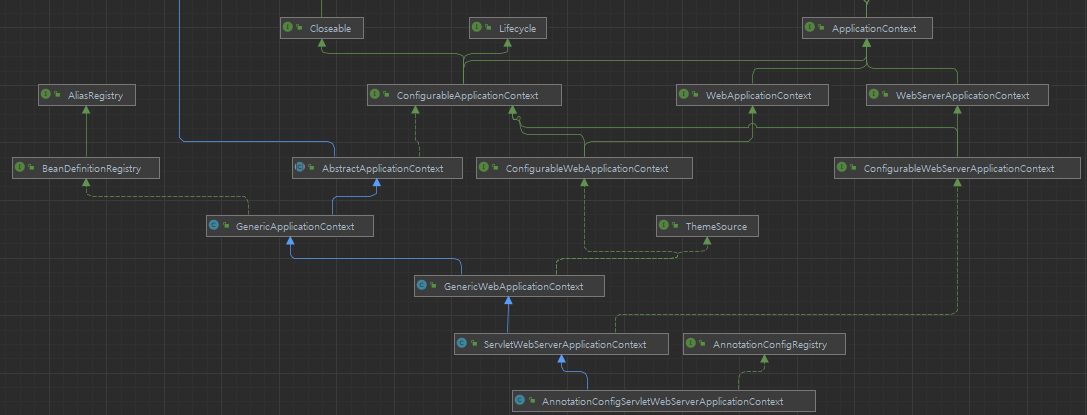
우리가 Annotation(Configuration, Component)을 통해 실제 Servlet기반의 WAS서버를 구축할 수 있게 도와주는 ApplicationContext이다
참고로 AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext는 SpringApplication이 run될 때 RootApplicationContext로서 초기화가 된다 (물론 Servlet을 사용해야 함)
여담 : XmlServletWebServerApplicationContext은 XML을 이용한 서버구축을 할때 사용된다
static class Factory implements ApplicationContextFactory {
@Override
public ConfigurableApplicationContext create(WebApplicationType webApplicationType) {
return (webApplicationType != WebApplicationType.SERVLET) ? null
: new AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext();
}
}
}
GenericApplicationContext.class
public GenericApplicationContext() {
this.beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
}해당 클래스가 생성될 때 그의 상위클래스인 GenericApplicationContext도 초기화가 되므로 DefaultListableBeanFactory가 생성되는걸 볼 수 있다

정상적으로 beanFactory에 DefaultListableBeanFactory가 들어온걸 확인할 수 있다
AbstractApplicationContext
DefaultListableBeanFactory.java
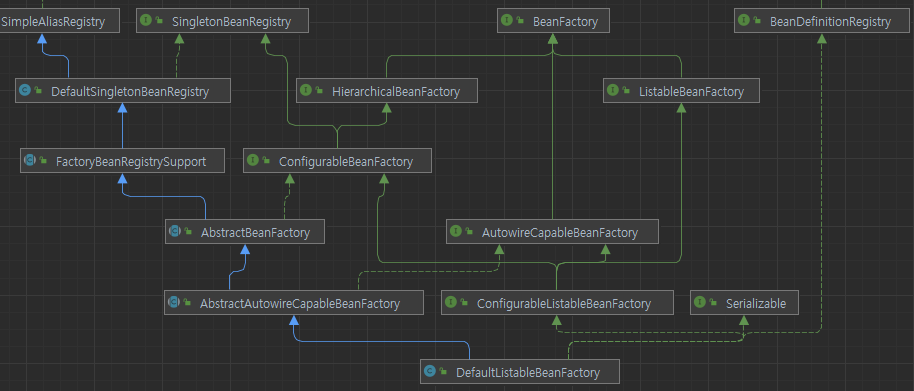
SingletonBeanRegistry(싱글톤 빈 저장), BeanDefinitionRegistry(빈 정의서 저장), ListableBeanFactory, AutowriteCapableBeanFactory(의존성 주입) 등의 많은 기능들을 포함하는 기본이되는 BeanFactory인걸 알 수 있다
BeanDefinition Init
ServletWebServerApplicationContext.class
@Override
public final void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
...
super.refresh();
...
}
AbstractApplicationContext.class
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
...
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
...
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
...
}AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext의 상위클래스인 ServletWebServetApplicationContext의 refresh가 호출될 시 refresh()작업이 시작되는걸 볼 수 있다
위 refresh()안에 있는 메서드들을 순차적으로 하나씩 살펴보자
protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
...
beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
...
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EmbeddedValueResolverAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationStartupAware.class);
...
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this);
...
}AbstractApplicationContext에서 prepareBeanFactory메서드를 통해 다양한 초기화 작업을 진행한다 ( 무시할내용들 사전에 등록할 내용들에 대한 처리작업 )
여담 : StandardBeanExpressionResolver얘는 우리가 스프링에서 SpEL을 사용할 수 있게 도와주는 Resolver이다
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
}
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.class
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
...
postProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
...
}
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
...
processConfigBeanDefinitions(registry);
...
enhanceConfigurationClasses(beanFactory);
...
}
public void processConfigBeanDefinitions(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
...
for (String beanName : candidateNames) {
BeanDefinition beanDef = registry.getBeanDefinition(beanName);
...
else if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(beanDef, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
configCandidates.add(new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDef, beanName));
}
...
}
} 위 부분을 통해 RootBeanDefinition들을 불러와 ConfigurationClass가 있는지 테스트를 하게되는데 이때 우리의 Application또한 RootBeanDefinition에 포함되어 같이 검사를 하게된다
위 부분을 통해 RootBeanDefinition들을 불러와 ConfigurationClass가 있는지 테스트를 하게되는데 이때 우리의 Application또한 RootBeanDefinition에 포함되어 같이 검사를 하게된다
여담 : processConfigBeanDefinitions 처리 후 등록된 BeanDefinition을 대상으로 enhanceConfigurationClasses(beanFactory)을 진행해 @Configruation이 달린 클래스에대해 BeanFactoryAwareMethodInterceptor, BeanMethodInterceptor인터셉터를 적용시킨 Proxy 객체를 반환한다
processConfigBeanDefinitions에 대해서 자세하게 살펴보면
ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.processConfigBeanDefinitions
ConfigurationClassUtils.class
static {
candidateIndicators.add(Component.class.getName());
candidateIndicators.add(ComponentScan.class.getName());
candidateIndicators.add(Import.class.getName());
candidateIndicators.add(ImportResource.class.getName());
}
public static boolean checkConfigurationClassCandidate(
BeanDefinition beanDef, MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory) {
...
AnnotationMetadata metadata;
...
}드디어 Componet와 관련된 Annotation을 찾았다
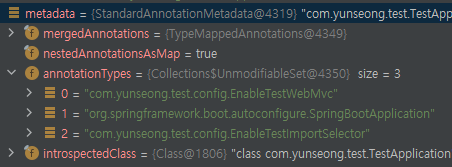
metadata를 통해 Application에 등록된 Annotation도 볼 수 있다
다시 processConfigBeanDefinitions메서드로 돌아와서 보면
public void processConfigBeanDefinitions(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
...
ConfigurationClassParser parser = new ConfigurationClassParser(
this.metadataReaderFactory, this.problemReporter, this.environment,
this.resourceLoader, this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator, registry);
parser.parse(candidates);
...
}
ConfigurationClassParaser.class
public void parse(Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates) {
...
parse(((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) bd).getMetadata(), holder.getBeanName());
...
}
protected final void parse(AnnotationMetadata metadata, String beanName) throws IOException {
processConfigurationClass(new ConfigurationClass(metadata, beanName), DEFAULT_EXCLUSION_FILTER);
}
protected void processConfigurationClass(ConfigurationClass configClass, Predicate<String> filter) throws IOException {
...
sourceClass = doProcessConfigurationClass(configClass, sourceClass, filter);
...
}
protected final SourceClass doProcessConfigurationClass(
ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass sourceClass, Predicate<String> filter)
throws IOException {
if (configClass.getMetadata().isAnnotated(Component.class.getName())) { // Component
processMemberClasses(configClass, sourceClass, filter);
}
for (AnnotationAttributes propertySource : AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(
sourceClass.getMetadata(), PropertySources.class,
org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource.class)) { // PropertySources
...
processPropertySource(propertySource);
}
...
Set<AnnotationAttributes> componentScans = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(
sourceClass.getMetadata(), ComponentScans.class, ComponentScan.class); // ComponentScan
...
for (AnnotationAttributes componentScan : componentScans {
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> scannedBeanDefinitions =
this.componentScanParser.parse(componentScan, sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : scannedBeanDefinitions) {
...
parse(bdCand.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName());
}
}
...
processImports(configClass, sourceClass, getImports(sourceClass), filter, true); // Import
AnnotationAttributes importResource =
AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ImportResource.class); // ImportResource
...
Set<MethodMetadata> beanMethods = retrieveBeanMethodMetadata(sourceClass); // Bean등록
for (MethodMetadata methodMetadata : beanMethods) {
configClass.addBeanMethod(new BeanMethod(methodMetadata, configClass));
}
...
}위의 주석순서대로 Scan이 진행된다
Parse부분에 대해서 좀더 확인해보면
ComponentScanAnnotationParser.class
public Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> parse(AnnotationAttributes componentScan, String declaringClass) {
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this.registry,
componentScan.getBoolean("useDefaultFilters"), this.environment, this.resourceLoader);
...
Set<String> basePackages = new LinkedHashSet<>();
...
for (String pkg : basePackagesArray) {
...
Collections.addAll(basePackages, tokenized);
}
for (Class<?> clazz : componentScan.getClassArray("basePackageClasses")) {
basePackages.add(ClassUtils.getPackageName(clazz));
}
...
return scanner.doScan(StringUtils.toStringArray(basePackages));
}ComponentScan Annotation에 등록된 Value들을 등록하고 Scan은 ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner에게 위임한다
처리결과에대해 디버깅을 해보면

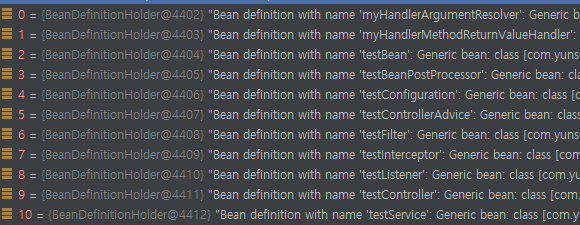 scanned된 BeanDefinition정보가 잡히게된다
scanned된 BeanDefinition정보가 잡히게된다
TestApplication또한 Bean으로 잡히는것도 확인할 수 있다
그렇다면 Configruation내에 있는 Bean 어떻게 처리될까 ?


ComponentScan도중 한번더 parse부분을 재귀적으르 처리하게 되는데 디버깅을 보면 위처럼 나오게된다 sourceClass가 Application이아닌 Configruation으로 잡히게되는 것이다
그리고 Bean처리부분에 의해 Bean으로 등록이 최종적으로 되는걸 볼 수 있다
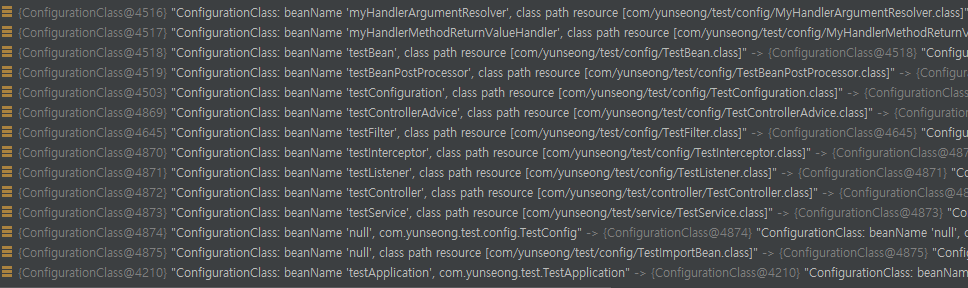
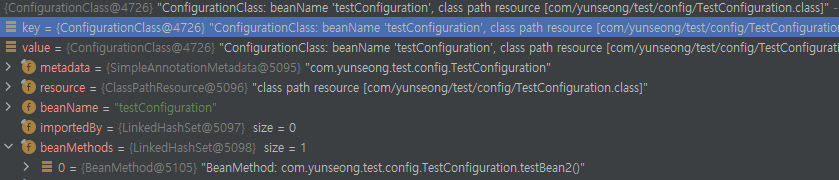
정상적으로 처리가 되면 위처럼 ConfigurationClass에 Bean정보가 담기게되고 Component내에 있는 Bean은 BeanMethod를 통해 관리되는걸 볼 수 있다
다시 processConfigBeanDefinitions으로 돌아와
public void processConfigBeanDefinitions(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
...
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configClasses);
...
}
ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader.class
private void loadBeanDefinitionsForConfigurationClass(
ConfigurationClass configClass, TrackedConditionEvaluator trackedConditionEvaluator) {
if (configClass.isImported()) {
registerBeanDefinitionForImportedConfigurationClass(configClass);
}
for (BeanMethod beanMethod : configClass.getBeanMethods()) {
loadBeanDefinitionsForBeanMethod(beanMethod);
}
...
}
private void loadBeanDefinitionsForBeanMethod(BeanMethod beanMethod) {
...
for (BeanMethod beanMethod : configClass.getBeanMethods()) {
loadBeanDefinitionsForBeanMethod(beanMethod);
}
...
}
private void loadBeanDefinitionsForBeanMethod(BeanMethod beanMethod) {
ConfigurationClassBeanDefinition beanDef = new ConfigurationClassBeanDefinition(configClass, metadata, beanName);
...
AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(metadata, Scope.class);
beanDef.setScope(attributes.getString("value"));
proxyMode = attributes.getEnum("proxyMode");
if (proxyMode == ScopedProxyMode.DEFAULT) {
proxyMode = ScopedProxyMode.NO;
}
...
BeanDefinition beanDefToRegister = beanDef;
if (proxyMode != ScopedProxyMode.NO) {
BeanDefinitionHolder proxyDef = ScopedProxyCreator.createScopedProxy(new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDef, beanName), this.registry, proxyMode == ScopedProxyMode.TARGET_CLASS);
beanDefToRegister = new ConfigurationClassBeanDefinition(
(RootBeanDefinition) proxyDef.getBeanDefinition(), configClass, metadata, beanName);
}
this.registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, beanDefToRegister);
}
loadBeanDefinition을 통해 reader에 모든 BeanDefinition을 등록한다
이 때 클래스 내부에있는 Method Bean은 위의 과정처럼 Scope를 확인하고 Proxy인경우 Proxy로 생성한 뒤 reader.registry에 저장하는걸 볼 수 있다
정리
- ApplicationContext에 포함되어있는 BeanFactory를 통해 Bean을 관리한다 ( 계층구조 가능 )
- ComponentScan이 어떻게 동작하는지 Method Bean은 어떻게 찾아내는지에 대해 알 수 있다
- BeanDefinition을 생성해 Scope전략, ProxyMode에 따라 유연성있게 Bean을 생성할 수 있다
