역할
보안에서 가장 중요한 두 축이있다. 인증과 인가라는 개념이다
인증은 말그대로 사용자가 정상적인 유저인지 아닌지를 판단하는 부분이며 인가는 정상적인 유저중에서도 어드민권한인지, 일반사용자인지 이렇게 권한을 나타낼때 사용한다
이렇게 중요한 두가지의 기능을 Authentication을 통해 스프링에서는 제공한다
출처 : https://gregor77.github.io/2021/05/18/spring-security-03/
Authentication
public interface Authentication extends Principal, Serializable {
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities();
Object getCredentials();
Object getDetails();
Object getPrincipal();
}Authentication은 인증을위해 Principal(ID나 사용자이름), Credentials(PW)를 제공하며 인가를위해 GrantedAuthority를 제공한다
추가로 인증에 필요한 메타데이터정보들(ex. IP, 인증서) 등을 저장하기위한 Details까지 저장한다
즉 해당 객체를 보유하고있으면 인증된 유저가 된다는 소리이다
그렇다면 Spring에서는 해당 인증서를 어떻게 발급해주는지 알아보자
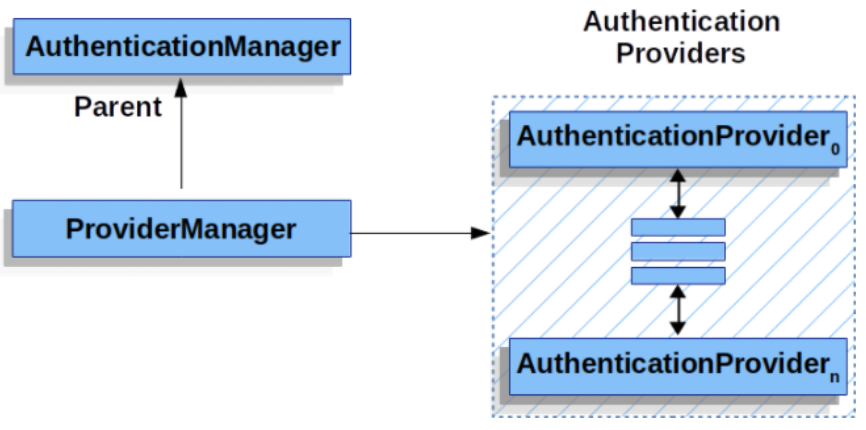
AuthenticationManager
AuthenticationManager는 Authentication를 발급해주는데 이 때 정상적으로 인증된 사용자는 데이터값이 들어있는 Authentication을 발급받게 된다
발급처리는 ProviderManager에게 위임한다
ProviderManager.class
private List<AuthenticationProvider> providers = Collections.emptyList();
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
for (AuthenticationProvider provider : getProviders()) {
...
result = provider.authenticate(authentication);
...
}
...
return result;
}다음과같이 ProviderManager클래스는 AuthenticationProvider들에게 처리를 위임시킨다
AuthenticationProvider
이제 실제 Authentication을 처리 및 발급해주는 부분에 대해서 살펴보자
AuthenticationProvider.interface
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication);
boolean supports(Class<?> authentication);AuthenticationProvider는 다음과같이 2개의 메서드를 구현해야한다
먼저 인증과 관련된 Authentication객체, 그리고 해당 Provider가 어떤 @Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> authentication) {
return (AnonymousAuthenticationToken.class.isAssignableFrom(authentication));
}Authentication객체를 지원하는지에 대한 여부이다
AnonymousAuthenticationProvider
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> authentication) {
return (AnonymousAuthenticationToken.class.isAssignableFrom(authentication));
}
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
if (!supports(authentication.getClass())) {
return null;
}
if (this.key.hashCode() != ((AnonymousAuthenticationToken) authentication).getKeyHash()) {
throw new BadCredentialsException(this.messages.getMessage("AnonymousAuthenticationProvider.incorrectKey",
"The presented AnonymousAuthenticationToken does not contain the expected key"));
}
return authentication;
}AnonymousAuthenticationProvider는 AnonymousAuthenticationToken이라는 Authentication객체를 지원하며 해당 Authentication객체가 들어오게되면 Pass를 하게된다
this(key, "anonymousUser", AuthorityUtils.createAuthorityList("ROLE_ANONYMOUS"));AnonymouseAuthenticationToken은 anonymousUser라는 사용자 객체와 ANONYMOUSE라는 인가를 가지고있다
RemeberMeAuthenticationProvider
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> authentication) {
return (RememberMeAuthenticationToken.class.isAssignableFrom(authentication));
}
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
if (!supports(authentication.getClass())) {
return null;
}
if (this.key.hashCode() != ((RememberMeAuthenticationToken) authentication).getKeyHash()) {
throw new BadCredentialsException(this.messages.getMessage("RememberMeAuthenticationProvider.incorrectKey",
"The presented RememberMeAuthenticationToken does not contain the expected key"));
}
return authentication;
}RemeberMeAuthentcationToken을 Authentication으로 가지고있으며 해당 클래스타입인경우 authenticate를 진행한다
AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
String username = determineUsername(authentication);
...
UserDetails user = this.userCache.getUserFromCache(username);
if (user == null) {
...
user = retrieveUser(username, (UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication);
...
}
...
Object principalToReturn = user;
...
return createSuccessAuthentication(principalToReturn, authentication, user);
}
protected Authentication createSuccessAuthentication(Object principal, Authentication authentication,
UserDetails user) {
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken result = UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.authenticated(principal,
authentication.getCredentials(), this.authoritiesMapper.mapAuthorities(user.getAuthorities()));
...
return result;
}Pricipal로부터 Username을찾고 Caching된값이 없으면 retriveUser를통해 UserDetails를 가져오며 이정보를 기반으로 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken을 만들어낸다
이중 retriveUser에 대해서 조금더 살펴보자
DaoAuthenticationProvider
@Override
protected final UserDetails retrieveUser(String username, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
UserDetails loadedUser = this.getUserDetailsService().loadUserByUsername(username);
...
return loadedUser;
}우리가 Bean으로 등록한 UserDetailsService를 가져와서 loadUserByUsername을 통해 User정보를 가져온다
AuthenticationManagerFactoryBean.class
@Override
public AuthenticationManager getObject() throws Exception {
...
UserDetailsService uds = getBeanOrNull(UserDetailsService.class);
DaoAuthenticationProvider provider = new DaoAuthenticationProvider();
provider.setUserDetailsService(uds);
PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder = getBeanOrNull(PasswordEncoder.class);
if (passwordEncoder != null) {
provider.setPasswordEncoder(passwordEncoder);
}
provider.afterPropertiesSet();
return new ProviderManager(Arrays.<AuthenticationProvider>asList(provider));
}실제 FactoryBean에서 AuthenticationManager를 등록할 때 UserDetailsService와 PasswordEncoder가 등록된다
UserDetailsService
실제 User들에 대한 정보를 관리하는 Service객체이다
InMemoryUserDetailsManager
private final Map<String, MutableUserDetails> users = new HashMap<>();말그대로 Map을통해 Memory에서 User를 관리할 수 있다
@Override
public void createUser(UserDetails user) {
this.users.put(user.getUsername().toLowerCase(), new MutableUser(user));
}
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
UserDetails user = this.users.get(username.toLowerCase());
return new User(user.getUsername(), user.getPassword(), user.isEnabled(), user.isAccountNonExpired(),
user.isCredentialsNonExpired(), user.isAccountNonLocked(), user.getAuthorities());
}위 메서드를 통해 User를 만들고 load해올 수 있다
이 외에 Jdbc를 통해서도 관리하고 있지만 사실 Customizing해서 쓸거기 때문에 더이상 알아볼 필요는 없다고 생각한다
정리
- Authentication은 인증과 인가를 담당하는 객체이다
- AuthenticationManager -> ProviderManager -> AuthenticationProvider -> Dao인경우 추가로 UserDetailsService 위와같은 프로세스로 Authentication객체를 가져오는 걸 알 수 있다
- 커스터마이징같은 경우 UserDetailsService를 작성하고 더 디테일하게 하려면 AuthenticationProvider와 Authentication객체까지 만들어주면된다
