아주대학교 김상훈 교수님의 운영체제 강의와 강의 자료를 바탕으로 작성된 글입니다.
what is a Process?
Process란 An instance of a program in execution이다.
storage에 있는 program을 실행하려면 memory에 올려야 한다. second storage에 file 형태로 저장된 게 program(static한 거)이다. 사용자가 프로그램을 실행시키면, 운영 시스템은 실행 파일을 메모리로 로드한다(https://wikidocs.net/230953). 이 과정에서 운영 시스템은 파일 시스템에서 실행 파일을 찾아 메모리에 적재하는데, 이렇게 메모리에 올라온 게 process이다.
하나의 프로그램으로 여러 개의 process를 만들 수 있다. (노트패드 여러 개 연 거) 또 여러 프로세스를 구분하기 위해 사용하는 게 PID이다.
Process Address Space
- Each process has its own address space in memory
- The program code, also called text section
- Data section containing global variables
- Stack containing temporary data
- Function parameters, return address, local variables
- Pointed by Stack Pointer($SP) register
- Heap containing memory dynamically allocated during run time
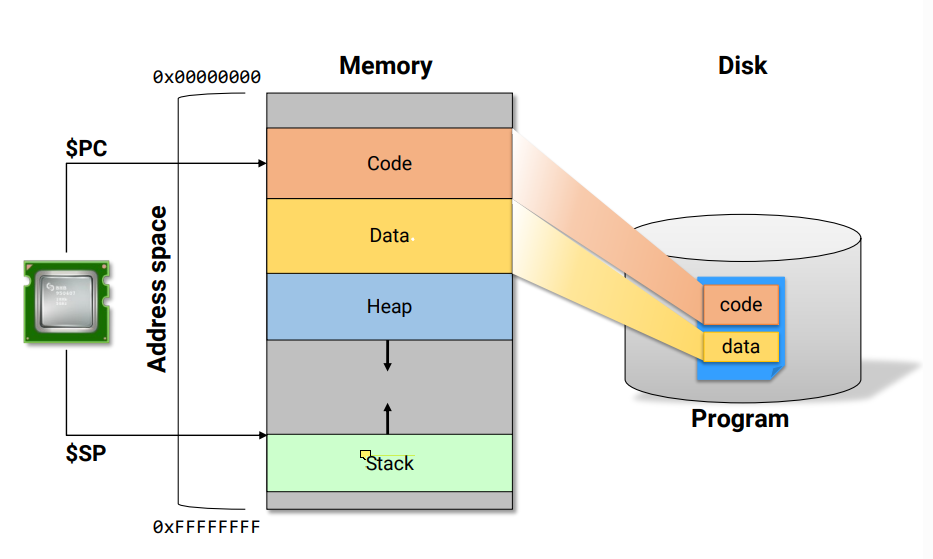
각 프로세스들이 동작하며 자신이 참조할 수 있는 메모리 영역이 생기는데, 그 영역을 Address space라고 한다. Address space는 code, data, heap, stack으로 구성돼 있다. Disk에 저장된 프로그램에는 code와 data밖에 없다. Heap과 Stack은 프로그램이 실행되면서 동적으로 공간을 확보하고 반환한다. (code와 data는 실행하면서 크기가 바뀌지 않는다.)
stack의 위치는 stack pointer($ SP)가 가리키고 있고 현재 실행 중인 instruction은 program counter($ PC)가 가리키고 있다
32bit 컴퓨터에서, 프로세스마다 할당되는 address space 크기는 2^32=4GB이다. 노트패드 5개를 실행시킨다고 하면 4GB짜리가 5개 생기는 거다.
States of Process
- As a process is running, its state is changed
- new: The process is being created
– ready: The process is waiting to be assigned to a processor
– running: Instructions are being executed
– blocked: The process is waiting for I/O completed
– exited: The process has finished execution
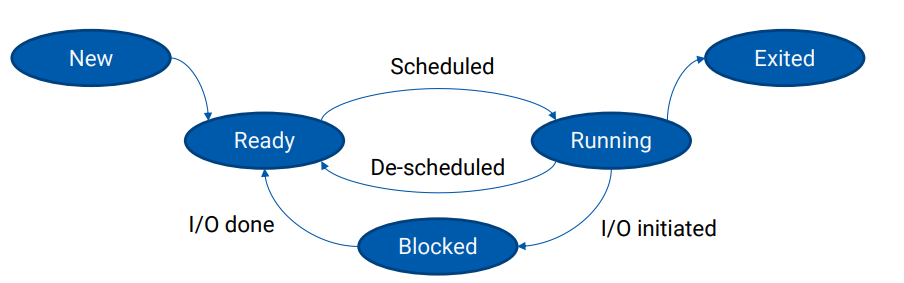
- scheduler는 ready 상태의 process를 가져와 실행시킨다. 실행 중인 process를 다시 ready 상태로 바꾸고 다른 process를 가져와 실행시킬 수도 있다.
- 실행 중인 process가 자기 logic이 다 끝나거나 error가 발생하면 종료될 수 있다(terminated). 이때 process에 할당된 resource를 os가 모두 회수한다.
- process가 I/O event를 기다릴 땐 running 상태에서 waiting 상태로 바뀐다. (I/O device마다 waiting queue가 존재함. I/O operation이 끝나면, I/O device가 CPU에게 interrupt를 날림.)
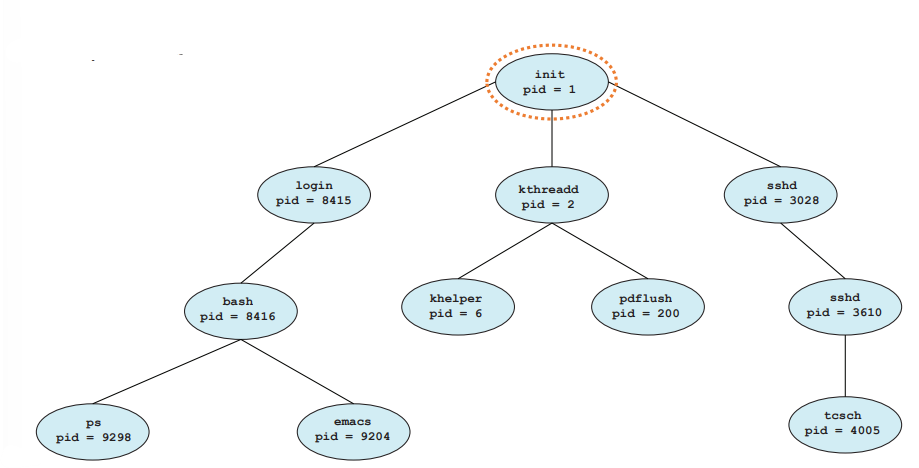
Process Hierarchy
컴퓨터가 처음 시작될 때, OS는 최초의 프로세스 init을 만든다. (init은 화면 띄우는 애, 탐색기, 시계 이런 프로세스들을 만들고 이 프로세스들이 다시 필요한 프로세스들을 만든다.)
- A process(parent) can create another processes(childern)
- Form a tree of processes
Process Creation
프로세스를 새로 만들 때 처음부터 그 프로세스의 상세 사항을 기술하는 건 너무 번거롭다. 일단 자신과 똑같은 프로세스를 만들고(fork) 그 프로세스를 변형시키는 것이 훨씬 낫다. (예를 들어, 탐색기에서 노트패드를 실행한다면, 먼저 탐색기가 탐색기를 만들고 그 탐색기를 다시 노트패드로 바꿈)
-
fork()
- Create a new process by cloning the current process
- Parent inherits most of resources and privileges: open files, UID, etc.
- Child duplicates the parent’s address space
-
addr space를 duplicate할 뿐 sharing하는 게 아님
(parent가 a 값을 수정했다고 해서 child의 a도 수정되지 x)
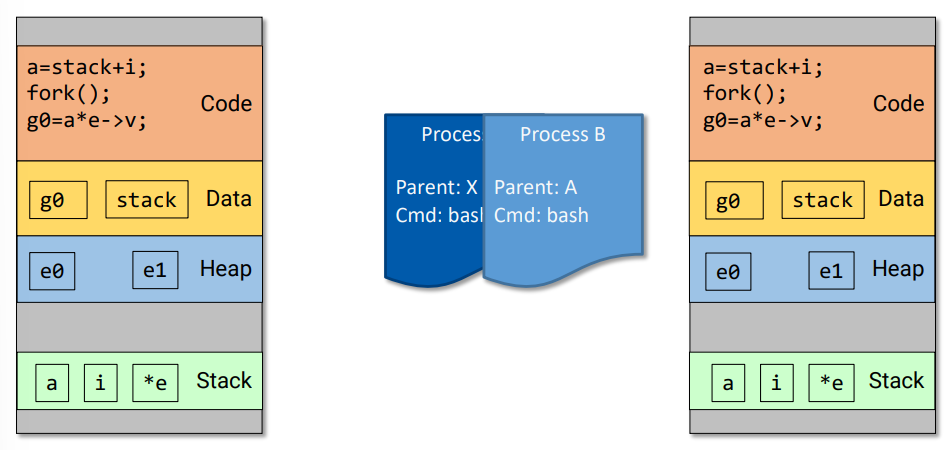
 (parent와 child의 PID는 서로 다르고, fork가 성공했을 때의 return value가 parent는 child의 pid, child는 0임)
(parent와 child의 PID는 서로 다르고, fork가 성공했을 때의 return value가 parent는 child의 pid, child는 0임)
- exec()
- Replace the current process image with a new process image
- The current address space is abandoned and re-constructed from scratch
(exec를 호출하면 기존 addr space가 다 날아가고 요청한 프로그램으로 reinitialize가 되어 새로운 addr space로 reconstruct됨)
Process Termination
-
Process may ask the OS to terminate itself using the exit() system call
-
운영체제는 exit을 호출한 프로세스와 associate된 모든 resource를 reclaim하고 return 값만 저장한다. 즉 운영체제에는 'pid n번의 return 값으로 x가 남았다.' 이 정보만 남게 된다.
-
A process can wait child process for termination with wait() system call
(자신의 자식 중에 죽은 애가 있으면 그 죽은 애의 return 값을 회수, 임의의 프로세스를 지정하는 건 waitpid) -
Zombie process
- A process which is terminated but its parent or other process has not called
wait()/waitpid() yet - 프로세스가 죽어서 addr space는 reclaim 됐는데 return 값을 아무도 가져가지 않은 대기 상태의 프로세스
- A process which is terminated but its parent or other process has not called
-
Orphan process
- A process whose parent exited without calling wait()
- 해결 방법 1. cascading termination (terminate all children, grandchildren, etc.)
- 해결 방법 2. 다른 process에게 reparanting
- 리눅스는 기본적으로 orphan process를 init(운영체제가 특별히 관리하는 프로세스)에게 reparanting시킴.
- init은 최초의 world를 만들고 나서부터는 while(1) {wait()} 처럼 다른 자식들만 wait하고 있다.
- orphan이 생기면 tree of process가 여러 tree로 분할이 되면서 root가 여러 개 생기고 구조가 복잡해지고 운영체제 코드가 복잡해지는 문제가 생긴다.
- reparanting을 통해 모든 프로세스는 항상 유효한 부모를 가지게 됨으로써 운영체제가 프로세스 자원을 효과적으로 관리할 수 있다.
Implementing Processes
- Process Control Block(PCB)
- Each PCB represents a process
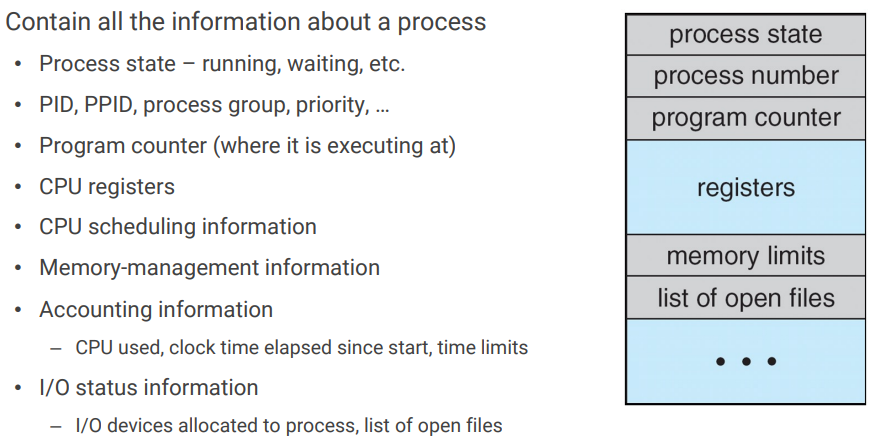
- Each PCB represents a process
Process Representation in Linux