다음 내용은 아주대학교 김상훈 교수님 운영체제 강의 및 강의 자료와 Operating Systems: Three Easy Pieces(https://pages.cs.wisc.edu/~remzi/OSTEP/)을 참고하여 작성한 글입니다.
Page Replacement
- When a page fault occurs, the OS loads the faulted page from disk into a page frame of memory
- At some point, processes have used all page frames available in the system
- OS must replace a page for each page faulted in
- evict a page (victim frame) to free up a page frame
- Which page in physical memory should be selected as a victim?
- The page fault penalty (cost of disk access) is so high
- E.g., memory access 200ns(), average disk accesses: 8ms(8 * )
- A tiny miss rate quickly dominates the overall effective access time
- p = page fault rate, (0 p 1)
- Effective access time =
- 예를 들어, p = 0.001인 경우, page를 1000번 읽으면 999번은 memory에서 hit이 나지만, 1번은 disk에 들려야 한다는 것이다. 이를 이용해 effective access time는 다음과 같이 구할 수 있다.
즉, 1000번의 access가 모두 hit이 났다면, 200ns로 계산될 effective access time이 1번만 fault가 나도 8.2ms로 엄청나게 오래 걸리게 된다.
- 예를 들어, p = 0.001인 경우, page를 1000번 읽으면 999번은 memory에서 hit이 나지만, 1번은 disk에 들려야 한다는 것이다. 이를 이용해 effective access time는 다음과 같이 구할 수 있다.
따라서 page replacement policy의 목표는 page fault rate를 최소화하는 것이다. 가장 좋은 방법은 다시는 안 쓸 page를 evict하는 것이겠지만 '다시는 안 쓸 시기'라는 건 예측하기 어렵고 이를 결정하는 데 시간이 많이 걸릴 수 있다. 따라서 page replacement policy의 목표는 다시는 안 쓸 것 '같은' page를 evict 하는 것이다.
OPT
- Also known as Belady's Algorithm
- Replace the page that will not used for the longest period in the future
- 즉, 제일 나중에 사용할 것 같은 page를 evict한다.
- The optimal page replaceent AL
- Has the lowest fault rate for any page reference stream
- Problem: Must predict the future
- 즉, 어떤 page가 미래의 어떤 시점에 쓰일지 이 미래 정보를 정확히 알고 있어야 한다. 그러나 보통은 미래 정보를 모르기 마련이다. 따라서 다른 AL의 성능을 나타낼 때 optimal 값을 제공함으로써 비교 목적으로 많이 쓰인다.
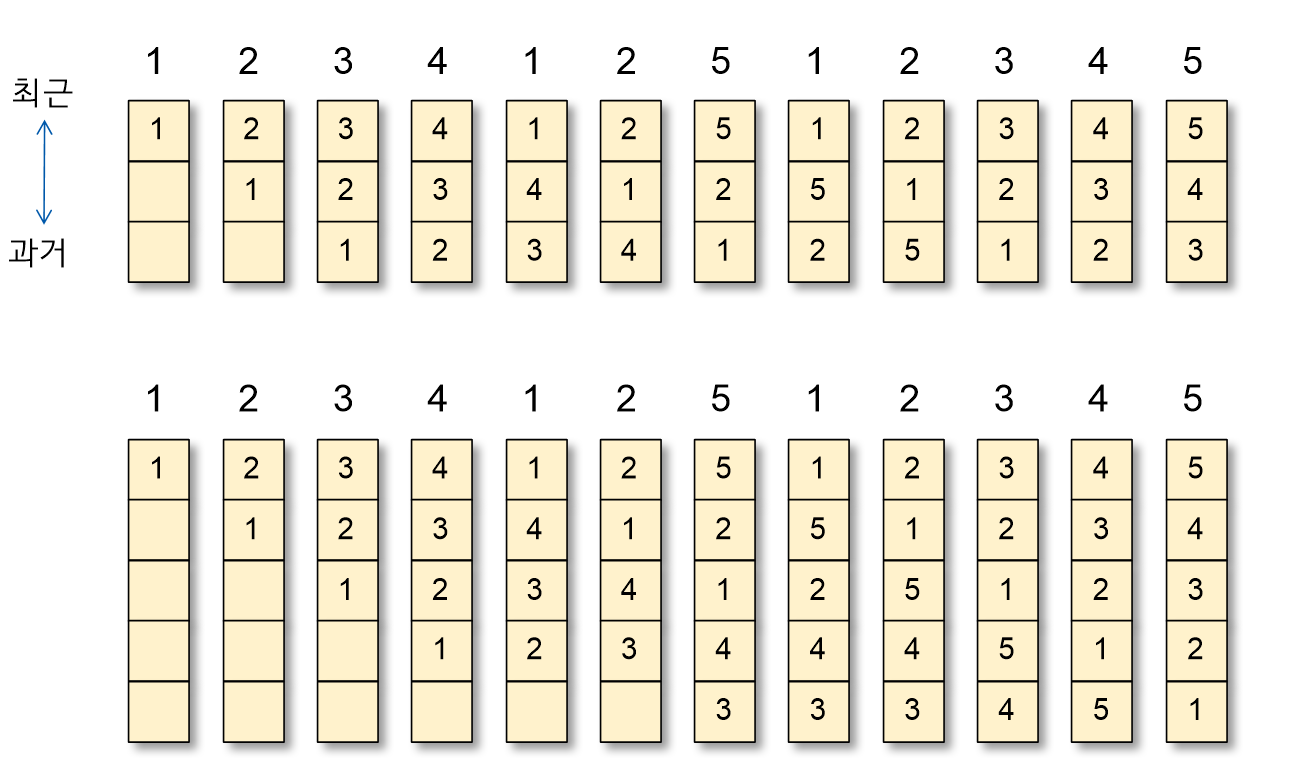
- Example
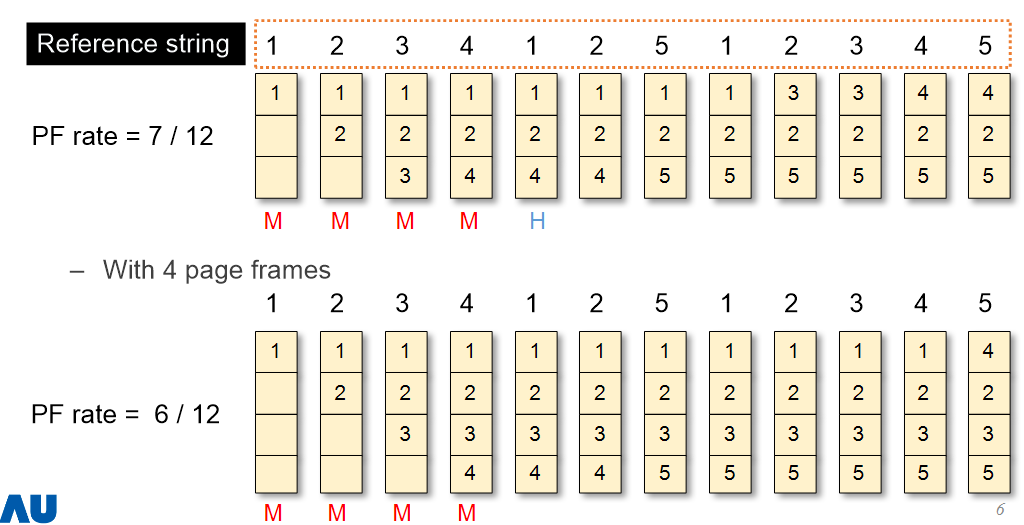
- 3개의 page frame과 4개의 page frame이 있을 때의 예시이다. 미래 정보가 부족할 경우 제일 상단의 page frame을 evict 했다. PF rate 값을 통해 page frame 개수가 늘어나니 PF rate가 작아진 것을 알 수 있다.
- 3 page frames에서 처음 3번의 경우처럼 page table이 empty 상태로 시작하여 발생하는 불가피한 miss를 cold start miss라고 한다. 아래의 4 page frames에서도 처음 4번은 불가피한 cold start miss가 발생한다.
FIFO (First-In First-Out)
- evict the one brought in longest time ago
- 가장 들어온 지 '오래된' page를 evict한다.
- 간단하고 구현이 쉽다. 또한 page frame의 수가 방대하더라도 evict하기 위해 tracking 해야 하는 page는 제일 먼저 들어온 page 하나이기 때문에 constant time에 evict할 수 있다는 장점이 있다.
- Problem: Belady's Anomaly
- Memory를 더 줘도 fault rate이 증가할 수 있다. 그 이유 중 한 가지는, Mem 참조 pattern을 생각하지 않기 때문이다. 즉, locality를 전혀 고려하지 않으니 page frame이 증가해도 fault rate이 증가할 수 있다.
- Example
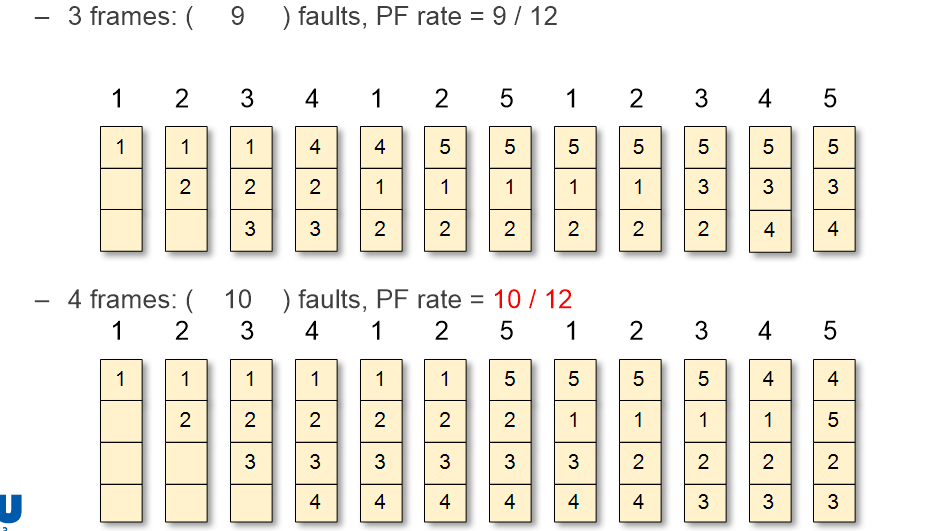
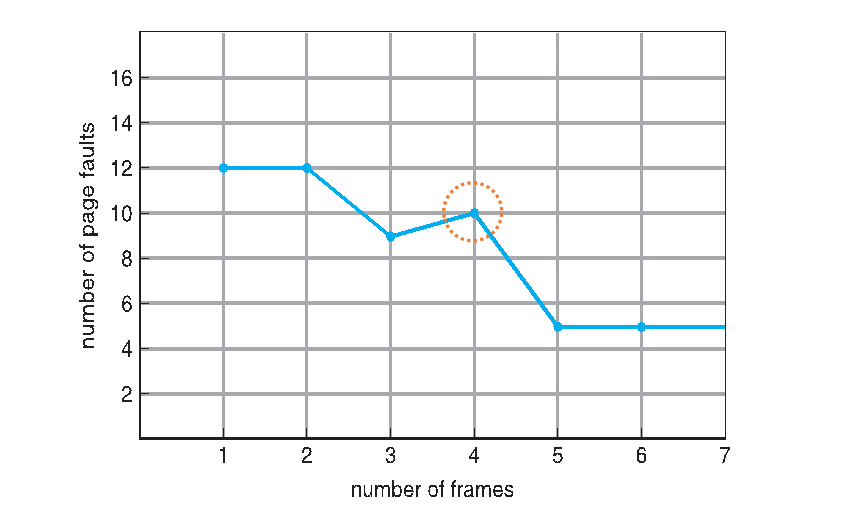
- Bealdy's Anomaly 의 이해를 돕는 사진이다. frame의 개수가 늘었음에도 faults가 증가한 시점을 관찰할 수 있다.
LRU (Least Recently Used)
- Evict the page that has not been used for the longest time in the past
- 마지막에 참조했던 시점을 기록해 두고, 제일 '마지막에 참조한' page를 evict한다.
- 과거의 reference history가 미래를 예측하는 데 도움이 될 것이라고 가정한다.
- An example of stack algorithms
- Any page in memory with n frames is also in memory with n*1 frames
- e.g., page frame의 개수가 3개일 때 존재했던 mapping 정보는 page frame의 개수가 3개 이상일 때도 존재한다.
- Guarantee incresing memory size does not incrase the number of page faults
- Free from the Belady's anomaly
- e.g., LRU나 앞에서 배운 OPT도 stack algorithm이다.
- Any page in memory with n frames is also in memory with n*1 frames
-
Example
- page frame의 개수가 3개일 때 존재했던 mapping 정보는 page frame의 개수가 5개일 때도 존재하는 것을 알 수 있다.
- page frame의 개수가 3개일 때 존재했던 mapping 정보는 page frame의 개수가 5개일 때도 존재하는 것을 알 수 있다.
-
Implemention
- Using clocks or counters
- Maintain a clock that increases for every memory reference
- Every page frame entry has a time-of-used field
- MMU updates the time-of-use field to the current clock value when accesses to a page frame
- Evict the page frame that has the smallest counter value
- Fast on memory reference, slow on replacement (especially as the size of memory grows)
- reference 시점에 clock 값만 update 하면 되므로 constant time에 update가 가능하다.
- victim page를 찾을 때 가장 큰 time-of-use field를 찾기 위해 모든 page를 다 뒤져야 한다. 즉, O(n)만큼 시간이 걸린다.
- Clock 값을 얼마나 증가시킬 것인지에 대한 부분이 모호하다. 또한, 컴퓨터를 오랜 시간 켜두면 참조 시점에서 clock 값이 매우 커져 있을 텐데 이로 인해 사용하는 bit 수가 부족해지거나 overflow 현상이 발생할 수 있다.
LRU 구현을 위해 clock을 쓸 경우, reference 시점에 page sorting을 하지 않으니 가장 마지막에 참조한 page를 찾기 위해 모든 page의 time-of-used field를 봐야 했다. 이로 인해 page replacment가 굉장히 느려졌다. 이 점을 개선하여 reference 시점에 sorting을 하는 아이디어가 doubly linked list를 사용한 아이디어이다.
- Using doubly linked list or stack
- Maintain a doubly linked list of page frames
- Move the page frame to the head of the list when it is accessed
- Evict the page at the tail
- Fast on replacement, slow on memory reference
- replace 시점에는 tail에 있는 page만 evict 하면 되므로 간단하다.
- reference 시점에 해야 할 게 상당히 많다. 최근에 참조한 시점 순으로 list를 sorting 해야 하고 entry를 하나 add/delete 할 때마다 해당 entry뿐만 아니라 다른 entry의 next, prev도 계속 update 해야 한다.
- Using clocks or counters
LRU Approximation Alogorithms
LRU AL의 단점은 구현이 어렵다는 것이다. 따라서 정확하게 reference 시점대로 sorting 하고 가장 예전에 참조한 page를 evict 하는 것이 아니라, 대략적으로나마 가장 예전에 참조된 page를 evict 하고자 한 AL이 LRU Approximation Algorithms이다.
Additional-Reference-Bits
- Each PTE has a reference bit
- MMU automatically sets the bit when it accesses the page

- OS periodically checks the reference bit of each page frame
- Shift the reference bit into the highest-order bit of the table value and discard its lowest-order bit
- R = 1이라면, v = 0b 10110101 -> 11011010로 update
- MMU가 ref update -> OS가 scan -> 모든 ref bit clear -> MMU가 ref update -> OS가 scan...이런 식으로 반복된다고 생각하면 된다.
- Evict the page with the smallest value
- 이 방법은 앞서 설명한 clock을 활용하는 방법보다는 overhead가 적지만, OS가 매번 모든 page의 reference bit을 scan 하고 ref bit을 옮기고 clear 하는 등 할 일이 너무나도 많다. 따라서 많이 사용하지는 않는다.
- MMU automatically sets the bit when it accesses the page
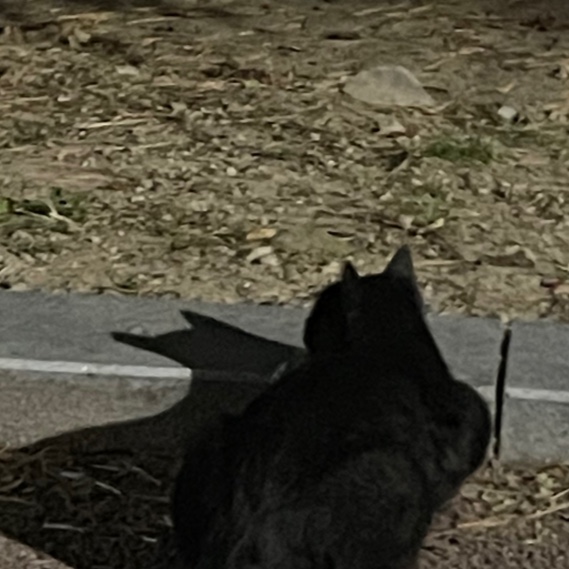
Second-Chance AL
- Also known as "clock" algorithm
- Use Reference bit in each PTE
- Arrange page frames into a big circle
- A clock hand points to the page to inspect on a page fault
- IF (R == 0), evict the page
- IF (R == 1), clear the bit and go to the next page (second chance)
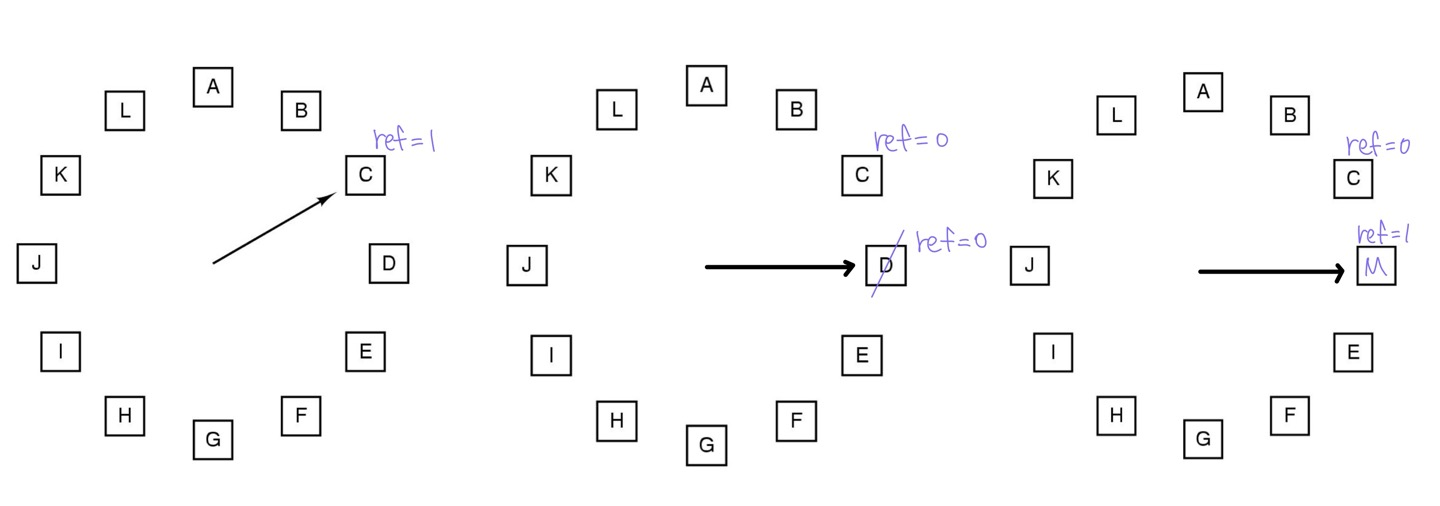
여기서 A~L은 PTE을 나타낸다. 만약 이 시점에서 C의 ref bit가 1이라면 해당 ref bit를 0으로 clear 하고 다음 PTE D로 넘어간다. D의 ref bit가 0이라면 이 page를 evict 하고 새로운 page를 추가한다. 이 page에 대한 ref bit는 1로 설정한다.