File system Implementation
Overview
- In this chapter, we study
very simple file system (vsfs)
- Basic on-disk structures, access methods, and various policies of vsfs
- We will study...
- How can we build a simple file system?
- What structures are needed on the disk?
- What do they need to track?
- How are they accessed?
- What types of data structures are utilized by the file system?
- How file system organize its data and metadata?
- Understand access methods of a file system.
- open(), read(), write(), etc.
Overall Organization
- Let’s develop the overall organization of the file system data structure.
- Divide the disk into blocks.
- Block size is 4 KB.
- The blocks are addressed from 0 to N -1.
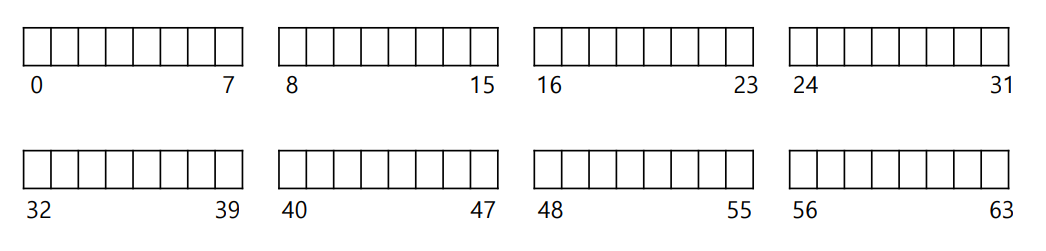
Data region in file system
- Reserve data region to store user data
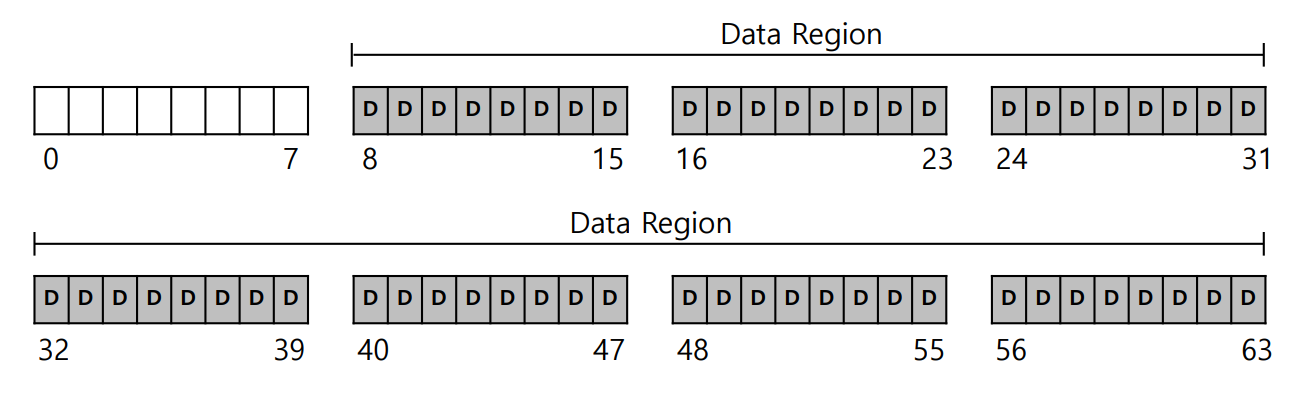
- File system has to track which data block comprise a file, the size of
the file, its owner, etc.
Inode table in file system
- Reserve some space for inode table
- This holds an array of on-disk inodes.
- Ex) inode tables : 3 ~ 7, inode size : 256 bytes
- 4-KB block can hold 16 inodes.
- The file system contains 80 inodes. (maximum number of files)
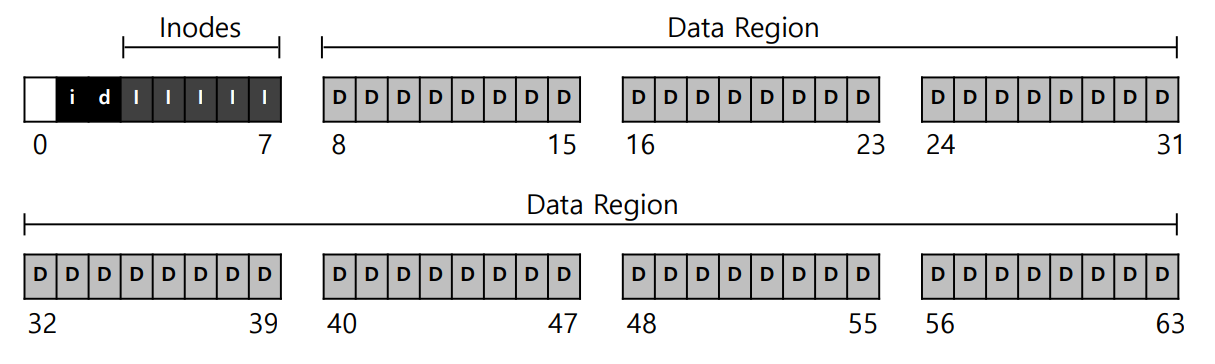
Allocation structures
- This is to track whether inodes or data blocks are free or allocated.
- Use bitmap, each bit indicates free(0) or in-use(1)
- data bitmap (d) : for data region
- inode bitmap (i) : for inode table



