🌈 힙(Heap)
🔥 힙(Heap) 이란?
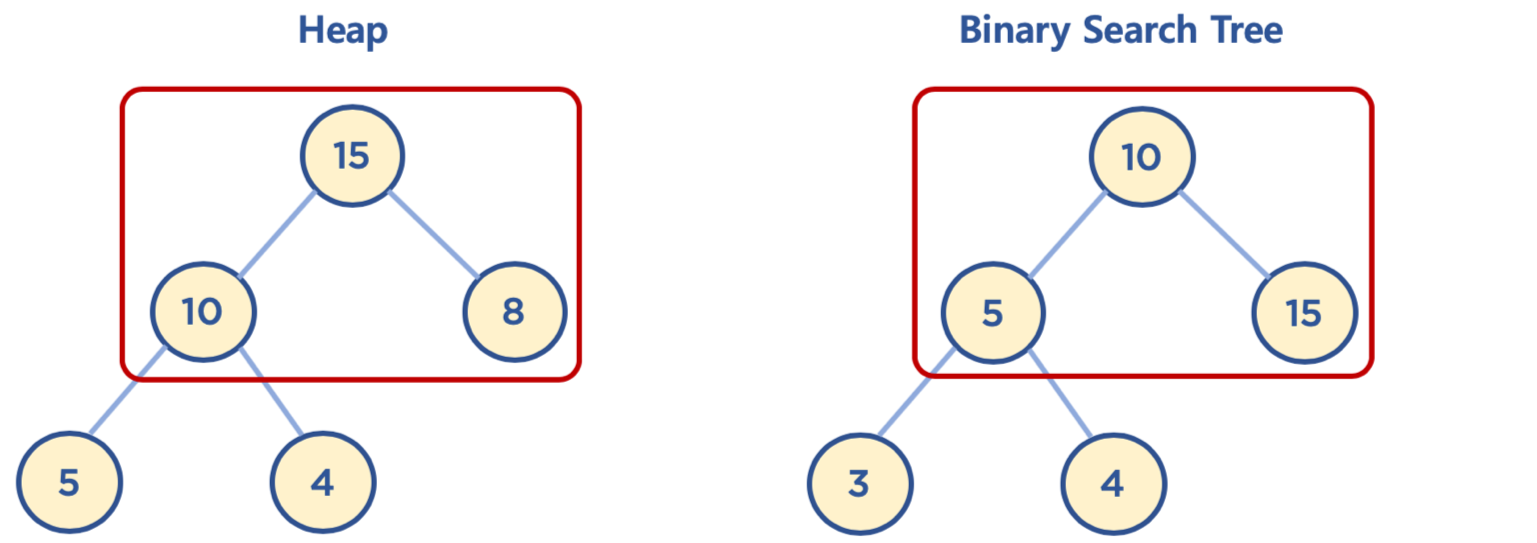
🔥 이진 탐색 트리와 heap의 공통점과 차이점
🔥 heap에 데이터 삽입
🔥 heap에 데이터 삭제
🔥 heap 연습 문제
1.힙(Heap) 이란?
- heap은 최대값과 최소값을 빠르게 찾기 위해 고안된 완전 이진 트리(Complete Binary Tree)
- 배열에 데이터를 넣고, 최대값과 최소값을 찾으려면 O(n)의 시간 복잡도가 소요되지만, heap에서 최대값과 최소값을 찾을 때 시간복잡도는 O(logN)임
- 즉, 우선순위 큐와 같이 최대값 또는 최소값을 빠르게 찾아야할 때 heap이 활용됨
- heap은 최대값을 구하기 위한 구조 Max heap(최대 힙)과 최소값을 구하기 위한 Min heap(최소 힙)으로 구분됨
- heap은 다음과 같이 두 가지 조건을 가지고 있는 자료구조임
- Parent 노드의 값은 언제나 Child 노드가 가진 값보다 같거나 크다.(최대 힙 일 경우)
- 최소힙은 맨 위의 Node의 값이 가장 작아지고, 최대힙은 맨 위의 Node의 값이 가장 큼
- 완전 이진 트리 형태를 가짐
2. 이진 탐색 트리와 heap(완전 이진 트리)의 공통점과 차이점
1) 공통점
- heap과 이진 탐색 트리는 모두 이진 트리임
2) 차이점
- heap은 각 노드의 값이 자식 노드 보다 크거나 같음(Max heap일 경우)
- 이진 탐색 트리는 왼쪽 자식 노드의 값이 가장 작고, 그 다음으로는 부모 노드 값이 작고, 오른쪽 자식 노드의 값이 가장 큼
- 부모 노드의 값과 비교해서 작으면 왼쪽, 크면 오른쪽에 삽입하기 때문
- heap은 이진 탐색 트리의 조건인 자식 노드에서 작은 값은 왼쪽, 큰 값은 오른쪽이라는 조건 없음
- 크기를 비교하지 않고, 이진 형태를 띄도록 왼쪽부터 값을 삽입함
- 서로 목적이 다름
- 이진 탐색 트리는 탐색을 위한 구조, 힙은 최대/최소값 검색을 위한 구조 중 하나로 이해하면 됨
3. heap에 데이터 삽입
- 힙은 완전 이진 트리이므로, 첫 데이터가 삽입되면 Root Node가 됨
- 추가로 데이터가 삽입되면, 왼쪽 Node가 있는지 판단하여 없으면 왼쪽 Node에 넣고, 인쪽 Node가 이미 있다면 오른쪽 Node를 탐색하여 없으면 넣음
- 오른쪽 Node까지 있다면, 다시 왼쪽 Node의 자식들이 존재하는지를 확인하여 왼쪽부터 삽입함
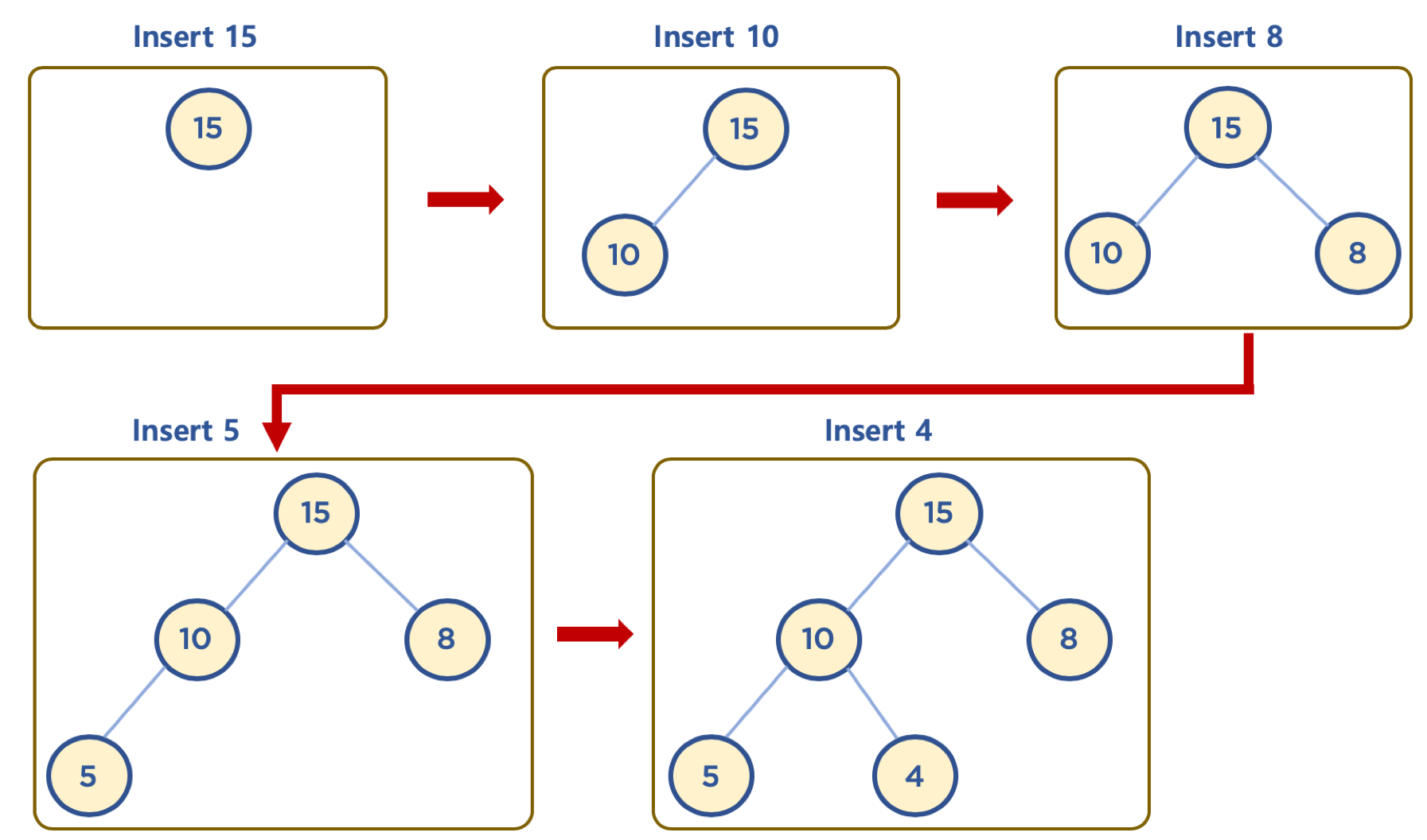
- Swap의 방법은 삽입시킨 Node의 값과 부모 Node의 값을 비교하여 삽입한 Node의 값이 더 크다면 크지 않을 때 까지 계속 Swap을 진행(Max Heap의 경우)
- 즉, 완전 이진 트리의 규칙 대로 왼쪽부터 자리를 잡게한 뒤, 삽입된 위치에서 자신의 값과 부모 Node의 값을 비교해 Swap함
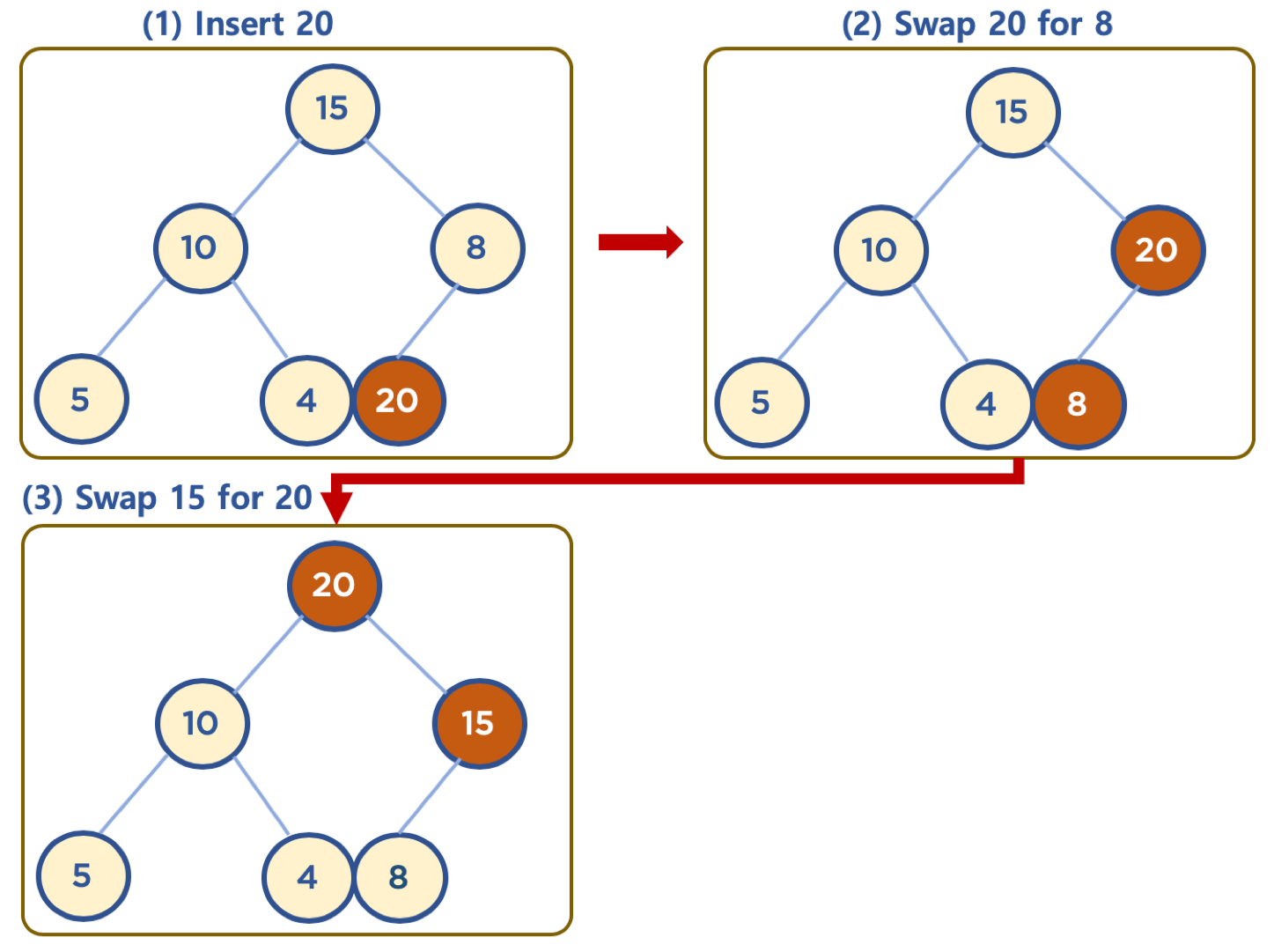
- 일반적으로 힙 구현 시, 배열을 활용하는데 heap 구현의 편의를 위해 Root Node 인덱스 번호를 1로 지정하면 구현이 보다 수월함(0번 index를 비움)
- 부모 Node 인덱스 번호는 자식 Node 인덱스를 2로 나눈 몫과 같음
🔍 parent node's index = child node's index // 2
- 왼쪽 자식 Node 인덱스 번호는 부모 Node 인덱스 번호에 2를 곱한 것과 같음
🔍 left child node's index = parent node's index * 2
- 오른쪽 자식 Node 인덱스 번호는 부모 Node 인덱스 번호에 2를 곱한 뒤 + 1 한 것과 같음
🔍 right child node's index = (parent node's index * 2) + 1
class Heap:
def __init__(self, data):
self.heap_array = list()
self.heap_array.append(None)
self.heap_array.append(data)
def move_up(self, inserted_idx):
if inserted_idx <= 1:
return False
parent_idx = inserted_idx // 2
if self.heap_array[inserted_idx] > self.heap_array[parent_idx]:
return True
else:
return False
def insert(self, data):
if len(self.heap_array) == 0:
self.heap_array.append(None)
self.heap_array.append(data)
return True
self.heap_array.append(data)
inserted_idx = len(self.heap_array) - 1
while self.move_up(inserted_idx):
parent_idx = inserted_idx // 2
self.heap_array[inserted_idx], self.heap_array[parent_idx] = self.heap_array[parent_idx], self.heap_array[inserted_idx]
inserted_idx = parent_idx
return True
heap = Heap(15)
print(heap.heap_array)
heap.insert(10)
print(heap.heap_array)
heap.insert(8)
print(heap.heap_array)
heap.insert(5)
print(heap.heap_array)
heap.insert(4)
print(heap.heap_array)
heap.insert(20)
print(heap.heap_array)
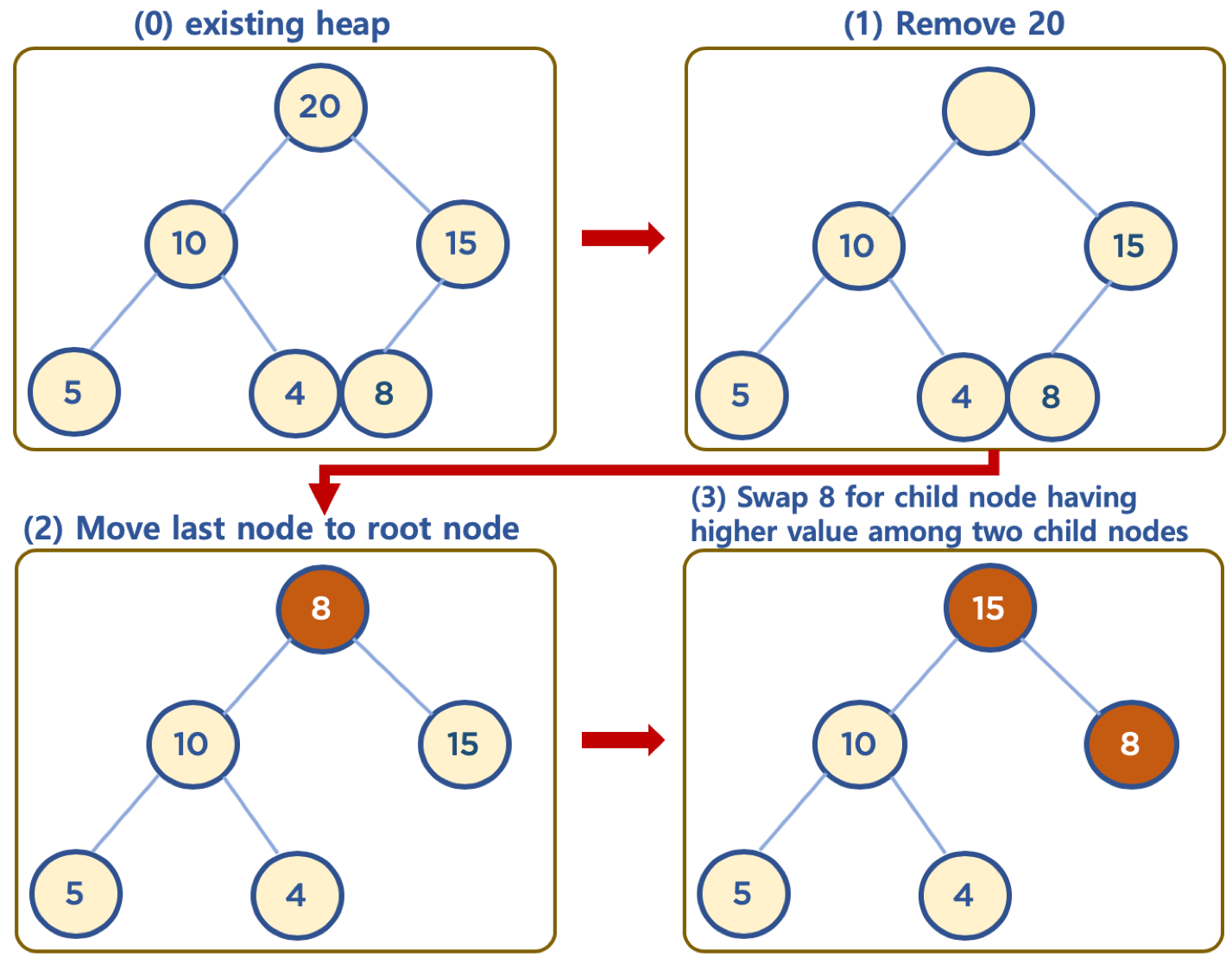
4. heap에 데이터 삭제
- 일반적으로 heap에서의 삭제는 최상단 노드(Root Node)를 삭제하는 것이 일반적임
- heap의 용도는 최대값 또는 최소값을 root에 놓고, 바로 꺼내 쓸수 있도록하는데 목적이 있기 때문
- 이에 상단에서 데이터 삭제 시, 가장 마지막에 추가한 Node를 Root Node로 이동 시킨 뒤, Parent Node와 Child Node의 값을 비교하면서 Swap시킴
- Swap 작업은 Root Node의 자식 Node 2개를 비교해서 더 큰 값과 Swap시킴(둘 중 큰 값을 올림)
- 이 Swap 작업은 자식 Node가 없거나, 부모 Node가 자식 Node보다 클 때까지 처리하고, 자식 Node의 유무에 따라 3가지 경우의 수로 나뉨
- case1 : 왼쪽 자식 노드가 없을때(자식 Node가 모두 없다는 의미)
- csee2 : 왼쪽 자식 노드만 있을 때(오른쪽 자식 노드는 없음)
- csee3 : 왼쪽, 오른쪽 자식 노드가 모두 있을 때
class Heap:
def __init__(self, data):
self.heap_array = list()
self.heap_array.append(None)
self.heap_array.append(data)
def move_up(self, inserted_idx):
if inserted_idx <= 1:
return False
parent_idx = inserted_idx // 2
if self.heap_array[inserted_idx] > self.heap_array[parent_idx]:
return True
else:
return False
def insert(self, data):
if len(self.heap_array) == 0:
self.heap_array.append(None)
self.heap_array.append(data)
return True
self.heap_array.append(data)
inserted_idx = len(self.heap_array) - 1
while self.move_up(inserted_idx):
parent_idx = inserted_idx // 2
self.heap_array[inserted_idx], self.heap_array[parent_idx] = self.heap_array[parent_idx], self.heap_array[inserted_idx]
inserted_idx = parent_idx
return True
def move_down(self, poped_idx):
left_child_poped_idx = poped_idx * 2
right_child_poped_idx = poped_idx * 2 + 1
if left_child_poped_idx >= len(self.heap_array):
return False
elif right_child_poped_idx >= len(self.heap_array):
if self.heap_array[poped_idx] < self.heap_array[left_child_poped_idx]:
return True
else:
return False
else:
if self.heap_array[left_child_poped_idx] > self.heap_array[right_child_poped_idx]:
if self.heap_array[poped_idx] < self.heap_array[left_child_poped_idx]:
return True
else:
return False
if self.heap_array[left_child_poped_idx] < self.heap_array[right_child_poped_idx]:
if self.heap_array[poped_idx] < self.heap_array[right_child_poped_idx]:
return True
else:
return False
def pop(self):
if len(self.heap_array) <= 1:
return None
returned_data = self.heap_array[1]
self.heap_array[1] = self.heap_array[-1]
del self.heap_array[-1]
poped_idx = 1
while self.move_down(poped_idx):
left_child_poped_idx = poped_idx * 2
right_child_poped_idx = poped_idx * 2 + 1
if right_child_poped_idx >= len(self.heap_array):
if self.heap_array[poped_idx] < self.heap_array[left_child_poped_idx]:
self.heap_array[poped_idx], self.heap_array[left_child_poped_idx] = self.heap_array[left_child_poped_idx], self.heap_array[poped_idx]
poped_idx = left_child_poped_idx
else:
if self.heap_array[left_child_poped_idx] > self.heap_array[right_child_poped_idx]:
if self.heap_array[poped_idx] < self.heap_array[left_child_poped_idx]:
self.heap_array[poped_idx], self.heap_array[left_child_poped_idx] = self.heap_array[left_child_poped_idx], self.heap_array[poped_idx]
if self.heap_array[left_child_poped_idx] < self.heap_array[right_child_poped_idx]:
if self.heap_array[poped_idx] < self.heap_array[right_child_poped_idx]:
self.heap_array[poped_idx], self.heap_array[right_child_poped_idx] = self.heap_array[right_child_poped_idx], self.heap_array[poped_idx]
return returned_data
heap = Heap(15)
heap.insert(10)
heap.insert(8)
heap.insert(5)
heap.insert(4)
print(heap.heap_array)
heap.insert(20)
print(heap.heap_array)
heap.pop()
print(heap.heap_array)
heap.pop()
print(heap.heap_array)
heap.pop()
print(heap.heap_array)
5. heap 연습 문제
- PriorityQueue는 put()으로 삽입하고, get()으로 추출할 수 있는 Heap 자료 구조를 위한 라이브러리임
- PriorityQueue을 사용하면, 자료 중 가장 작은 것 부터 순서데로 꺼내올 수 있음
import sys
from queue import PriorityQueue
pq = PriorityQueue()
pq.put(200)
pq.put(1)
pq.put(20)
pq.put(300)
pq.put(90)
pq.put(8)
pq.put(33)
for i in range(pq.qsize()):
print(pq.get())
"""
1
8
20
33
90
200
300
"""
- 이에 가장 작은 2개의 카드 수를 추출한 뒤, 이를 더해서 다시 PriorityQueue에 넣는 작업을 PriorityQueue가 비어있을 때 까지 반복함
- PriorityQueue는 len()을 사용할 수 없기 때문에 PriorityQueue 비어있을 때 까지 반복하기 위해 qsize() 함수를 사용
- 또한 출력값은 가장 작은 2개의 수를 추출하여 더한 값을 계속 ans 변수에 더함으로써 마지막에 출력
import sys
from queue import PriorityQueue
n = int(sys.stdin.readline())
pq = PriorityQueue()
for i in range(n):
a = int(sys.stdin.readline())
pq.put(a)
ans = 0
while pq.qsize() > 1:
min1 = pq.get()
min2 = pq.get()
next = min1 + min2
ans += next
pq.put(next)
print(ans)