Asynchronous JavaScript
Single Threan Non-Blocking
1. Web APIs
2. Async/Await
3. Callbacks
4. Microtask Queue (Job Queue)
5. Task Queue (Callback Queue)
6. Promises
7. Event loop
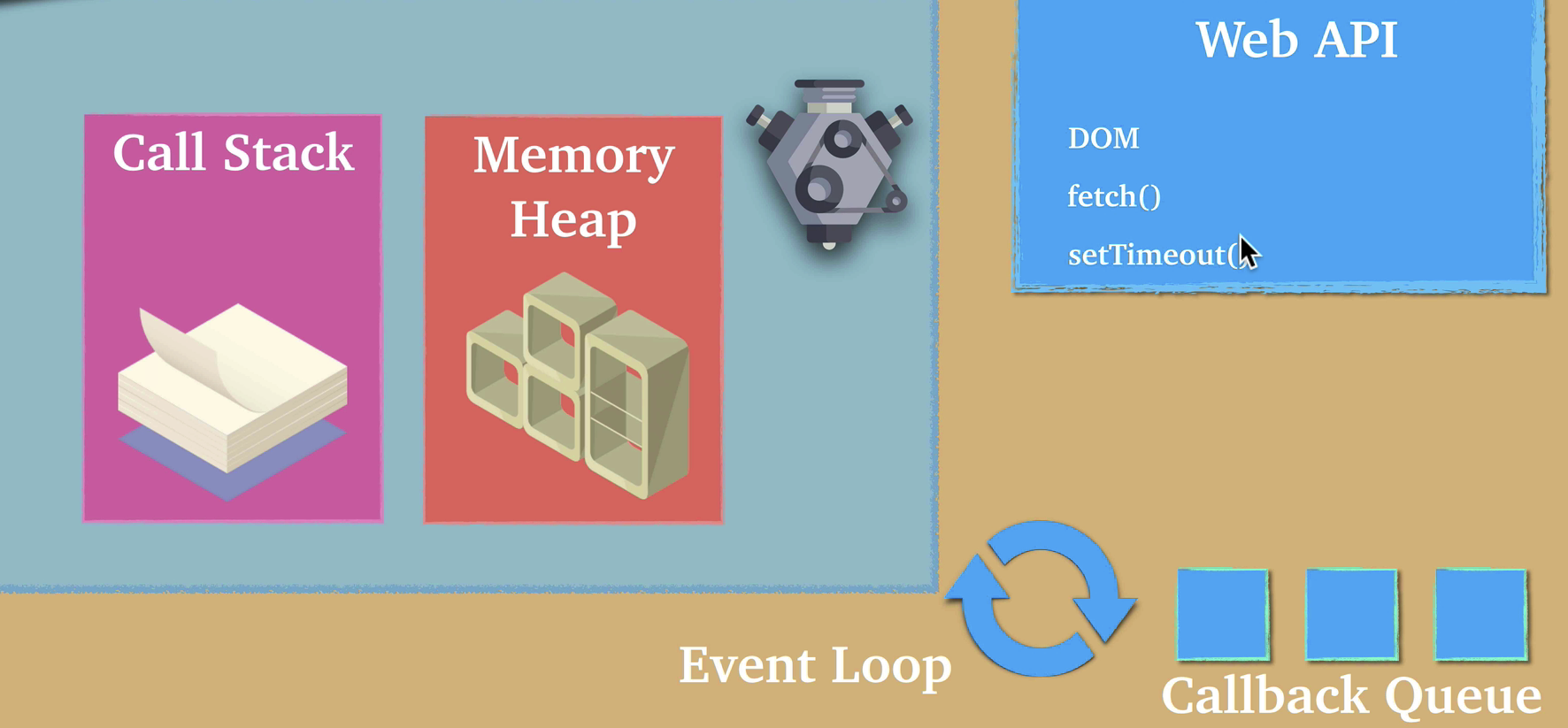
setTimeout(()=>{
console.log("something hello");
},0)
setTimeout(()=>{
console.log("somthing world");
},10)
Promise.resolve('hello').then(data=>console.log("data :",data))
console.log(":)")
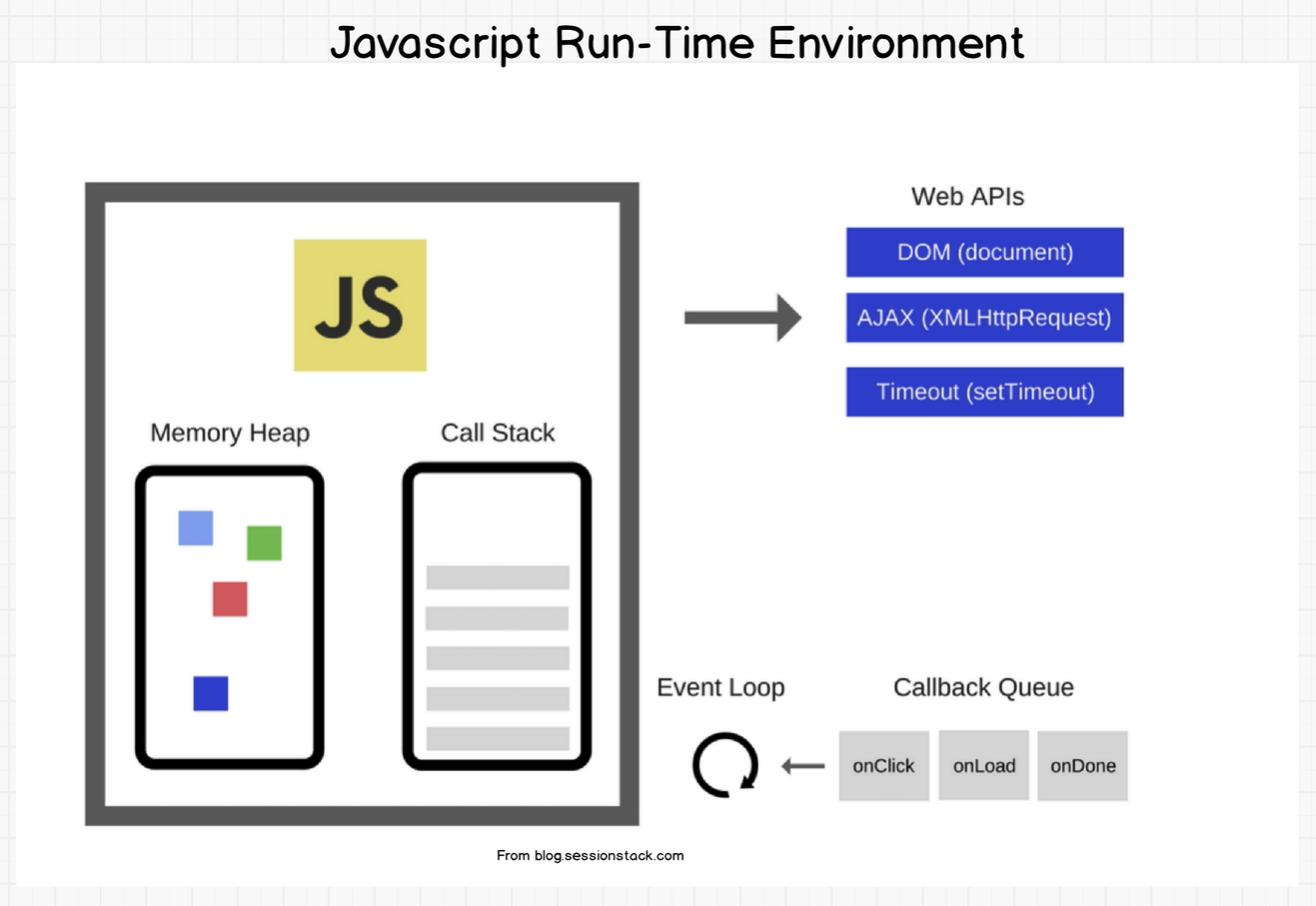
//call stack
console.log(1)
setTimeout(()=>{ // Web APIs -> Callback Queue
console.log(2)
},0)
console.log(3)
// 1, 3, 2
//1 call stack
//2 call stack -> pop -> web Api -> callback queue -> call stack
//3 call stack [event loop]
//empty ------------------------------------------->
Promise
A promise is an object that may produce a single value some time in the future, Either a resolved value, or a reson that it's not resolved(rejected)
const promise = new Promise((res, rej)=>{
if(true){
return res("true")
}
return rej("false")
})
//pending
//resolved or rejected === settled ot fullfiled
promise
.then(result => console.log(result,1))
.then(result2 => console.log(result2,2))
.catch(()=>console.log("error",3))
.then(result3 => { throw Error })
const urls = [
...
]
Promise.all(urls.map(url => {
return fetch(url).then(result => result.json())
}))
.then(results => console.log(results))
.catch(console.log)
// [{...},{...},{...}...]Async Await
ES8
const player = async () => {
const firstMove = await move(100,'l');
await move(100,'l');
await move(100,'l');
await move(100,'l');
}Micro Task Queue
// js > microtask queue > callback queue
setTimeout(()=>{
console.log("something hello");
},0)
setTimeout(()=>{ // Callback queue - Task queue
console.log("somthing world");
},10)
// micotask queue - job queue ; higher than task queue
Promise.resolve('hello').then(data=>console.log("data :",data))
console.log(":)")
Promise.addSettled([promise, promise])
worker
const worker = new Worker('worker.js');
worker.postMessage("hello~~");
addEventListener('message')
