1. Layered Tasks
Layered Architecture
- A single machine, each layer calls upon the services of the layer just below it.
Peer-to-Peer
두 컴퓨터끼리의 통신 → 다른 컴퓨터가 어떻게 통신하는지는 알 필요 없다.
2. The OSI Model
OSI 7 Layers
💡 계층을 나누는 이유 → 독립적으로 작동하게 하여 편리하게 할 수 있다. 하나의 레이어가 달라지더라도 인터페이스만 동일하다면 다른 레이어들 고칠 필요 없다.
- 왜 Internet 모델로 다시 돌아왔는가?
- 빨라지려면 단순해야 한다.
- OSI 7계층은 ? 복잡하다.
4. TCP/IP Protocol Suite
💡 TCP(Transmission Control Protocol) / IP(Internetworking Protocol)
5. Addressing
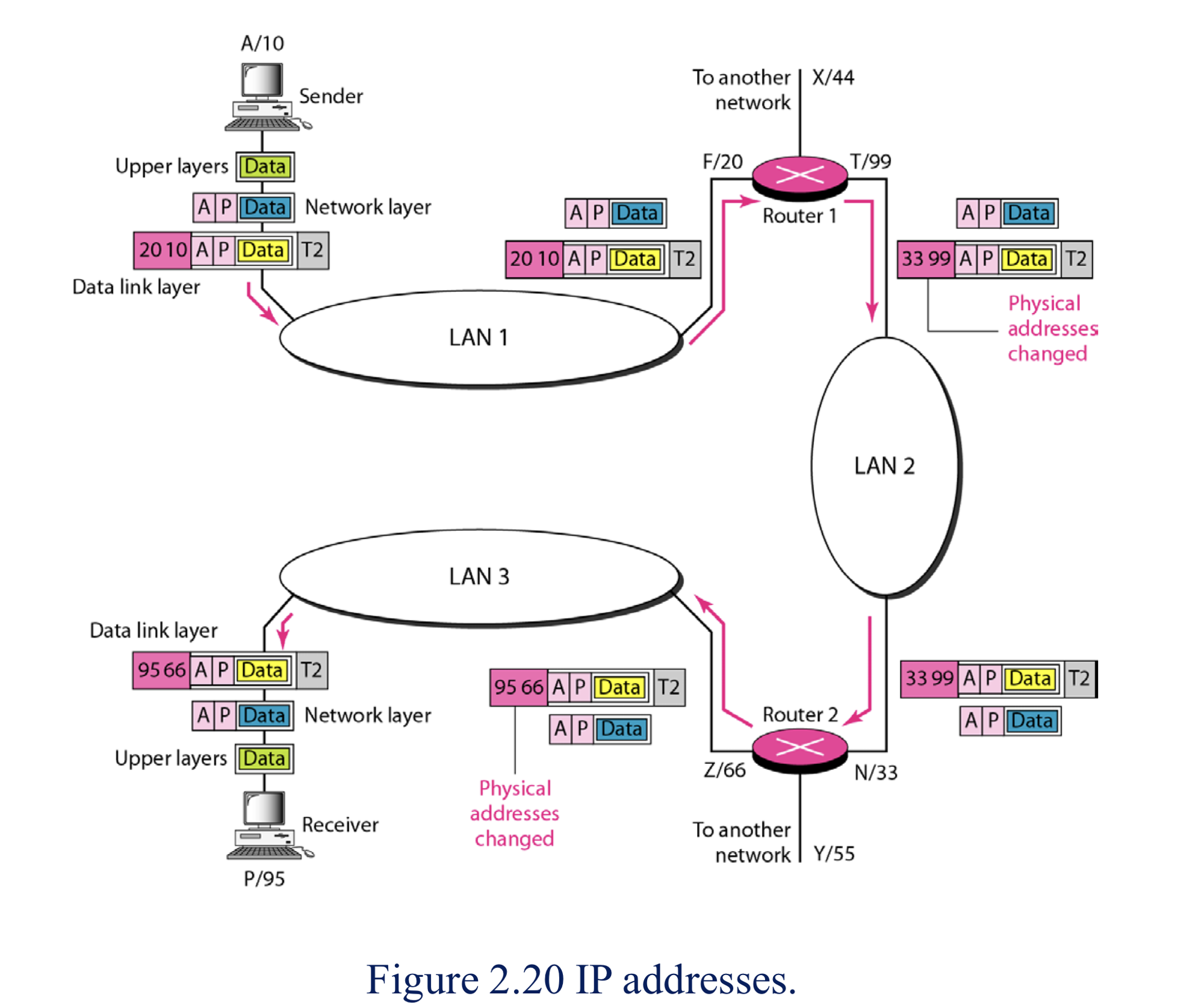
Physical Address
- Physical Address : 보드에 적힌 Ethernet 주소
- LAN이나 WAN 에 의해 정해지는 주소
- Data Link Layer에서 사용 되는 Frame 안에 포함된다.
- 가장 낮은 레벨의 주소
- 모든 사람이 받아보지만 자기 주소랑 안맞으면 프레임 버린다.
Logical Address(IP 주소)
- 문자로 표기 된 것은 논리 주소
- 컴퓨터 물리 주소 알 수는 있지만 실제로 통신 할 때에는 논리 주소인 IP주소를 사용한다
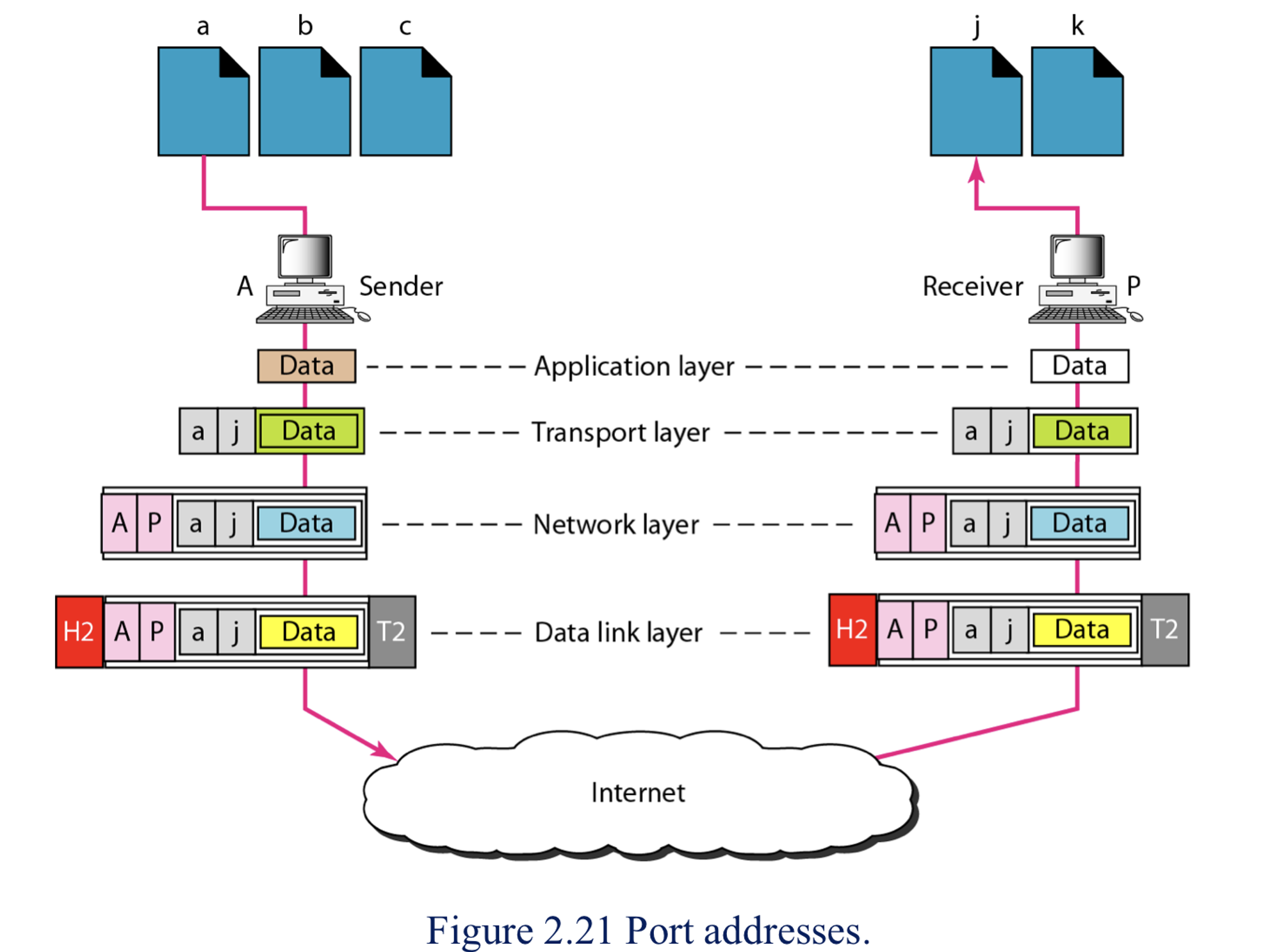
Port Address
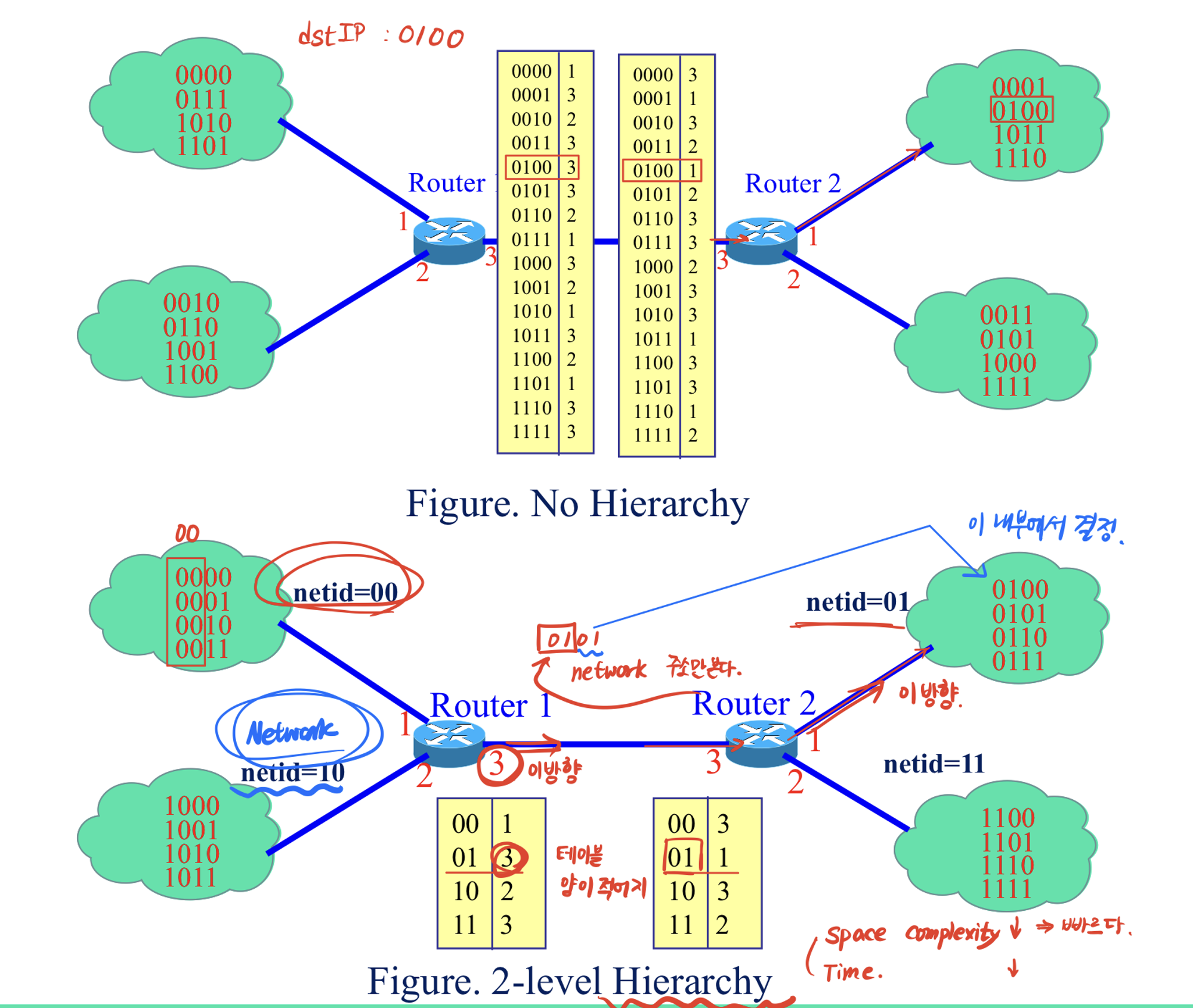
6. Basic of Internet Routing
Routong Table Hierarchy
Class of Internet Address
- Class A (1.0.0.0 - 127. 255. 255.255) : 7bits(netid- 부여받은 주소) + 24bits(hostId- 정한 주소)
- Class B (128.0.0 - 191. 255.255.255) : 14bits(netid- 부여받은 주소) + 16bits(hostId- 정한 주소)
- Class C (192.0.0.0 - 223.255.255.255) : 21bits(netid- 부여받은 주소) + 8bits(hostId- 정한 주소)
Step for Basic Routing
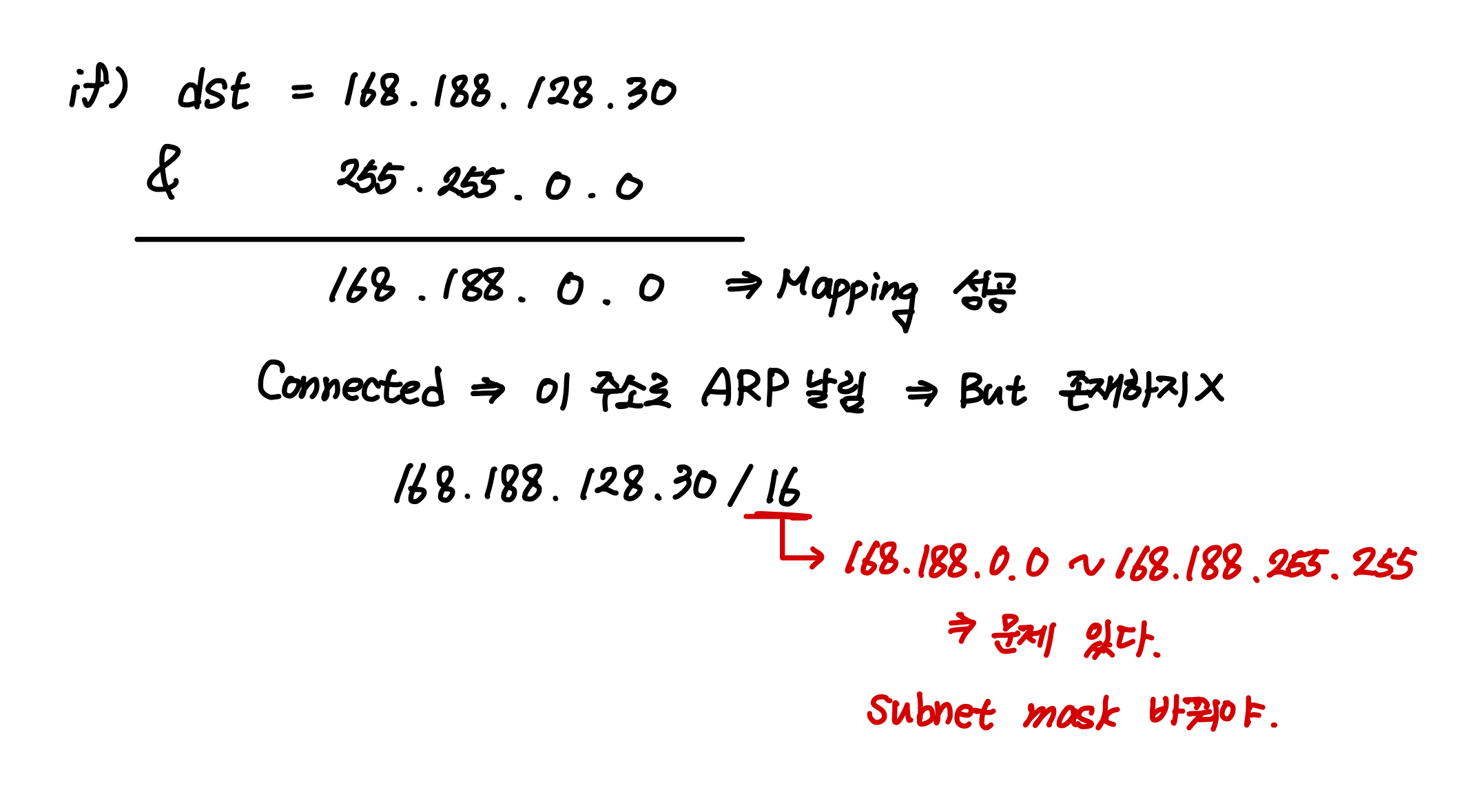
- packet을 받으면 dst addr 추출
- Network Address = Dst addr & SubNet Mask in Entry
- network address == dst network address?
- matching → send
- else → repeat until right match
- No match ⇒ select default
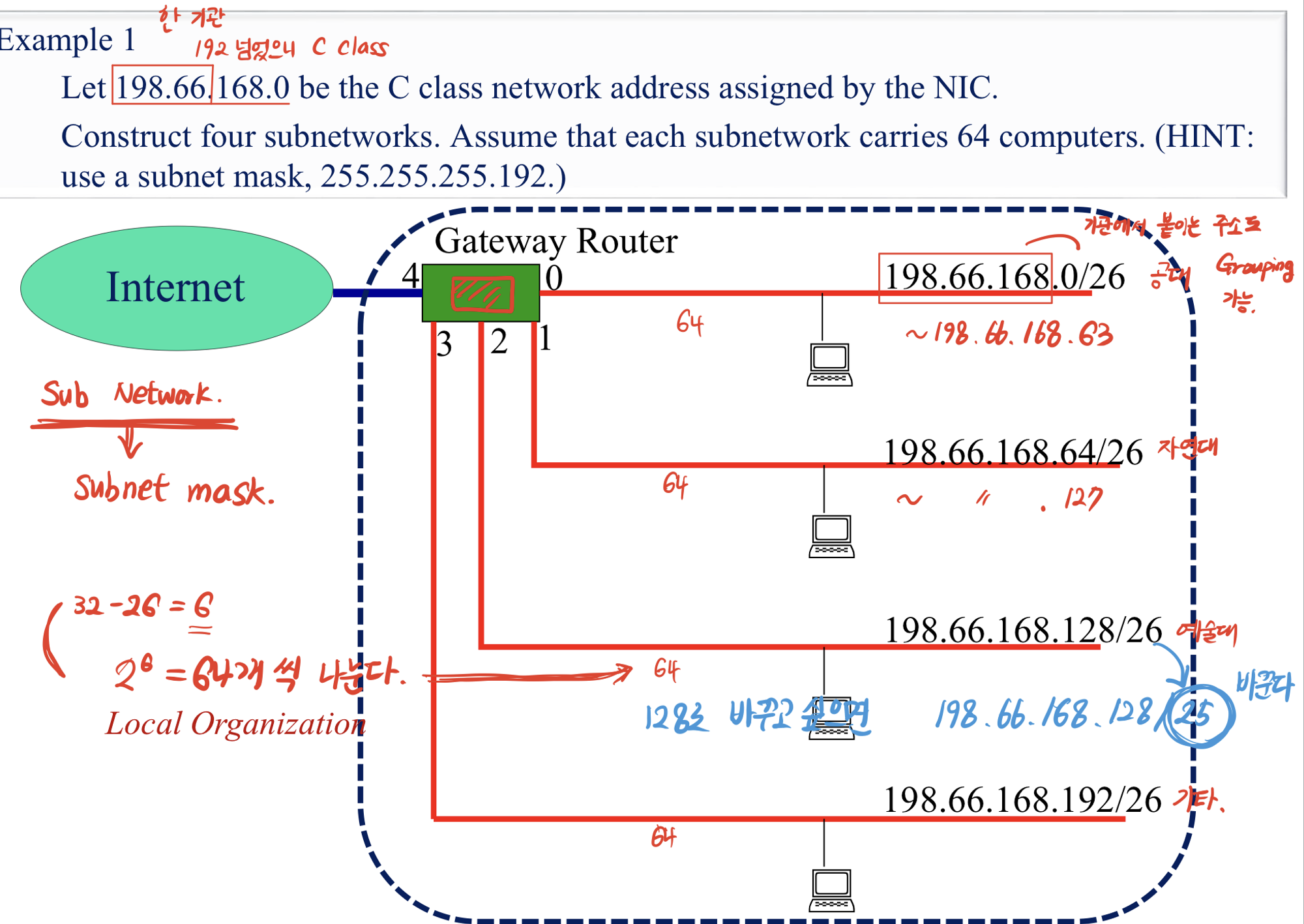
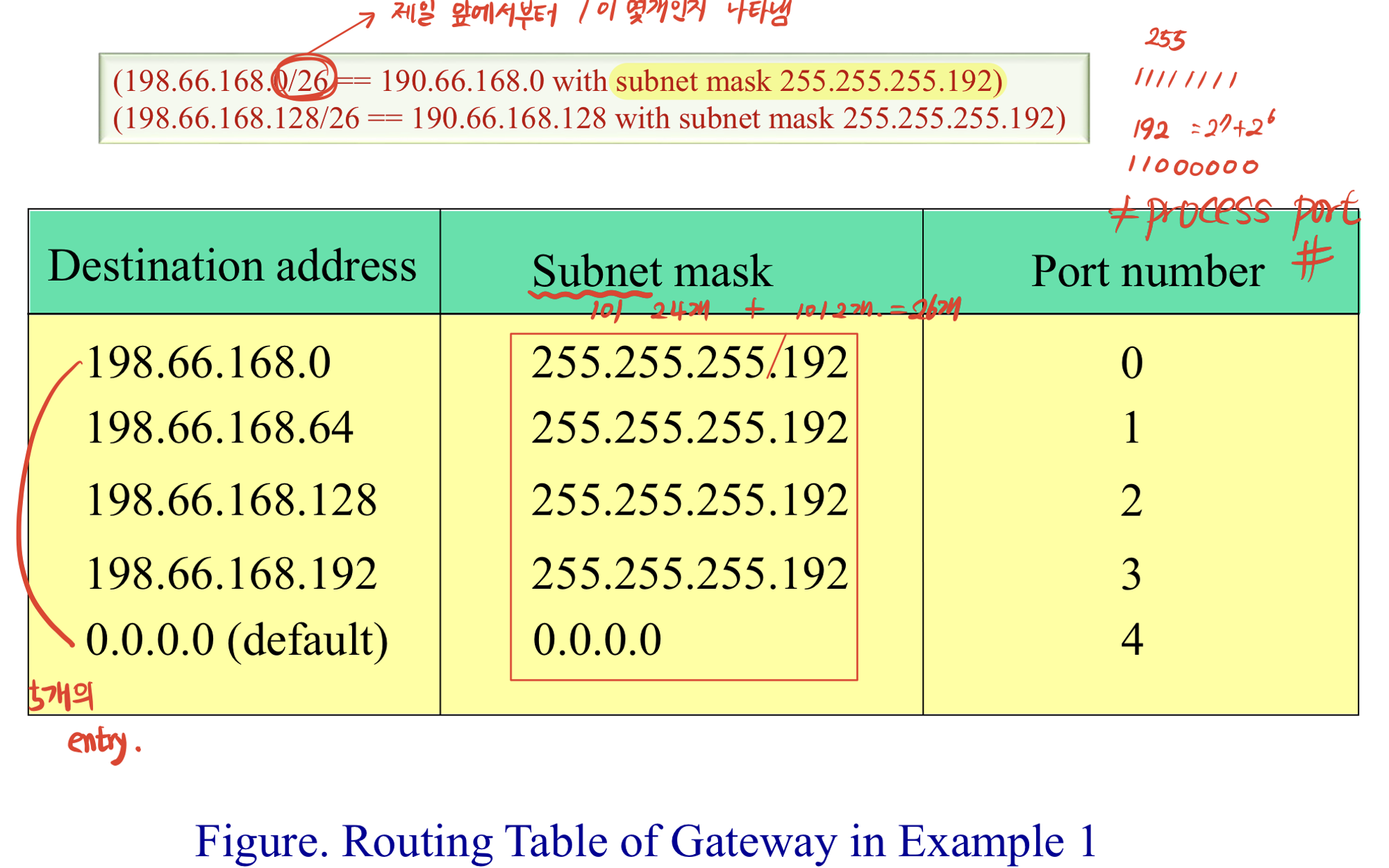
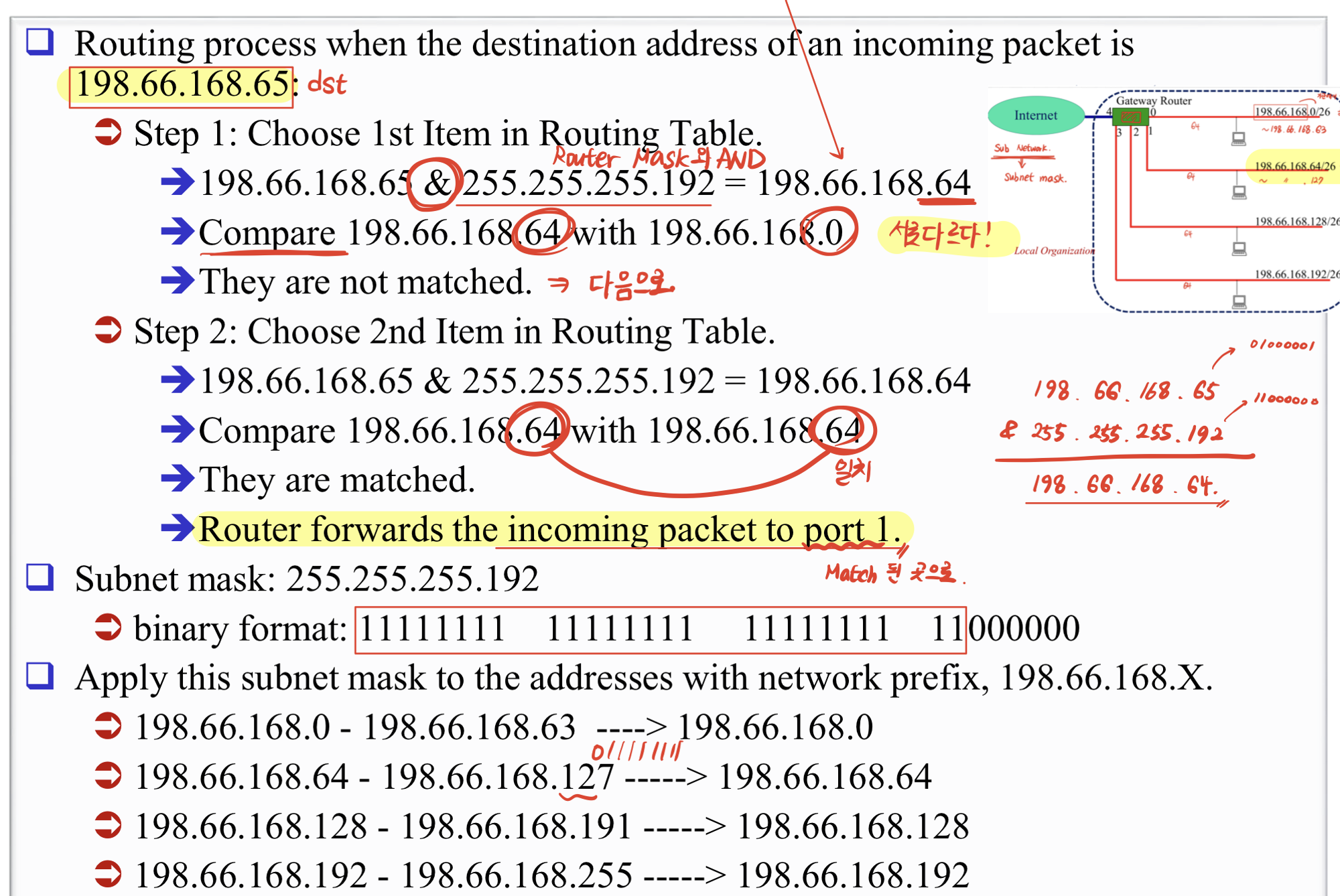
- 000.000.000.000/26
- 뒤에 붙는 숫자 ⇒ 앞에서부터 1의 갯수 → 32 - 26 = 6 ⇒ 64개씩 그룹
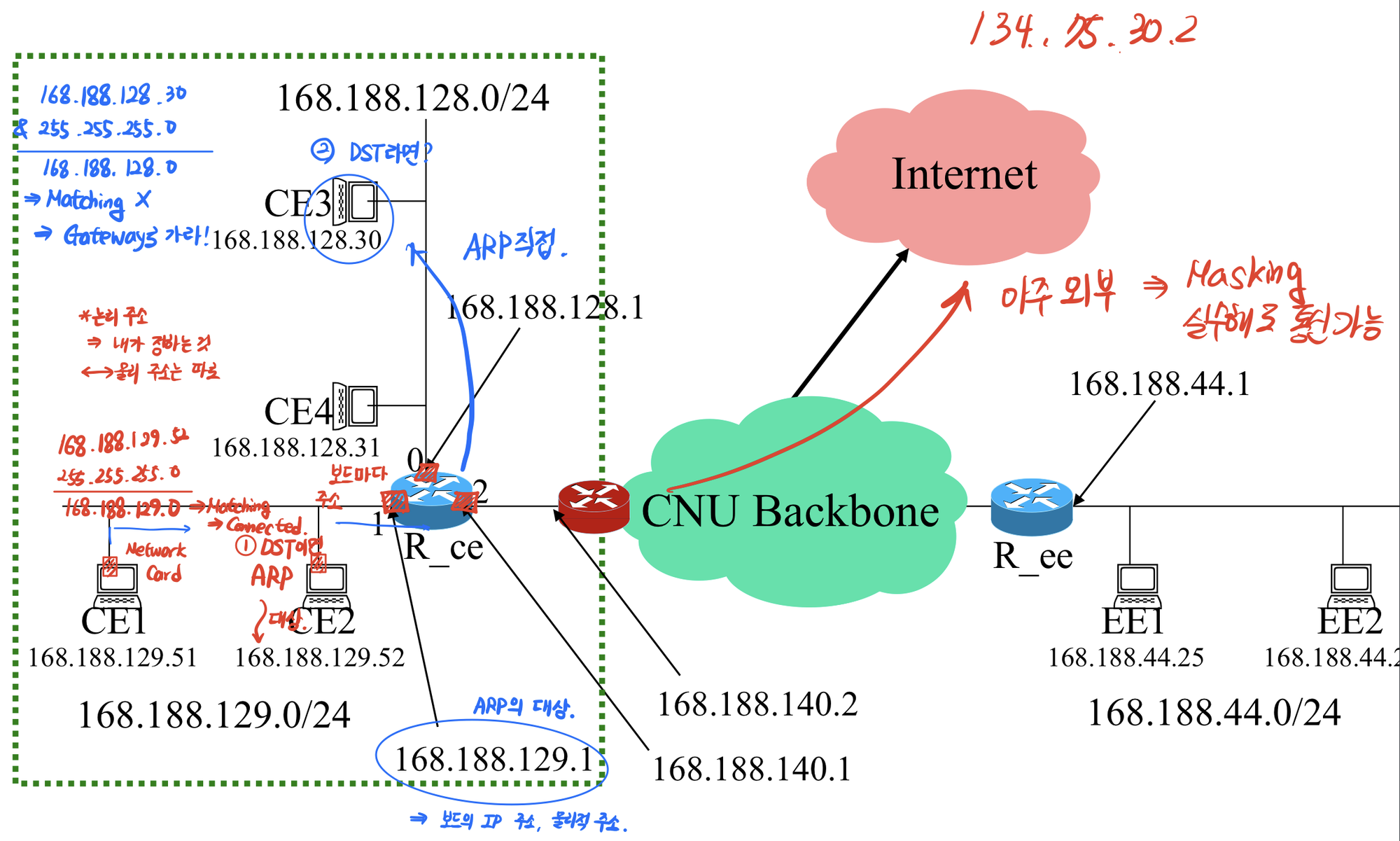
- 네트워크 계층이 있다 == Routing Table이 있다.
- connected ⇒ 직접 연결되어 있다 : ARP 날려서 논리 주소 얻는다
- else ⇒ Gateway로 가면 된다